A donatario is the individual or entity receiving a donation, typically in legal or property transfer contexts, with specific rights and responsibilities outlined by the grantor. Understanding the role and obligations of the donatario ensures your interests are protected in such transactions. Explore the rest of the article to learn more about the legal implications and best practices for donatarios.
Table of Comparison
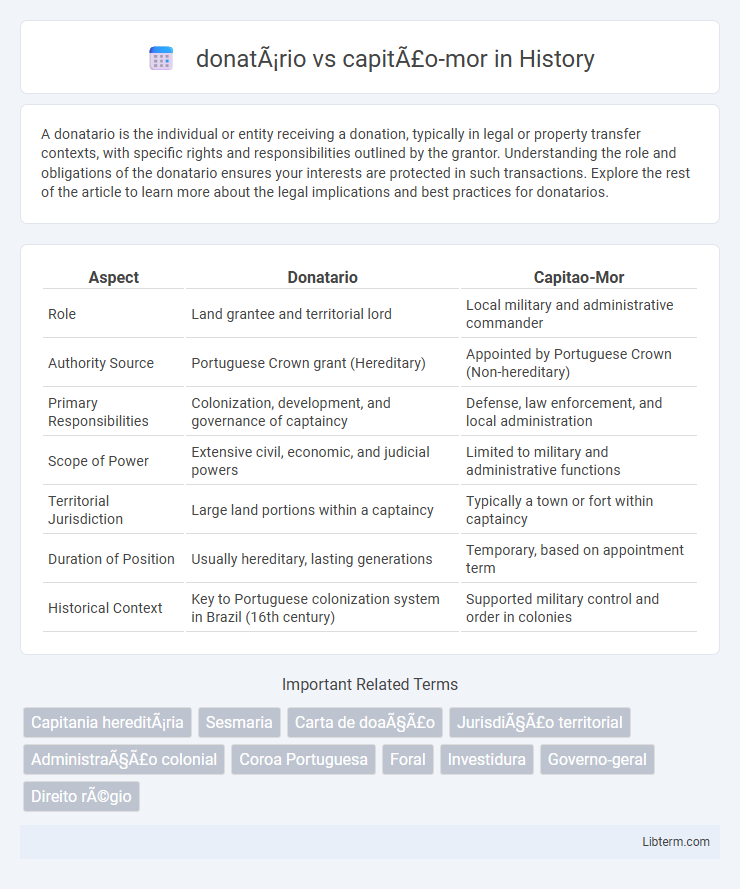
| Aspect | Donatario | Capitao-Mor |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Land grantee and territorial lord | Local military and administrative commander |
| Authority Source | Portuguese Crown grant (Hereditary) | Appointed by Portuguese Crown (Non-hereditary) |
| Primary Responsibilities | Colonization, development, and governance of captaincy | Defense, law enforcement, and local administration |
| Scope of Power | Extensive civil, economic, and judicial powers | Limited to military and administrative functions |
| Territorial Jurisdiction | Large land portions within a captaincy | Typically a town or fort within captaincy |
| Duration of Position | Usually hereditary, lasting generations | Temporary, based on appointment term |
| Historical Context | Key to Portuguese colonization system in Brazil (16th century) | Supported military control and order in colonies |
Definição de Donatário
Donatario refers to an individual granted land and administrative authority over a specific territory in Portuguese colonial administration, responsible for its settlement and development. This role involved overseeing economic activities, justice, and defense within the donataria, acting under the Crown's authority but with significant autonomy. In contrast, a Capitao-mor primarily served as a military leader focusing on defense and order, often subordinate to the donatario in administrative matters.
Definição de Capitão-mor
O Capitao-mor era uma autoridade colonial responsavel pela defesa, administracao militar e organizacao das tropas em uma capitania no periodo colonial portugues. Seu papel incluia a manutencao da ordem, supervisao dos soldados e coordenacao das expedicoes militares, diferindo do donatario, que exercia poderes civis e administrativos mais amplos sobre a capitania. Enquanto o donatario possuia poderes de governanca e exploracao economica, o Capitao-mor tinha uma funcao mais focada na seguranca e controle militar da regiao.
