Journals serve as essential tools for capturing thoughts, tracking progress, and organizing ideas across various fields. Whether you use digital or traditional formats, maintaining a journal can boost creativity, improve focus, and enhance personal growth. Discover how journaling can transform your routine by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
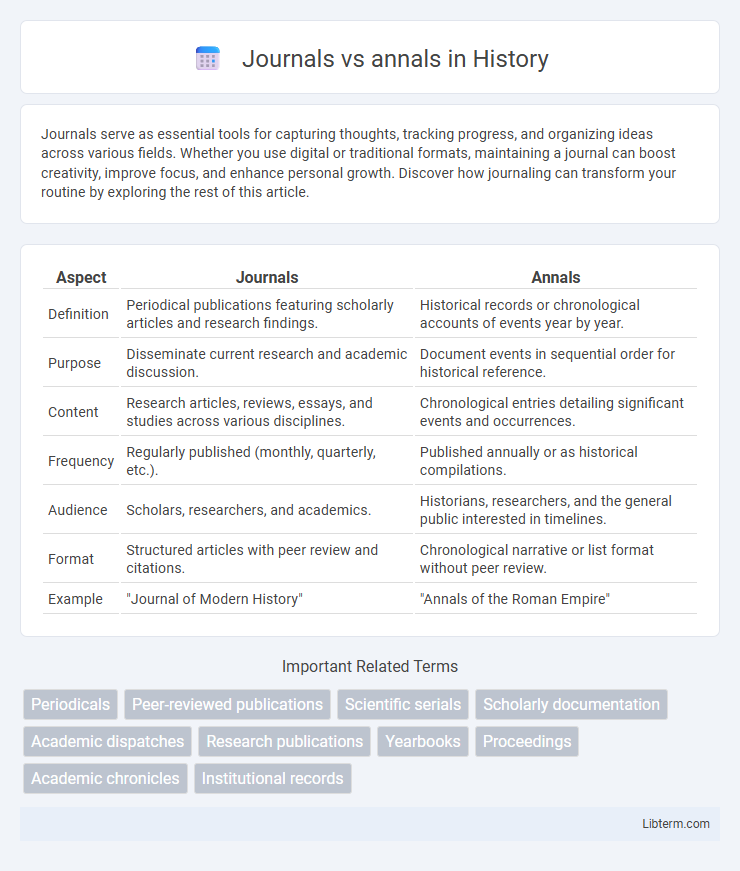
| Aspect | Journals | Annals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Periodical publications featuring scholarly articles and research findings. | Historical records or chronological accounts of events year by year. |
| Purpose | Disseminate current research and academic discussion. | Document events in sequential order for historical reference. |
| Content | Research articles, reviews, essays, and studies across various disciplines. | Chronological entries detailing significant events and occurrences. |
| Frequency | Regularly published (monthly, quarterly, etc.). | Published annually or as historical compilations. |
| Audience | Scholars, researchers, and academics. | Historians, researchers, and the general public interested in timelines. |
| Format | Structured articles with peer review and citations. | Chronological narrative or list format without peer review. |
| Example | "Journal of Modern History" | "Annals of the Roman Empire" |
Introduction to Journals and Annals
Journals are periodic publications that present contemporary research, studies, and articles across various disciplines, serving as primary sources of up-to-date knowledge. Annals are historical records or chronicles documenting events year by year, often providing detailed narratives and analysis over extended periods. Both serve as vital academic resources, with journals emphasizing current developments and annals focusing on historical continuity.
Defining Journals: Purpose and Scope
Journals serve as scholarly platforms dedicated to publishing original research, critical reviews, and theoretical discussions across various academic disciplines. Their primary purpose is to disseminate new knowledge, promote intellectual exchange, and uphold rigorous peer-review standards to ensure validity and credibility. Journals typically cover specialized fields and maintain periodic publication schedules, ranging from monthly to quarterly issues, targeting researchers, practitioners, and educators.
Understanding Annals: Origins and Meaning
Annals originated as chronological records documenting important events year by year, primarily used in medieval Europe to track historical occurrences systematically. Unlike journals, which often capture personal reflections or daily experiences, annals emphasize the precise dating and factual reporting of events without subjective commentary. Understanding annals involves recognizing their role as structured historical documents that serve as foundational sources for researching past societies and significant milestones.
Historical Evolution: Journals vs Annals
Journals evolved as periodic publications that document ongoing research and discoveries with detailed analyses, whereas annals originated as chronological records focusing on yearly events or historical summaries. The historical evolution of journals reflects the shift towards specialized, peer-reviewed academic discourse, contrasting with annals that preserve broader historical narratives in a sequential format. This distinction highlights journals' role in advancing scientific knowledge, while annals serve as archival records of significant historical developments.
Key Differences Between Journals and Annals
Journals are periodic publications featuring a collection of peer-reviewed articles on specific academic disciplines, while annals are chronological records that document events or developments over time in a systematic manner. Journals emphasize current research findings and scholarly discourse, whereas annals prioritize historical documentation and archival content. The format of journals typically includes research papers, reviews, and editorials, whereas annals present a continuous timeline of notable occurrences or institutional records.
Publication Frequency and Content Focus
Journals typically publish issues regularly, such as monthly or quarterly, featuring peer-reviewed articles centered on specific academic disciplines or research topics. Annals often release volumes annually or less frequently, compiling comprehensive reviews, historical records, or significant developments within a particular field over a set period. The publication frequency and content focus distinguish journals as sources for current research updates, whereas annals serve as detailed retrospectives or authoritative summaries.
Academic Impact: Journals Compared to Annals
Journals typically have a higher academic impact compared to annals due to their frequent publication cycles, rigorous peer-review processes, and broader dissemination in scientific databases. The citation metrics for journals are often more favorable, reflecting their influence and relevance within scholarly communities. Annals, while valuable for documenting proceedings or specific events, generally exhibit lower impact factors and less visibility in academic indexing platforms.
Common Fields Using Journals and Annals
Journals and annals are extensively used in academic fields such as medicine, history, and social sciences to document ongoing research and annual summaries respectively. Common fields like biology and chemistry favor journals for detailed, peer-reviewed articles on experiments and discoveries, while disciplines such as history and archaeology rely on annals to chronicle yearly events and significant milestones. Both formats support scholarly communication by providing authoritative, time-stamped records critical for research progression and historical reference.
How to Choose: Journal vs Annal for Researchers
Selecting between a journal and an annal depends on the research scope and audience; journals typically publish peer-reviewed articles focusing on specific disciplines, offering timely dissemination of current studies, while annals often compile comprehensive annual records or proceedings relevant to broader, historical, or institutional research contexts. Researchers seeking rapid publication and targeted academic engagement should prioritize journals to maximize impact and citation potential. For extensive reviews or longitudinal data, annals provide valuable archival significance and authoritative documentation.
Conclusion: Importance in Academic Publishing
Journals and annals both play crucial roles in academic publishing by disseminating research findings and advancing scholarly communication. Journals typically offer more frequent publication cycles and diverse article formats, enhancing timely knowledge sharing across disciplines. Annals often provide comprehensive, thematic collections of research, serving as authoritative records in specific academic fields.
Journals Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com