Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the adenoids, which are lymphatic tissues located behind the nasal cavity that can cause breathing difficulties, recurrent infections, or sleep apnea when enlarged. This surgery is commonly performed in children to improve airway function and reduce ear or sinus infections. Explore the full article to understand the benefits, risks, and recovery process of adenoidectomy to determine if it might be right for you or your child.
Table of Comparison
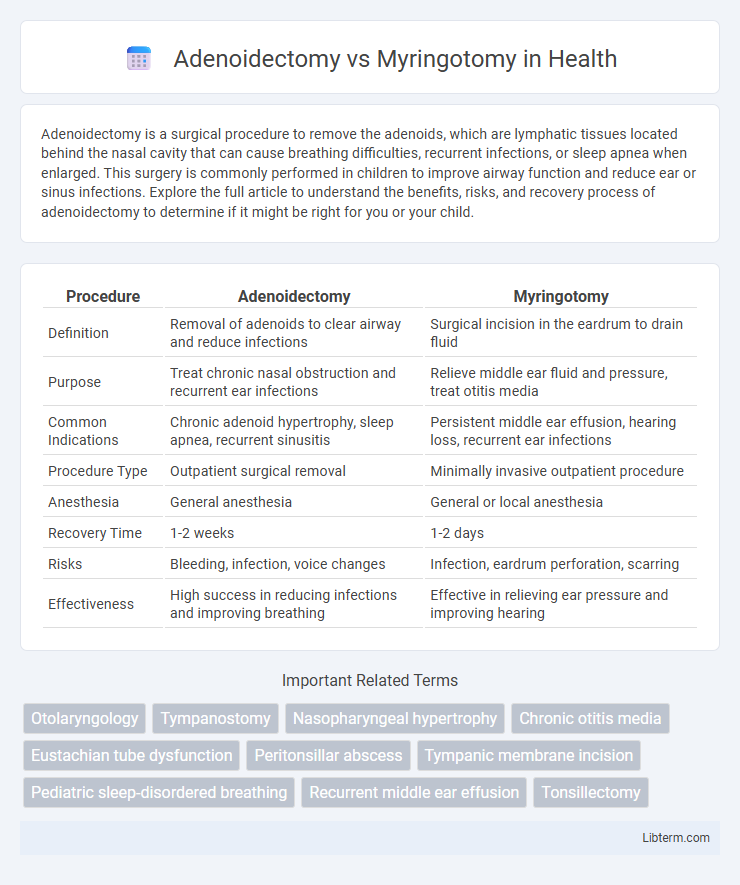
| Procedure | Adenoidectomy | Myringotomy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removal of adenoids to clear airway and reduce infections | Surgical incision in the eardrum to drain fluid |
| Purpose | Treat chronic nasal obstruction and recurrent ear infections | Relieve middle ear fluid and pressure, treat otitis media |
| Common Indications | Chronic adenoid hypertrophy, sleep apnea, recurrent sinusitis | Persistent middle ear effusion, hearing loss, recurrent ear infections |
| Procedure Type | Outpatient surgical removal | Minimally invasive outpatient procedure |
| Anesthesia | General anesthesia | General or local anesthesia |
| Recovery Time | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 days |
| Risks | Bleeding, infection, voice changes | Infection, eardrum perforation, scarring |
| Effectiveness | High success in reducing infections and improving breathing | Effective in relieving ear pressure and improving hearing |
Introduction to Adenoidectomy and Myringotomy
Adenoidectomy involves the surgical removal of the adenoids to treat chronic infections and breathing difficulties, commonly performed in children with recurrent ear infections or sleep apnea. Myringotomy is a procedure that creates a small incision in the eardrum to drain fluid and relieve pressure, often combined with the insertion of tympanostomy tubes for persistent middle ear effusion. Both procedures address ear-related conditions but target different anatomical structures and symptoms within the upper respiratory tract and middle ear.
Understanding Adenoidectomy: Procedure and Purpose
Adenoidectomy involves the surgical removal of the adenoid glands located in the upper part of the throat behind the nose, primarily to treat chronic infections or breathing difficulties caused by enlarged adenoids. This procedure is commonly performed under general anesthesia and helps improve airway obstruction, reduce recurrent ear infections, and alleviate nasal congestion. Understanding the adenoidectomy process is essential for distinguishing it from myringotomy, which targets the middle ear to drain fluid and equalize pressure without removing tissue.
