Understanding geology unlocks the secrets of Earth's history, from the formation of mountains to the distribution of natural resources. Rock formations, soil types, and tectonic activity reveal vital information about our planet's past and future. Dive into this article to explore how geology impacts your world and why it matters.
Table of Comparison
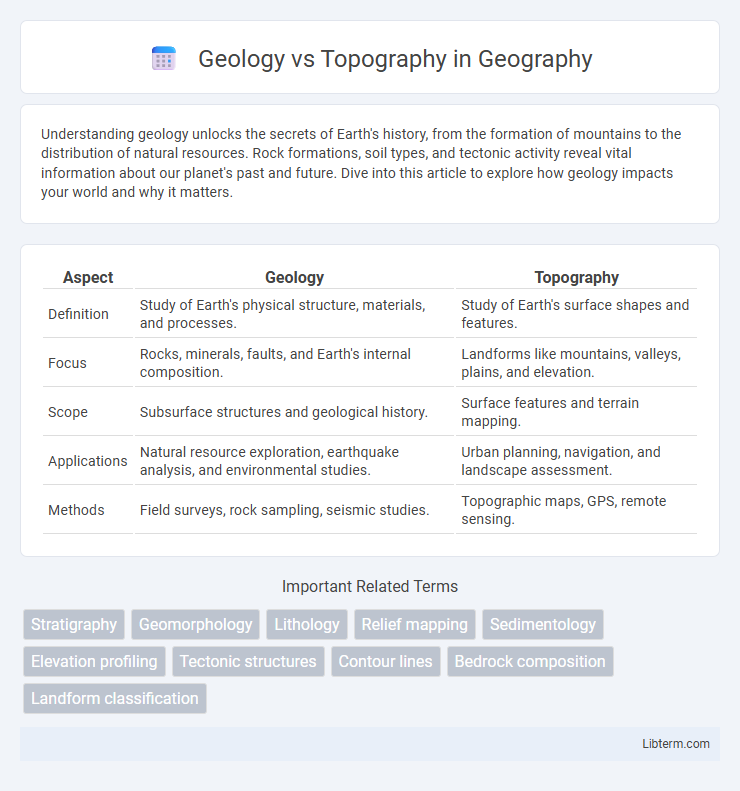
| Aspect | Geology | Topography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of Earth's physical structure, materials, and processes. | Study of Earth's surface shapes and features. |
| Focus | Rocks, minerals, faults, and Earth's internal composition. | Landforms like mountains, valleys, plains, and elevation. |
| Scope | Subsurface structures and geological history. | Surface features and terrain mapping. |
| Applications | Natural resource exploration, earthquake analysis, and environmental studies. | Urban planning, navigation, and landscape assessment. |
| Methods | Field surveys, rock sampling, seismic studies. | Topographic maps, GPS, remote sensing. |
Introduction: Understanding Geology and Topography
Geology studies the Earth's physical structure, its materials, and the processes shaping its formation over time, including rock types, faults, and tectonic activity. Topography examines the Earth's surface features, such as mountains, valleys, and plains, describing their shapes, elevations, and spatial relationships. Understanding both geology and topography provides critical insights into landscape evolution, natural resource distribution, and environmental planning.
Defining Geology: Study of Earth's Structure
Geology examines the Earth's structure, composition, and the processes shaping its crust, including rock formations, tectonic activity, and mineral resources. It reveals the history recorded in rock layers, helping to understand earthquakes, volcanic activity, and mountain building. Unlike topography, which maps surface features like elevation and landforms, geology focuses on the underlying physical and chemical characteristics of the Earth.
What is Topography? Mapping Surface Features
Topography refers to the detailed mapping and description of the Earth's surface features, including elevations, landforms, and natural or artificial structures. It involves the use of contour lines, elevation points, and other graphical methods to represent terrain accurately on maps. Distinct from geology, which studies the Earth's materials and processes, topography focuses specifically on the spatial arrangement and shape of surface features.
Key Differences Between Geology and Topography
Geology examines the Earth's physical structure, composition, and processes shaping its formation over time, focusing on rock types, minerals, and tectonic activity. Topography describes the Earth's surface features, including elevation, slope, and landforms like mountains, valleys, and plains. While geology investigates subsurface materials and historical development, topography maps surface contours and spatial relationships crucial for land use and environmental planning.
Methods of Geologic Analysis
Methods of geologic analysis include rock sampling, stratigraphic profiling, radiometric dating, and seismic reflection surveys, which reveal the Earth's subsurface structure and composition. Geologists use petrographic microscopy and X-ray diffraction to determine mineralogy and rock textures, while geochemical assays analyze elemental concentrations. These techniques contrast with topographic methods like LiDAR and GPS mapping, which primarily focus on surface elevation and landform morphology.
Techniques Used in Topographical Surveying
Topographical surveying uses techniques such as GPS (Global Positioning System), total stations, and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) to accurately capture the Earth's surface features and elevation data. Photogrammetry, including drone-based aerial imaging, enhances topographical maps by providing high-resolution, three-dimensional terrain models. These modern methods distinguish topographical surveying from geological studies by focusing on surface detail rather than subsurface composition.
Importance of Geology in Environmental Studies
Geology plays a crucial role in environmental studies by providing insights into Earth's materials, structures, and processes that shape ecosystems and influence natural hazards. Understanding rock formations, soil composition, and groundwater flow is essential for assessing environmental risks, managing natural resources, and guiding sustainable land use planning. Unlike topography, which focuses on surface features and landforms, geology offers a deeper analysis of subsurface conditions critical for environmental impact assessments and remediation strategies.
Role of Topography in Urban Planning
Topography plays a crucial role in urban planning by influencing land use, infrastructure development, and disaster risk management. The elevation, slope, and natural features of the terrain guide the placement of buildings, roads, and drainage systems to optimize safety and functionality. Integrating topographic data helps planners design resilient cities that accommodate natural landforms and mitigate hazards such as flooding and landslides.
How Geology and Topography Interact
Geology, the study of Earth's materials and processes, influences topography by determining the resistance of rocks to erosion and shaping landforms over time. Variations in rock types, faults, and tectonic activity directly affect the elevation, slope, and relief of landscapes. As a result, topography reflects underlying geological structures and processes, revealing the dynamic interaction between Earth's crust and surface features.
Applications: Practical Uses of Geology vs Topography
Geology plays a critical role in resource exploration, natural hazard assessment, and environmental management by analyzing Earth's materials and processes. Topography is essential for urban planning, land use management, and infrastructure development through detailed mapping of surface features and elevation. Integrating geological and topographical data enhances decision-making in construction, agriculture, and disaster mitigation projects.
Geology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com