Volvulus is a serious medical condition caused by the twisting of the intestine, which can block blood flow and lead to severe complications like tissue death. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, bloating, vomiting, and constipation, requiring immediate medical attention to prevent life-threatening outcomes. Discover more about volvulus symptoms, causes, and treatment options to safeguard your health in the full article ahead.
Table of Comparison
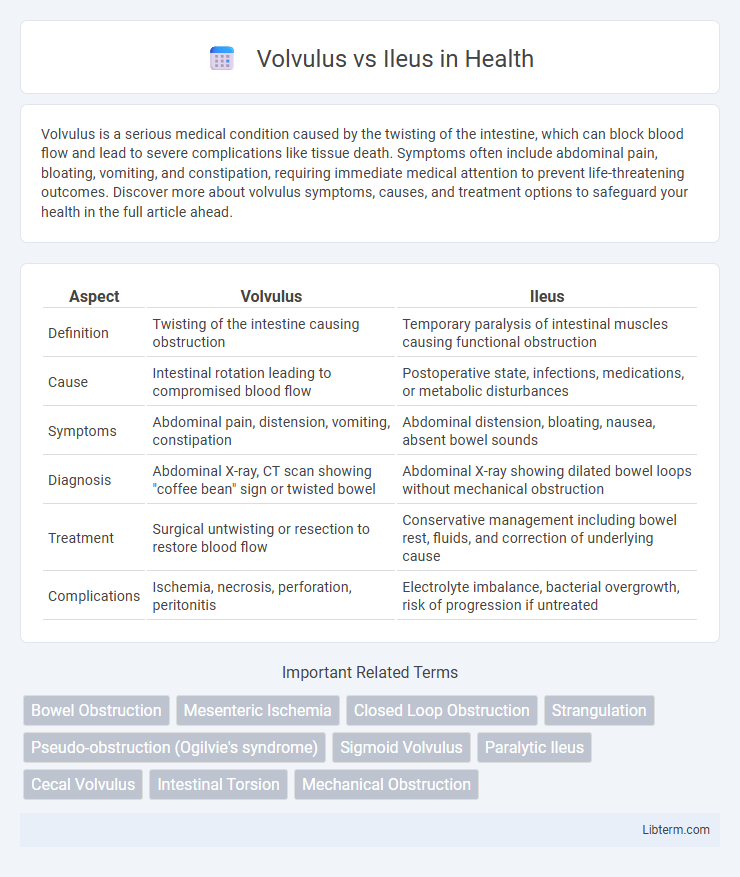
| Aspect | Volvulus | Ileus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Twisting of the intestine causing obstruction | Temporary paralysis of intestinal muscles causing functional obstruction |
| Cause | Intestinal rotation leading to compromised blood flow | Postoperative state, infections, medications, or metabolic disturbances |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, distension, vomiting, constipation | Abdominal distension, bloating, nausea, absent bowel sounds |
| Diagnosis | Abdominal X-ray, CT scan showing "coffee bean" sign or twisted bowel | Abdominal X-ray showing dilated bowel loops without mechanical obstruction |
| Treatment | Surgical untwisting or resection to restore blood flow | Conservative management including bowel rest, fluids, and correction of underlying cause |
| Complications | Ischemia, necrosis, perforation, peritonitis | Electrolyte imbalance, bacterial overgrowth, risk of progression if untreated |
Introduction to Volvulus and Ileus
Volvulus occurs when a loop of intestine twists around itself and the mesentery, causing bowel obstruction and ischemia. Ileus refers to a temporary impairment of bowel motility without mechanical obstruction, often resulting in abdominal distension and pain. Both conditions present with symptoms of bowel obstruction but differ in their underlying pathophysiology and treatment approaches.
Definition of Volvulus
Volvulus is a medical condition characterized by the twisting of a loop of intestine, which causes bowel obstruction and compromises blood flow to the affected segment. Unlike ileus, which refers to a functional paralysis of the bowel without mechanical obstruction, volvulus involves a physical twist that requires urgent surgical intervention to prevent ischemia and necrosis. Early diagnosis of volvulus is critical, as untreated cases can lead to severe complications such as bowel infarction or perforation.
