Traditionalist values emphasize preserving long-established customs, beliefs, and practices that have shaped cultures and societies over generations. Rooted in respect for heritage and continuity, these principles often guide social behavior, education, and governance. Explore the rest of the article to understand how traditionalist perspectives influence modern life and your worldview.
Table of Comparison
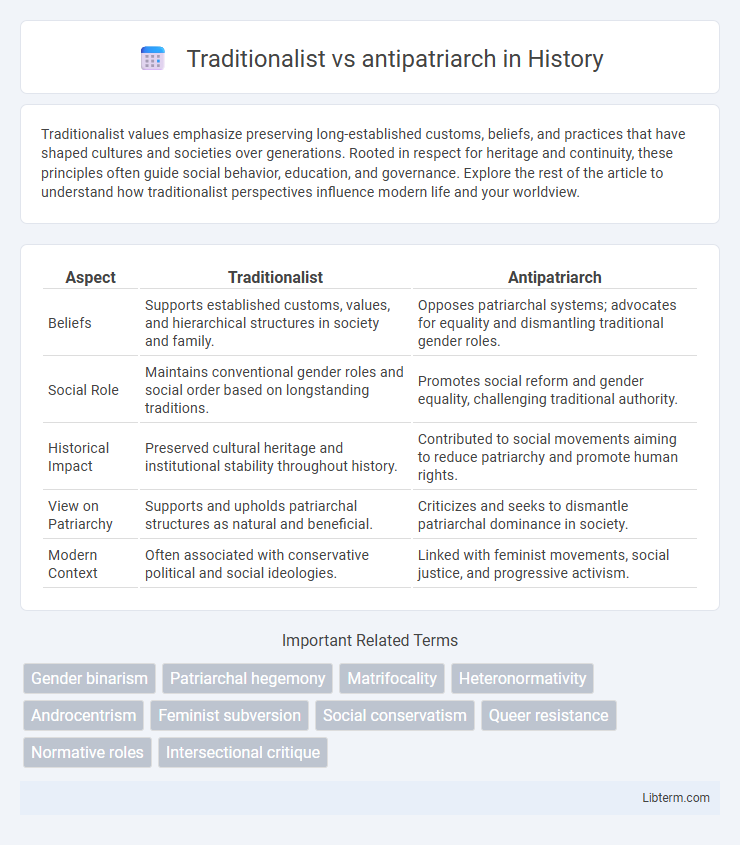
| Aspect | Traditionalist | Antipatriarch |
|---|---|---|
| Beliefs | Supports established customs, values, and hierarchical structures in society and family. | Opposes patriarchal systems; advocates for equality and dismantling traditional gender roles. |
| Social Role | Maintains conventional gender roles and social order based on longstanding traditions. | Promotes social reform and gender equality, challenging traditional authority. |
| Historical Impact | Preserved cultural heritage and institutional stability throughout history. | Contributed to social movements aiming to reduce patriarchy and promote human rights. |
| View on Patriarchy | Supports and upholds patriarchal structures as natural and beneficial. | Criticizes and seeks to dismantle patriarchal dominance in society. |
| Modern Context | Often associated with conservative political and social ideologies. | Linked with feminist movements, social justice, and progressive activism. |
Understanding Traditionalism: Core Beliefs
Traditionalism centers on preserving established customs, religious practices, and social hierarchies, emphasizing continuity and respect for ancestral wisdom. Core beliefs include upholding patriarchal family structures, valuing communal identity over individualism, and maintaining rituals that reinforce collective cultural heritage. This worldview often resists rapid social change, advocating for stability through adherence to long-standing moral and institutional norms.
Defining Antipatriarchy: Principles and Goals
Antipatriarchy challenges the traditionalist emphasis on male dominance by advocating for the dismantling of patriarchal systems that perpetuate gender inequality and oppression. Its core principles include gender egalitarianism, intersectionality, and the rejection of hierarchical power structures that privilege men over women and marginalized groups. The primary goals of antipatriarchy involve promoting social justice, dismantling systemic sexism, and fostering inclusive environments where all genders have equal rights and opportunities.
