Laboratores are individuals engaged in manual work, often contributing significantly to industries such as agriculture, manufacturing, and construction. Their skills and efforts form the backbone of economic productivity, emphasizing the value of skilled labor in sustaining societal growth. Explore the article to understand how laboratores impact today's workforce and economy.
Table of Comparison
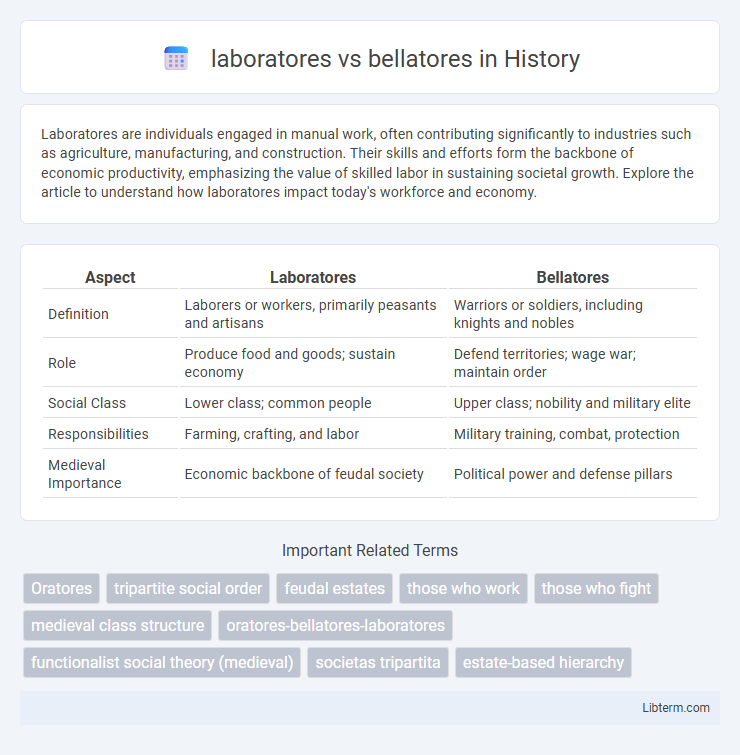
| Aspect | Laboratores | Bellatores |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Laborers or workers, primarily peasants and artisans | Warriors or soldiers, including knights and nobles |
| Role | Produce food and goods; sustain economy | Defend territories; wage war; maintain order |
| Social Class | Lower class; common people | Upper class; nobility and military elite |
| Responsibilities | Farming, crafting, and labor | Military training, combat, protection |
| Medieval Importance | Economic backbone of feudal society | Political power and defense pillars |
Understanding Laboratores and Bellatores
Laboratores and bellatores represent the two primary social classes in medieval society, with laboratores comprising peasants and workers responsible for agricultural and manual labor that sustained the economy. Bellatores consisted of the warrior class, including knights and nobles, who provided military protection and upheld feudal authority. Understanding the distinct roles of laboratores and bellatores reveals the interdependence of economic production and military power in maintaining medieval social structure.
Historical Origins of Laboratores and Bellatores
The historical origins of laboratores and bellatores trace back to the early medieval European feudal system, where laboratores represented the working class, primarily peasants and serfs engaged in agriculture and manual labor. Bellatores comprised the warrior nobility, including knights and lords, responsible for military protection and governance. This division of labor and martial roles institutionalized social hierarchy and economic functions crucial to medieval society's stability.
Key Roles and Functions in Medieval Society
Laboratores were the working class in medieval society responsible for agriculture, craftsmanship, and trade, ensuring the production of essential goods and sustenance. Bellatores comprised the warrior and noble class, primarily focused on military defense, governance, and the administration of feudal territories. Their functions were interdependent, with laboratores supporting the economic foundation while bellatores maintained social order and protection.
Social Status and Hierarchy
Laboratores, comprising peasants and serfs, occupied the lowest tiers in medieval social hierarchy, tasked with agricultural labor and essential production. Bellatores, including knights and nobility, held higher social status, responsible for military protection and governance, often enjoying privileges and land ownership. This division reinforced feudal structure, where laborers sustained the economy while warriors maintained order and authority.
Economic Contributions of Laboratores
Laboratores, representing the working class including peasants, artisans, and merchants, were essential to the medieval economy through their production of food, goods, and services that sustained society. Their agricultural output ensured food security while their crafts and trade activities facilitated local and regional commerce, driving economic growth. The economic contributions of laboratores laid the foundation for urbanization and market development, distinguishing them as vital contributors beyond the battlefield role of bellatores.
Military Duties of Bellatores
Bellatores, the warrior class in medieval society, were primarily responsible for military duties including fighting in wars, defending territories, and maintaining order through armed force. They trained extensively in combat skills, horseback riding, and weaponry such as swords, lances, and bows to fulfill their role as protectors of the realm. Their military service was essential for safeguarding the domain and upholding the feudal system's power structure.
Interactions and Relationships Between Classes
Interactions between laboratores (workers) and bellatores (warriors) were foundational to medieval society's stability, with laboratores providing essential agricultural and artisanal production that sustained the bellatores' military and ruling functions. Relationships were often hierarchical but interdependent, as bellatores relied on laboratores for economic support, while laboratores depended on bellatores for protection and societal order. These dynamics shaped feudal obligations and reciprocal duties, reinforcing a balanced ecosystem where each class fulfilled distinct but complementary roles.
Laboratores and Bellatores in Medieval Literature
Laboratores, representing the working class in medieval literature, often embody the virtues of diligence and humility, reflecting the agrarian and artisanal backbone of medieval society. Bellatores, or the warrior class, symbolize honor, valor, and martial prowess, frequently depicted in epic tales and chivalric romances emphasizing the feudal system's hierarchical nature. The contrast between Laboratores and Bellatores in medieval texts highlights the societal roles and moral ideals assigned to each estate, shaping narratives around duty and social order.
Modern Perspectives on Medieval Social Orders
Modern perspectives on medieval social orders emphasize the dynamic interactions between laboratores, the working and producing class, and bellatores, the warrior nobility. Contemporary scholarship highlights the economic and social interdependence between these groups, challenging earlier views of rigid hierarchical segregation. Studies reveal how laboratores' agricultural and artisanal labor underpinned the military and political dominance of bellatores, reshaping understandings of medieval societal structure and function.
Legacy of Laboratores and Bellatores Today
The legacy of Laboratores and Bellatores shapes modern society by underscoring the essential roles of workers and warriors in historical social structures. Laboratores, representing the laboring class, laid the foundation for economic stability and technological progress, while Bellatores, the warrior class, influenced political power and territorial security. Today, this dual legacy informs contemporary discussions on labor rights, military service, and social hierarchy.
laboratores Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com