Holograph technology creates three-dimensional images by recording light patterns and reconstructing them with precise clarity, offering immersive visual experiences. This cutting-edge innovation is transforming fields from entertainment to medical imaging with its ability to project lifelike, interactive displays. Explore the rest of the article to discover how holographs can redefine your perception of reality.
Table of Comparison
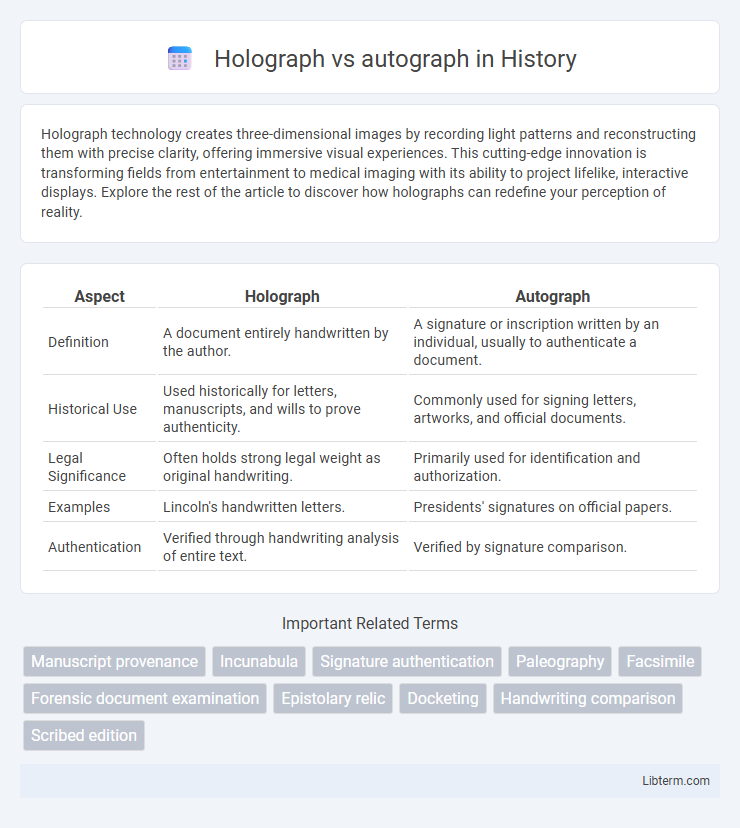
| Aspect | Holograph | Autograph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A document entirely handwritten by the author. | A signature or inscription written by an individual, usually to authenticate a document. |
| Historical Use | Used historically for letters, manuscripts, and wills to prove authenticity. | Commonly used for signing letters, artworks, and official documents. |
| Legal Significance | Often holds strong legal weight as original handwriting. | Primarily used for identification and authorization. |
| Examples | Lincoln's handwritten letters. | Presidents' signatures on official papers. |
| Authentication | Verified through handwriting analysis of entire text. | Verified by signature comparison. |
Introduction to Holographs and Autographs
Holographs are documents entirely handwritten by the author, often valued for their authenticity and personal connection to the creator, while autographs specifically refer to a person's handwritten signature. In legal contexts, holographs can serve as valid wills or contracts provided they are signed and dated by the author. Collectors and historians prize both holographs and autographs for their uniqueness, linking tangible personal expression with provenance and historical significance.
Defining Holographs: Meaning and Characteristics
Holographs are handwritten documents authored entirely by the individual whose signature they bear, often valued in legal and historical contexts for their authenticity and uniqueness. These manuscripts showcase the distinct penmanship and personal style of the writer, distinguishing them from autographs, which may be merely signed prints or copies not fully handwritten by the signer. The intrinsic characteristic of holographs lies in their manual creation, serving as verifiable evidence of origin and intent in wills, letters, and official records.
Understanding Autographs: Core Concepts
Autographs refer to original, handwritten signatures or documents created by the author, establishing authenticity and personal verification. Holographs are a specific subset of autographs characterized by being entirely handwritten by the individual, often used in legal contexts like wills. Understanding autographs involves recognizing their role in provenance, authenticity verification, and legal validation.
Key Differences Between Holographs and Autographs
Holographs are documents handwritten and signed entirely by the author, emphasizing originality and legal authenticity, whereas autographs refer primarily to the handwritten signatures of a person, often collected as memorabilia. A holograph holds legal significance in wills or contracts due to its full handwritten nature, while autographs serve more as personal endorsements or collectible items. The primary distinction lies in the comprehensive handwritten content of holographs versus the signature-only nature of autographs.
Legal Implications of Holographs vs Autographs
Holographs, which are handwritten documents authored entirely in the handwriting of the signatory, often carry significant legal weight as they can serve as authentic evidence of intent or testamentary capacity, especially in wills and contracts. Autographs, while primarily valued for their signature or endorsement, may require additional verification to establish authenticity, as they could be reproduced or affixed by proxy. Legal systems frequently prioritize holographs for their inherent proof of authorship and reduce the risk of forgery or disputes compared to standard autographs.
Collectors’ Perspectives: Value and Authenticity
Collectors value holographs for their direct connection to the creator, as these handwritten documents or signatures provide undeniable authenticity and a unique personal touch. Autographs, while also prized, may be more common and thus sometimes less valuable unless linked to rare events or individuals. The distinction significantly influences market value, with holographs often commanding higher prices due to their scarcity and verified origin.
Historical Significance of Holographs and Autographs
Holographs, handwritten documents entirely created by the author, hold immense historical significance as primary sources that provide direct insight into the creator's thoughts and intentions, often revealing authentic signatures, annotations, or corrections that authenticate historical narratives. Autographs, typically signatures or inscriptions by notable figures, carry cultural and historical value by serving as tangible links to influential personalities and pivotal events, often preserved in archives, museums, and collections to validate provenance and enhance scholarly research. The preservation and study of holographs and autographs enrich understanding of historical contexts, authorship authenticity, and the evolution of written communication across centuries.
Modern Usage: Digital vs Physical Documentation
Holograph refers to a document entirely handwritten by its author, often used in legal and historical contexts to verify authenticity, whereas autograph denotes a person's signature, commonly collected for memorabilia. In modern usage, digital documentation increasingly replaces physical holographs and autographs through electronic signatures and digital certificates, providing enhanced security and convenience. Despite this shift, physical handwritten documents and signatures remain vital for certain legal, archival, and sentimental purposes.
Common Misconceptions and Confusions
Holograph signatures often cause confusion because they are entirely handwritten by the document's author, whereas autographs refer specifically to signatures as a form of personal identification or memorabilia. A common misconception is that all handwritten signatures qualify as holographs, but only documents or wills wholly written and signed by the same person are considered holographic. Autographs are primarily valued for their collectible nature, while holographs have significant legal implications in proving authenticity and intent.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Holographs and Autographs
Holographs, being documents entirely handwritten by the author, carry significant legal weight and authenticity, often preferred in wills and historical manuscripts. Autographs, while still valuable, primarily refer to signatures or writings by famous individuals and are widely collected for their memorabilia value. Choosing between holographs and autographs depends on the need for legal enforceability versus collectible or sentimental significance.
Holograph Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com