Historical Roots of Patriarchal Societies
Patriarchal societies trace their origins to ancient agrarian civilizations where male dominance was reinforced through land ownership, kinship systems, and warrior cultures, establishing hierarchical structures favoring men. Traditionalists uphold these historical frameworks as natural social orders rooted in biological and cultural evolution, emphasizing family lineage and social stability. In contrast, antipatriarchal perspectives critically examine these origins, highlighting how patriarchal systems institutionalized gender inequality and restricted women's roles across historical epochs.
Cultural Significance of Traditional Gender Roles
Traditionalist views emphasize the cultural significance of gender roles as foundational to social stability, often linking them to historical customs and religious doctrines that shape identity and community cohesion. Antipatriarch perspectives challenge these roles, arguing that they restrict individual freedom and perpetuate systemic inequality, advocating for a more fluid understanding of gender that respects personal autonomy and diversity. The cultural debate highlights the tension between preserving heritage and promoting progressive values in shaping modern societal norms.
Antipatriarchal Movements: Origins and Evolution
Antipatriarchal movements originated during the late 19th and early 20th centuries as responses to entrenched patriarchal systems that limited women's rights and social roles. These movements evolved through waves of feminism, emphasizing gender equality, dismantling male dominance, and challenging traditional family structures. Key milestones include the suffragette campaigns, second-wave feminism's focus on workplace and reproductive rights, and contemporary intersectional activism addressing systemic gender oppression globally.
Key Arguments of Traditionalists vs Antipatriarchs
Traditionalists argue that patriarchal structures uphold social order, cultural heritage, and familial stability by maintaining clear roles and responsibilities. Antipatriarchs contend that patriarchy perpetuates systemic gender inequality, limits individual freedoms, and reinforces power imbalances detrimental to social progress. Both perspectives clash on interpretations of gender roles, authority, and the impact of tradition on modern societal values.
Impact on Family Dynamics and Relationships
Traditionalists prioritize established family roles and hierarchies, reinforcing clear authority structures that often emphasize parental control and respect for elders, which can foster stability but may limit individual expression. Antipatriarch perspectives challenge these norms by promoting egalitarian and fluid family roles, encouraging open communication and shared responsibilities that can lead to more democratic decision-making and emotional closeness. The contrast between traditionalist and antipatriarch views significantly shapes family dynamics, influencing parental authority, gender roles, and intergenerational relationships, ultimately impacting emotional bonds and conflict resolution strategies.
Societal Change: Resistance and Adaptation
Traditionalists often resist societal change by upholding established norms and patriarchal values, emphasizing continuity and stability in social roles and family structures. Antipatriarch groups advocate for dismantling these power hierarchies, promoting gender equality and inclusive reforms that challenge conventional authority. This dynamic tension shapes how societies navigate adaptation, balancing preservation of heritage with progressive transformation.
The Role of Media in Shaping Narratives
Traditionalist media outlets often emphasize patriarchal values by framing narratives that reinforce established social hierarchies and gender roles. Antipatriarch media challenges these norms by highlighting stories of gender equality, feminist movements, and social justice, thereby reshaping public perception and discourse. Social media platforms play a critical role in amplifying diverse voices, allowing antipatriarch perspectives to gain visibility and contest traditionalist narratives.
Future Perspectives: Bridging Traditionalism and Antipatriarchy
Future perspectives on bridging Traditionalism and Antipatriarchy emphasize creating inclusive dialogues that respect cultural heritage while challenging patriarchal structures. Integrative approaches promote gender equity within traditional frameworks by reinterpreting customs to align with contemporary social justice values. Emerging movements focus on collaborative reforms that honor identity and foster progressive change without erasing historical contexts.
Traditionalist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com