Definition of Ileus
Ileus is a functional obstruction of the intestines caused by a disruption in normal bowel motility, leading to impaired transit of intestinal contents without any physical blockage. It differs from volvulus, which is a mechanical obstruction characterized by twisting of the intestine that compromises blood flow and causes acute symptoms. Understanding ileus involves recognizing factors such as postoperative states, infections, and metabolic imbalances that impair intestinal muscle contractions.
Etiology: Causes of Volvulus vs Ileus
Volvulus is primarily caused by torsion of a bowel segment around its mesentery, leading to obstruction and ischemia, often associated with congenital malformations, intestinal malrotation, or postoperative adhesions. Ileus results from impaired gastrointestinal motility due to factors such as postoperative inflammation, electrolyte imbalances, medications (e.g., opioids), infections, or metabolic disturbances. Understanding these distinct etiologies is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted management of bowel obstruction.
Pathophysiology: Mechanisms of Obstruction
Volvulus involves the twisting of a bowel segment around its mesenteric axis, leading to luminal obstruction and vascular compromise, resulting in ischemia. Ileus is characterized by a functional obstruction due to impaired intestinal motility without an actual physical blockage, often caused by neural or muscular dysfunction. The pathophysiology of volvulus centers on mechanical strangulation, whereas ileus results from disrupted peristalsis and paralysis of the bowel.
Clinical Presentation: Signs and Symptoms
Volvulus typically presents with sudden, severe abdominal pain, abdominal distension, vomiting, and signs of bowel obstruction such as absence of flatus or bowel movements. Ileus manifests with diffuse abdominal discomfort, bloating, decreased bowel sounds, and delayed passage of flatus and stool without a mechanical blockage. Both conditions may exhibit nausea, vomiting, and abdominal tenderness, but volvulus often progresses rapidly with signs of ischemia, while ileus presents as a more gradual functional obstruction.
Diagnostic Approaches and Imaging
Volvulus is typically diagnosed through abdominal X-rays revealing a "coffee bean" or "bird beak" sign, while CT scans provide detailed imaging of twisted bowel loops and ischemic changes. Ileus diagnosis relies on plain abdominal radiographs showing diffuse gas-filled dilated bowel loops without mechanical obstruction, with CT scans used to identify underlying causes. Contrast studies and ultrasound may further assist in differentiating volvulus from ileus by evaluating bowel motility and obstruction patterns.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Volvulus treatment requires prompt surgical intervention to untwist the affected bowel segment and restore blood flow, often involving resection of necrotic tissue if present. Ileus management prioritizes supportive care, including bowel rest, nasogastric decompression, fluid and electrolyte correction, and addressing underlying causes such as infections or medications. Both conditions necessitate close monitoring for complications like ischemia or perforation, with individualized treatment plans based on severity and patient condition.
Prognosis and Potential Complications
Volvulus, characterized by twisting of the intestine causing obstruction, often leads to ischemia and necrosis, resulting in a more severe prognosis if not treated promptly. Ileus involves a functional blockage without mechanical obstruction, typically having a better prognosis but risks such as bowel perforation and sepsis if prolonged. Potential complications of volvulus include bowel gangrene and perforation, while ileus complications primarily entail electrolyte imbalances and secondary infections.
Key Differences Between Volvulus and Ileus
Volvulus involves a twisting of the intestine causing obstruction and compromised blood flow, while ileus is a functional paralysis of the bowel without mechanical blockage. Volvulus typically presents with sudden severe abdominal pain, distension, and signs of ischemia, whereas ileus manifests as gradual abdominal distension, absence of bowel sounds, and diffuse discomfort. Imaging for volvulus often reveals a "coffee bean" sign or whirlpool sign, contrasting with ileus which shows diffuse bowel dilation and air-fluid levels without a discrete transition point.
Volvulus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com