Dehumanization occurs when individuals or groups are stripped of their human qualities, leading to discrimination, violence, and social exclusion. This phenomenon undermines empathy and justifies harmful behaviors by portraying others as less than human. Explore the full article to understand how dehumanization impacts society and what steps you can take to combat it.
Table of Comparison
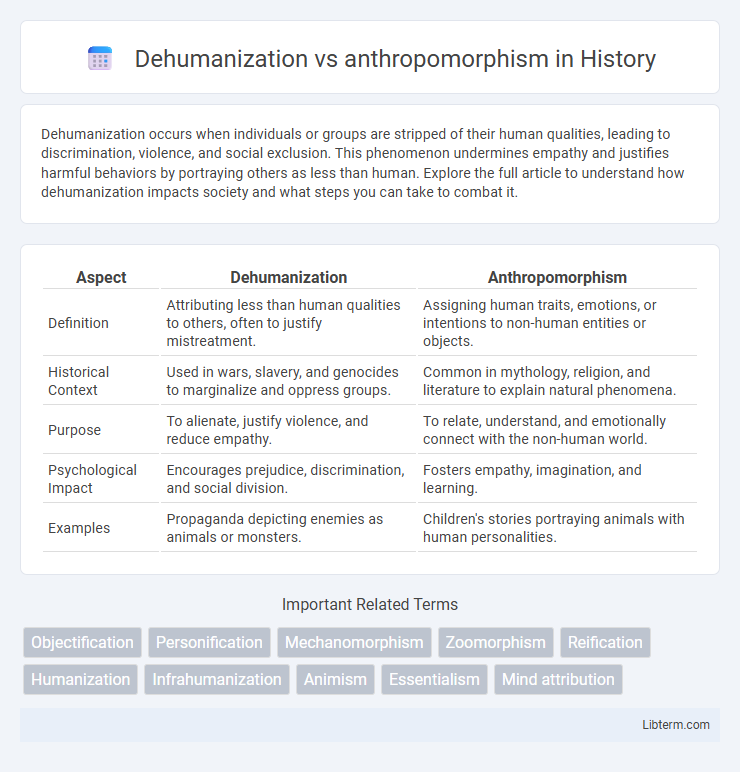
| Aspect | Dehumanization | Anthropomorphism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Attributing less than human qualities to others, often to justify mistreatment. | Assigning human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities or objects. |
| Historical Context | Used in wars, slavery, and genocides to marginalize and oppress groups. | Common in mythology, religion, and literature to explain natural phenomena. |
| Purpose | To alienate, justify violence, and reduce empathy. | To relate, understand, and emotionally connect with the non-human world. |
| Psychological Impact | Encourages prejudice, discrimination, and social division. | Fosters empathy, imagination, and learning. |
| Examples | Propaganda depicting enemies as animals or monsters. | Children's stories portraying animals with human personalities. |
Understanding Dehumanization: Definition and Effects
Dehumanization involves perceiving or treating individuals as less than human, often by denying their emotions, intelligence, or individuality, which can lead to increased aggression and justification of harmful actions. This psychological process reduces empathy and facilitates social exclusion, contributing to discrimination and violence in various contexts such as conflict, racism, and bullying. Understanding dehumanization is crucial for developing interventions that promote humanization, empathy, and social cohesion.
What Is Anthropomorphism? Origins and Usage
Anthropomorphism refers to attributing human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities, such as animals, objects, or natural phenomena. Its origins trace back to ancient mythology and religious practices where humans personified gods and animals to better understand the world. Today, anthropomorphism is widely used in literature, animation, and marketing to create relatable characters and forge emotional connections with audiences.
Psychological Drivers Behind Dehumanization
Dehumanization stems from psychological drivers such as fear, social dominance, and cognitive biases that simplify complex human traits into less relatable or threatening categories. This process often involves mechanisms like stereotype activation and empathy reduction, leading individuals to perceive others as lacking human qualities or moral consideration. Understanding these drivers is crucial for addressing behaviors related to intergroup conflict, discrimination, and social exclusion.
Anthropomorphism in Everyday Life
Anthropomorphism in everyday life manifests through assigning human traits and emotions to non-human entities such as pets, robots, and digital assistants, enhancing emotional connections and user experience. This tendency drives design in technology, exemplified by virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa, which respond using human-like language and behaviors to foster engagement. Recognizing anthropomorphism's role improves interaction design and social bonding with artificial agents in both consumer products and social robotics.
Media Portrayals: Dehumanization and Anthropomorphism Compared
Media portrayals of dehumanization often depict marginalized groups through stereotypes that strip away individuality and emotional depth, reinforcing social biases and justifying exclusion or violence. In contrast, anthropomorphism in media attributes human traits, emotions, or intentions to animals, objects, or abstract concepts, fostering empathy and relatable narratives. This contrast highlights the powerful role of representation in shaping audience perceptions of human and non-human entities, influencing social attitudes and ethical considerations.
Cultural Differences in Perceiving Nonhumans and Humans
Cultural differences significantly influence how societies perceive nonhumans and humans through dehumanization and anthropomorphism processes. Western cultures often emphasize individualism, leading to distinctions that heighten dehumanization in conflict scenarios, whereas many Indigenous cultures practice animism, attributing human-like qualities to animals and nature. These contrasting worldviews shape interactions with nonhuman entities, affecting environmental ethics, social behaviors, and conflict resolution strategies worldwide.
Ethical Implications: Dehumanization’s Social Consequences
Dehumanization erodes empathy and justifies discrimination, often leading to social exclusion, increased violence, and human rights abuses. This process undermines social cohesion and perpetuates systemic inequalities by stripping individuals or groups of their inherent dignity. Ethical concerns arise as dehumanization facilitates harmful ideologies and policies that marginalize vulnerable populations.
Anthropomorphism in Technology and AI Design
Anthropomorphism in technology and AI design involves attributing human traits, emotions, and intentions to machines, enhancing user engagement and trust. This approach improves interaction by making AI systems appear more relatable and intuitive, fostering natural communication. Effective anthropomorphic design balances realism to prevent uncanny valley effects, ensuring users feel comfortable and confident in technology usage.
Combating Dehumanization: Empathy and Awareness
Combating dehumanization involves fostering empathy by recognizing shared human experiences and emotions, which counteracts the psychological distancing that dehumanization creates. Awareness campaigns and educational programs emphasizing the value of human dignity and diversity promote understanding and reduce prejudice. Implementing these strategies in social and institutional contexts enhances social cohesion and discourages harmful stereotypes.
Finding Balance: Humanizing and Dehumanizing in Society
Finding balance between dehumanization and anthropomorphism involves recognizing the complexity of human traits without reducing individuals to stereotypes or oversimplified representations. Dehumanization strips people of their individuality and empathy, leading to discrimination and social division, while excessive anthropomorphism attributes human characteristics to non-human entities, distorting reality and expectations. Achieving a balanced perspective fosters empathy and respect for human dignity while maintaining clear distinctions between humans and objects or animals, crucial for ethical decision-making and social cohesion.
Dehumanization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com