Chapter titles set the tone and guide readers through your content with clarity and precision. Effective chapter naming enhances navigation, improves SEO, and boosts reader engagement by clearly outlining the subject matter. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to craft compelling chapter titles that captivate Your audience.
Table of Comparison
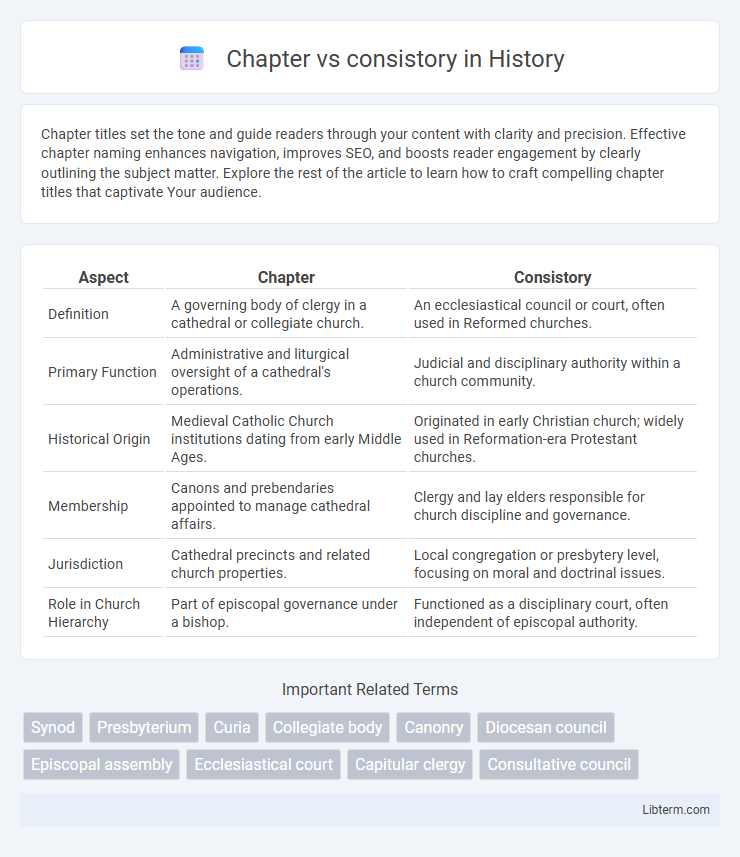
| Aspect | Chapter | Consistory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A governing body of clergy in a cathedral or collegiate church. | An ecclesiastical council or court, often used in Reformed churches. |
| Primary Function | Administrative and liturgical oversight of a cathedral's operations. | Judicial and disciplinary authority within a church community. |
| Historical Origin | Medieval Catholic Church institutions dating from early Middle Ages. | Originated in early Christian church; widely used in Reformation-era Protestant churches. |
| Membership | Canons and prebendaries appointed to manage cathedral affairs. | Clergy and lay elders responsible for church discipline and governance. |
| Jurisdiction | Cathedral precincts and related church properties. | Local congregation or presbytery level, focusing on moral and doctrinal issues. |
| Role in Church Hierarchy | Part of episcopal governance under a bishop. | Functioned as a disciplinary court, often independent of episcopal authority. |
Introduction to Chapter and Consistory
A chapter is a formal body of clergy or canons responsible for the administration of a cathedral or collegiate church, often tasked with managing liturgical functions and church property. A consistory, by contrast, is an assembly of ecclesiastical officials, typically including bishops and cardinals, that advises the pope or higher church authority on matters of governance, discipline, and appointments within the Catholic Church. While chapters primarily focus on local church administration, consistories serve broader ecclesiastical judicial and consultative roles.