Myringotomy Explained: Indications and Process
Myringotomy is a surgical procedure involving a small incision in the eardrum to relieve middle ear pressure or drain fluid, commonly indicated for recurrent otitis media with effusion or acute otitis media unresponsive to antibiotics. The process typically involves inserting a tiny tube called a tympanostomy tube to maintain aeration and prevent fluid accumulation, improving hearing and reducing infection risk. Compared to adenoidectomy, myringotomy offers a minimally invasive option targeting middle ear issues directly, while adenoidectomy focuses on removing adenoid tissue to address airway obstruction or recurrent infections.
Common Conditions Requiring Adenoidectomy or Myringotomy
Adenoidectomy is commonly performed to treat recurrent adenoid infections, chronic nasal obstruction, and obstructive sleep apnea in children. Myringotomy is typically indicated for persistent middle ear infections, fluid buildup (otitis media with effusion), and hearing loss caused by eustachian tube dysfunction. Both procedures effectively address conditions related to upper respiratory tract issues and middle ear problems, improving breathing and hearing outcomes.
Key Differences Between Adenoidectomy and Myringotomy
Adenoidectomy involves the surgical removal of the adenoids to treat chronic nasal obstruction and recurrent infections, while myringotomy entails creating a small incision in the eardrum to drain fluid and relieve ear infections. Adenoidectomy primarily addresses breathing and sinus-related issues, whereas myringotomy targets middle ear problems such as otitis media with effusion. Recovery times differ, with adenoidectomy generally requiring a longer healing period compared to the minimally invasive nature of myringotomy.
Risks and Potential Complications of Each Procedure
Adenoidectomy carries risks such as bleeding, infection, nasal dryness, and potential changes in voice, with rare complications including damage to surrounding tissues or anesthesia-related issues. Myringotomy risks include persistent perforation of the eardrum, infection, scarring, and, when tubes are inserted, possible early extrusion or blockage leading to recurrent ear infections. Both procedures require careful evaluation of patient history to minimize complications and ensure optimal recovery outcomes.
Recovery and Aftercare: What to Expect
Recovery after adenoidectomy typically involves mild throat pain and nasal congestion, with most children returning to normal activities within 7 to 10 days. Myringotomy recovery is generally quicker, often resolving within 1 to 2 days, with ear drainage or mild discomfort being common post-procedure symptoms. Aftercare for both includes monitoring for signs of infection, managing pain with recommended medications, and avoiding water exposure to the ears following myringotomy to ensure proper healing.
Comparing Outcomes: Effectiveness and Patient Satisfaction
Adenoidectomy demonstrates higher effectiveness in reducing recurrent otitis media and improving airway obstruction compared to myringotomy, which primarily addresses middle ear effusion and acute ear infections. Patient satisfaction tends to be greater with adenoidectomy due to more sustained symptom relief and fewer repeat interventions, whereas myringotomy offers quicker recovery but may require additional procedures. Both surgeries have distinct indications, but adenoidectomy's long-term benefits in airway and infection control often lead to better overall clinical outcomes.
Choosing the Right Procedure: Factors to Consider
Choosing between adenoidectomy and myringotomy depends on the patient's specific symptoms and underlying conditions, such as recurrent ear infections or chronic nasal obstruction. Adenoidectomy is often recommended for children with enlarged adenoids causing breathing difficulties or sleep apnea, while myringotomy is preferred for relieving middle ear fluid and recurrent otitis media. Factors like age, severity of symptoms, presence of tympanostomy tubes, and potential impact on hearing guide physicians in selecting the optimal procedure.
Frequently Asked Questions About Adenoidectomy and Myringotomy
Adenoidectomy removes enlarged adenoids to improve breathing and reduce infections, while myringotomy involves creating a small ear incision to drain fluid and relieve pressure. Common questions about adenoidectomy address recovery time, potential complications, and its effectiveness in treating chronic infections or sleep apnea. For myringotomy, patients often inquire about the procedure's safety, duration of tube placement, and impact on hearing improvement.
Adenoidectomy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com