Demography examines the statistical study of populations, focusing on variables such as birth rates, death rates, age distribution, and migration patterns to understand societal changes. Accurate demographic data helps shape policies in healthcare, education, and urban planning, directly impacting Your community's development and resource allocation. Explore the rest of the article to discover how demographic trends influence economic growth and social structures worldwide.
Table of Comparison
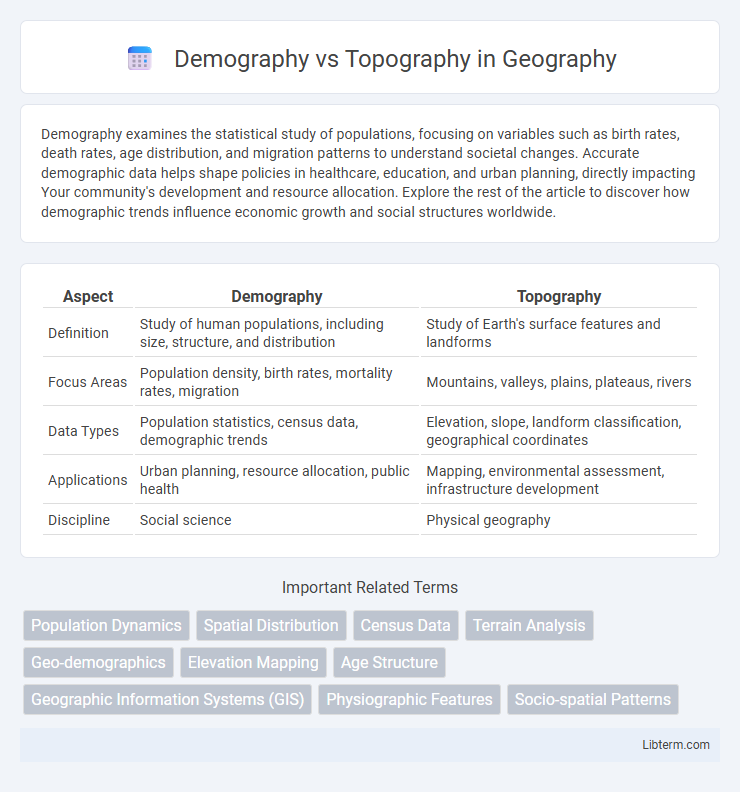
| Aspect | Demography | Topography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of human populations, including size, structure, and distribution | Study of Earth's surface features and landforms |
| Focus Areas | Population density, birth rates, mortality rates, migration | Mountains, valleys, plains, plateaus, rivers |
| Data Types | Population statistics, census data, demographic trends | Elevation, slope, landform classification, geographical coordinates |
| Applications | Urban planning, resource allocation, public health | Mapping, environmental assessment, infrastructure development |
| Discipline | Social science | Physical geography |
Introduction to Demography and Topography
Demography studies population dynamics including size, structure, and distribution, essential for understanding human populations and societal trends. Topography examines the arrangement of natural and artificial physical features on Earth's surface, influencing climate, habitation, and infrastructure development. Together, demography and topography provide crucial insights into how populations interact with geographical environments and resources.
Defining Demography: Scope and Significance
Demography is the scientific study of human populations, focusing on their size, structure, distribution, and changes over time through births, deaths, migration, and aging. It provides critical insights for public policy, economic planning, healthcare, and social services by analyzing population trends and demographics such as age, gender, ethnicity, and income. Unlike topography, which deals with physical land features, demography centers on socio-economic and cultural aspects of human populations.
Understanding Topography: Key Concepts
Topography involves the detailed mapping and description of land surface features, including elevation, slope, and terrain shapes such as mountains, valleys, and plateaus. Understanding contour lines, relief, and landform classifications is essential for interpreting topographical maps and analyzing physical landscapes. These elements help in assessing geographical patterns, planning infrastructure, and managing natural resources effectively.
Major Differences Between Demography and Topography
Demography studies human populations, analyzing data such as age, gender, birth rates, and migration patterns to understand population dynamics. Topography describes the physical features of the land, including elevation, terrain, and natural formations like mountains and rivers. While demography focuses on statistical characteristics of people, topography emphasizes the spatial and physical aspects of geographic landscapes.
Methods of Data Collection in Demography
Demography employs methods like censuses, surveys, and vital statistics registration to collect data on population size, structure, and distribution. Sampling techniques and administrative records provide detailed information about birth rates, death rates, migration patterns, and population composition. These methods enable comprehensive analysis of demographic trends and inform policy planning and social services.
Techniques for Analyzing Topographical Features
Techniques for analyzing topographical features include remote sensing, geographic information systems (GIS), and digital elevation models (DEMs), which provide detailed spatial data on terrain variations. LiDAR technology captures precise elevation information by using laser pulses to measure distances, enabling accurate mapping of landforms and surface structures. These methods facilitate comprehensive analysis of elevation, slope, and landform characteristics essential for environmental planning and hazard assessment.
Real-World Applications of Demography
Demography, the statistical study of populations, plays a crucial role in urban planning, public health, and marketing by analyzing population size, age distribution, and migration patterns to predict future trends. Unlike topography, which maps the physical features of the land, demography informs resource allocation, infrastructure development, and policy decisions by understanding human behavior and population dynamics. Real-world applications include improving healthcare services by identifying high-risk groups, optimizing transportation routes based on population density, and tailoring products to demographic segments for targeted marketing.
Practical Importance of Topography
Topography plays a crucial role in urban planning, agriculture, and infrastructure development by providing detailed information about landforms, elevations, and slopes. Understanding topographic features helps engineers design effective drainage systems, roads, and buildings suited to the terrain, reducing construction risks and costs. Unlike demography, which analyzes population characteristics, topography directly influences land use decisions and environmental management.
Interconnections Between Demographic and Topographic Data
Demographic data, including population density, age distribution, and migration patterns, closely interacts with topographic features such as elevation, landforms, and climate conditions. These interactions influence settlement patterns, economic activities, and resource management, with mountainous or flood-prone areas often showing distinct demographic trends compared to plains or coastal regions. Integrating demographic and topographic data enhances urban planning, disaster risk assessment, and environmental sustainability efforts by providing a comprehensive understanding of human-environment dynamics.
Conclusion: Integrating Demographic and Topographic Perspectives
Integrating demographic and topographic perspectives enhances urban planning by aligning population trends with physical landscape constraints, promoting sustainable development. Demographic data reveals population density, migration patterns, and age distribution, while topographic analysis informs infrastructure placement, hazard risk, and resource management. Combining these disciplines supports informed decision-making for resilient communities and efficient resource allocation.
Demography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com