Origem Histórica dos Cargos
Donatario and Capitao-mor originated in the Portuguese colonial administration system during the Age of Discoveries, with the donatario being a grantee of land and jurisdictional privileges in newly conquered territories under a donataria. The Capitao-mor was appointed as the military commander responsible for defense and order within these territories, particularly in captaincies along the Brazilian coast. These roles emerged from the 15th and 16th-century Portuguese crown strategies to delegate authority and facilitate territorial control and settlement in overseas colonies.
Funções e Responsabilidades Principais
O donatario exercia funcoes de administracao territorial, gestao economica e justica local nos territorios do Brasil colonia, recebendo sesmarias para promover o desenvolvimento da capitania. O capitao-mor tinha como responsabilidade principal a defesa militar, a manutencao da ordem publica e a coordenacao das forcas armadas na regiao designada. Ambos desempenhavam papeis essenciais na organizacao politica e social das capitanias hereditarias, dividindo atribuicoes civis e militares.
Relação com a Coroa Portuguesa
The donatario held extensive administrative and economic powers granted directly by the Portuguese Crown to promote colonization, often operating with semi-autonomous authority over territories known as captaincies. The capitao-mor, typically appointed by the donatario or the Crown, was responsible for the military defense and local governance within a captaincy, executing orders to maintain Crown's interests. Both roles reflected the Crown's strategy to delegate power for effective territorial control while ensuring loyalty and resource extraction from colonial holdings.
Direitos e Privilégios de Cada Cargo
Donatarios held territorial rights granted by the Portuguese Crown, enabling them to govern, distribute land, and collect taxes within their donataria, enjoying extensive administrative and economic privileges. Capitaes-mores acted as royal representatives with military and judicial authority over a captaincy, responsible for defense, maintaining order, and implementing royal policies, but with fewer economic privileges than donatarios. Both positions carried significant power in colonial governance, though donatarios traditionally wielded broader autonomy and economic benefits.
Diferenças na Administração Colonial
The donatario held extensive land grants and administrative powers in the colonial system, overseeing settlement and economic exploitation in designated captaincies. The capitao-mor functioned as a military and administrative leader appointed by the donatario or the crown, responsible for local defense and maintaining order within the captaincy. Unlike the donatario's broad governance role, the capitao-mor's authority was often limited to military and judicial functions, reflecting a hierarchical structure in colonial administration.
Processo de Nomeação e Substituição
The processo de nomeacao do donatario envolve a outorga pela Coroa Portuguesa, conferindo-lhe direitos e responsabilidades sobre uma capitania hereditaria, com substituicao geralmente limitada a herdeiros legitimos ou por decreto regio. Ja o capitao-mor e nomeado diretamente pela autoridade regia, exercendo funcao administrativa e militar, com substituicao mais flexivel mediante ordens superiores ou locais, atendendo a criterios de competencia e confianca. Ambos os cargos refletem a estrutura administrativa colonial, mas diferem na rigidez e formalidade do processo de nomeacao e substituicao.
Exemplos Notáveis de Donatários e Capitães-mores
Donatarios such as Martim Afonso de Sousa, who established the Sao Vicente captaincy, played a crucial role in early Brazilian colonization by managing land grants and promoting settlement. Capitaes-mores like Mem de Sa, the third Governor-General of Brazil, were responsible for military defense and administering colonial territories under the donatarios' jurisdiction. These figures exemplify the distinct but complementary roles in Portuguese colonial administration, with donatarios focusing on land management and economic development, while capitaes-mores ensured security and governance.
Impacto no Desenvolvimento Colonial
The donatario system granted large land tracts with administrative autonomy, accelerating colonization by incentivizing private investment and local governance development. Capitao-mor roles concentrated military and administrative authority, ensuring territorial defense and order but often limiting economic diversification. This division of powers shaped colonial development by balancing territorial control with economic expansion in Portuguese America.
donatário Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com