Diseases and infections disrupt the body's normal functions, often caused by pathogens like bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, leading to symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe health complications. Understanding the mechanisms behind infections and recognizing early signs can significantly improve treatment outcomes and prevent the spread to others. Explore the rest of this article to learn how you can protect yourself and maintain your health effectively.
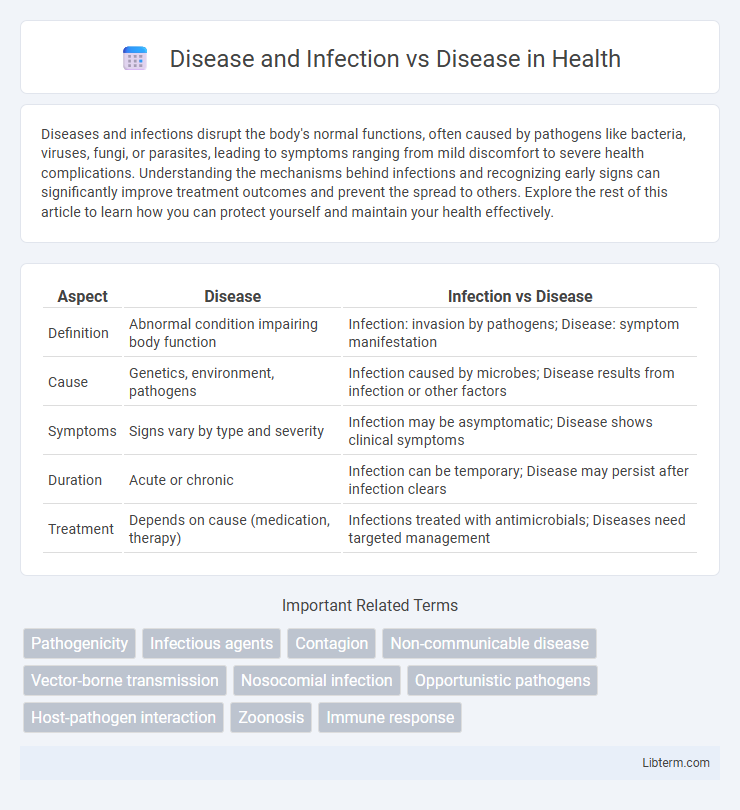
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Disease | Infection vs Disease |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Abnormal condition impairing body function | Infection: invasion by pathogens; Disease: symptom manifestation |
| Cause | Genetics, environment, pathogens | Infection caused by microbes; Disease results from infection or other factors |
| Symptoms | Signs vary by type and severity | Infection may be asymptomatic; Disease shows clinical symptoms |
| Duration | Acute or chronic | Infection can be temporary; Disease may persist after infection clears |
| Treatment | Depends on cause (medication, therapy) | Infections treated with antimicrobials; Diseases need targeted management |
Understanding Disease: Definitions and Concepts
Disease refers to a pathological condition characterized by specific signs and symptoms affecting the body's normal functioning, while infection describes the invasion and multiplication of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites within the host. Understanding disease involves distinguishing between infectious diseases caused by pathogens and non-infectious diseases resulting from genetic, environmental, or lifestyle factors. Accurate definitions and concepts aid in diagnosing, preventing, and treating various health conditions effectively.
What Is an Infection?
An infection occurs when harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites invade the body, multiply, and trigger an immune response. Disease refers to the resulting condition caused by infections or other factors like genetic disorders, environmental influences, or lifestyle choices. Understanding the difference between infection and disease is crucial for effective diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of health complications.
Difference Between Disease and Infection
Disease refers to a condition characterized by impaired health or abnormal functioning of the body or mind, while infection specifically involves the invasion and multiplication of harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites within the host. Infection can cause disease but not all diseases are caused by infections; for example, genetic disorders and autoimmune diseases are non-infectious. Understanding the distinction between disease and infection is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies in medical science.
How Infections Lead to Disease
Infections occur when harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites invade and multiply within the body, disrupting normal physiological functions. This invasion triggers immune responses and cellular damage, which can manifest as various diseases characterized by specific signs and symptoms. Understanding the mechanisms by which infections lead to diseases aids in developing targeted treatments and preventive measures to control the spread and impact of infectious agents.
Non-Infectious Diseases Explained
Non-infectious diseases are medical conditions that are not caused by pathogens and therefore cannot be transmitted between individuals. These diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancers, result from genetic, environmental, or lifestyle factors rather than infectious agents like bacteria or viruses. Understanding the distinction between non-infectious and infectious diseases is crucial for developing appropriate prevention, diagnosis, and treatment strategies.
Transmission Modes of Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases spread through various transmission modes, including direct contact, airborne droplets, vector-borne carriers, and contaminated surfaces or fomites. Understanding these transmission pathways is crucial for controlling outbreaks and implementing effective prevention strategies like vaccination, hygiene, and quarantine. Non-infectious diseases do not transmit between individuals, distinguishing them from infectious diseases based on transmissibility and pathogen presence.
Symptoms: Infection Versus Disease
Infections often trigger localized symptoms such as fever, inflammation, and fatigue caused by the immune system's response to pathogens like bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Diseases represent the broader impact of infections or other causes, manifesting in specific clinical symptoms and possible organ dysfunction, such as pneumonia causing respiratory distress or chronic conditions like diabetes altering metabolism. Differentiating infection from disease requires understanding that infection is the presence and multiplication of microbes, whereas disease encompasses the symptomatic expression and physiological disruption resulting from infections or other factors.
Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases
Effective prevention and control of infectious diseases rely on understanding the transmission modes of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Implementing strategies such as vaccination, proper sanitation, quarantine measures, and public health education significantly reduces disease spread and infection rates. Surveillance systems and rapid diagnostic techniques play crucial roles in early detection and containment of outbreaks to minimize the impact on public health.
Diagnosis: Distinguishing Infection from Disease
Diagnosis plays a crucial role in distinguishing infection from disease by identifying the presence of a pathogen and assessing the host's response. Diagnostic tools such as culture tests, PCR, and serology detect microbial agents, while clinical symptoms and biomarkers indicate disease manifestation. Accurate differentiation enables targeted treatment strategies and effective infection control measures.
Treatment Approaches for Diseases and Infections
Treatment approaches for diseases and infections prioritize targeted strategies based on the underlying cause; infections typically require antimicrobial therapies such as antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals to eliminate pathogens. Chronic diseases often involve long-term management through medication, lifestyle modifications, and supportive care to control symptoms and prevent complications. Advances in precision medicine enable personalized treatments that optimize efficacy for both infectious and non-infectious diseases by considering genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Disease and Infection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com