Historical Origins of Chapter and Consistory
Chapters originated in the early medieval church as assemblies of clergy, typically canons, responsible for administering cathedrals and collegiate churches, evolving from Roman administrative councils. Consistories, on the other hand, emerged as formal ecclesiastical courts or assemblies within the Catholic Church, dating back to the papal curia's judicial and consultative functions in the Middle Ages. The historical differentiation highlights chapters as communal governing bodies tied to clergy residence, while consistories developed as juridical or advisory councils under higher church authority.
Definition: What Is a Chapter?
A chapter is a formal assembly of clergy or canons attached to a cathedral or collegiate church, responsible for the administration, worship, and governance within the religious institution. It serves as the governing body that oversees liturgical functions, property management, and clerical appointments. Unlike a consistory, which is primarily a judicial or administrative council within ecclesiastical courts, a chapter emphasizes collective leadership and decision-making related to church operations and religious duties.
Definition: What Is a Consistory?
A consistory is an ecclesiastical council or assembly, often comprising clergy and church officials, responsible for advising bishops and governing church matters within a diocese. Unlike a chapter, which typically refers to a college of canons associated with a cathedral or collegiate church, a consistory primarily functions as a judicial or administrative body in church governance. Consistories play a crucial role in disciplinary actions, doctrinal decisions, and the supervision of clergy, distinguishing them from the liturgical and ceremonial duties of chapters.
Key Differences Between Chapter and Consistory
A chapter is a governing body of clergy in a cathedral or collegiate church responsible for administrative and liturgical matters, while a consistory serves as a council or tribunal in some Protestant churches, mainly handling disciplinary and doctrinal issues. Chapters typically consist of canons and a dean or provost, whereas consistories include elders and ministerial leadership focused on church governance and discipline. The key distinction lies in chapters managing cathedral functions and worship, whereas consistories oversee church discipline and moral oversight within the congregation.
Functions and Roles of a Chapter
A Chapter functions as the governing body of a cathedral or collegiate church, responsible for overseeing liturgical practices, managing church property, and ensuring the maintenance of ecclesiastical discipline. It consists of canons or prebendaries who collectively make decisions on administrative, financial, and spiritual matters within the cathedral community. Unlike a consistory, which often deals with judicial and disciplinary issues within a diocese, the Chapter primarily focuses on the internal governance and ceremonial roles of the cathedral.
Functions and Roles of a Consistory
A consistory primarily functions as a church court responsible for overseeing ecclesiastical discipline, resolving disputes, and supervising clergy conduct within its jurisdiction. It often handles administrative tasks such as the approval of marriages, church property management, and doctrinal enforcement. Unlike a chapter, which mainly manages cathedral worship and governance, the consistory emphasizes judicial and regulatory roles in church governance.
Chapter vs Consistory: Governance Structures
Chapters and consistories serve as distinct governance structures within ecclesiastical organizations, each with specific administrative roles and authority. Chapters typically comprise clergy members responsible for overseeing cathedral functions, liturgical practices, and property management, while consistories often act as governing bodies managing broader diocesan or regional church matters. Their structural differences impact decision-making processes, jurisdictional reach, and the execution of ecclesiastical policies within religious institutions.
Importance in Religious and Ecclesiastical Contexts
Chapters and consistories serve as essential governing bodies within various Christian denominations, with chapters primarily responsible for the administration of cathedrals and clerical duties, while consistories hold judicial authority in church matters, including discipline and doctrinal enforcement. The chapter's role in maintaining liturgical functions and managing cathedral property underscores its significance in preserving religious traditions and community organization. Consistories contribute critically to ecclesiastical governance by ensuring doctrinal conformity and resolving disputes, thereby safeguarding the church's spiritual integrity and hierarchical order.
Conclusion: Chapter vs Consistory Overview
A chapter typically refers to a body of clergy organized to manage a cathedral or collegiate church, emphasizing liturgical functions and governance. A consistory is a broader ecclesiastical council, often judicial, involved in church discipline and administrative decisions within a diocese. Understanding the distinct roles highlights that chapters focus more on worship and internal management, while consistories address legal and pastoral oversight in church hierarchy.
Chapter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com