A seal is a marine mammal known for its streamlined body and flippers that enable efficient swimming in cold ocean waters. Seals play a crucial role in marine ecosystems by maintaining fish populations and serving as prey for larger predators. Discover more about their behaviors, habitats, and significance by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
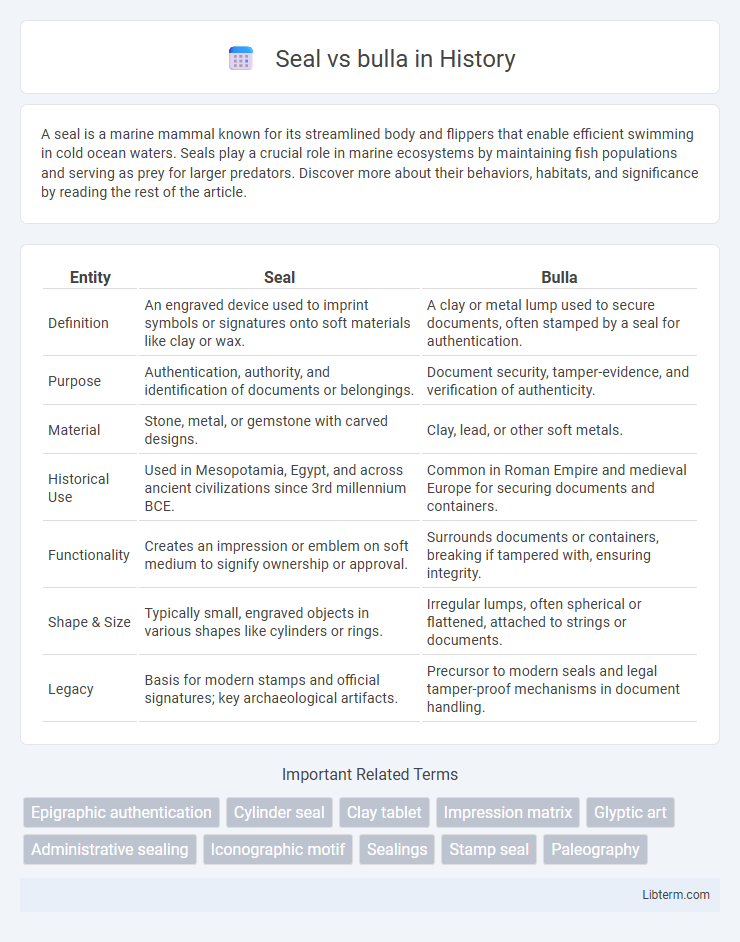
| Entity | Seal | Bulla |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An engraved device used to imprint symbols or signatures onto soft materials like clay or wax. | A clay or metal lump used to secure documents, often stamped by a seal for authentication. |
| Purpose | Authentication, authority, and identification of documents or belongings. | Document security, tamper-evidence, and verification of authenticity. |
| Material | Stone, metal, or gemstone with carved designs. | Clay, lead, or other soft metals. |
| Historical Use | Used in Mesopotamia, Egypt, and across ancient civilizations since 3rd millennium BCE. | Common in Roman Empire and medieval Europe for securing documents and containers. |
| Functionality | Creates an impression or emblem on soft medium to signify ownership or approval. | Surrounds documents or containers, breaking if tampered with, ensuring integrity. |
| Shape & Size | Typically small, engraved objects in various shapes like cylinders or rings. | Irregular lumps, often spherical or flattened, attached to strings or documents. |
| Legacy | Basis for modern stamps and official signatures; key archaeological artifacts. | Precursor to modern seals and legal tamper-proof mechanisms in document handling. |
Introduction: Understanding Seals and Bullae
Seals and bullae are ancient artifacts used to secure and authenticate documents or goods, with seals typically being engraved devices used to imprint designs onto soft materials like clay or wax. Bullae are the hardened clay or metal pieces that bear the impression of a seal, serving as evidence that a container or document remains unopened. Understanding the distinction between seals as the stamping tool and bullae as the sealed evidence illuminates their critical roles in historical administration and communication systems.
Definition and Historical Background
A seal is an engraved device used to create an impression on soft materials like clay or wax, serving as a form of identification or authentication in ancient and medieval documents. A bulla is a specific type of seal impression typically found on ancient Roman documents, made of clay or lead, which secured and validated the contents of official correspondence. Historically, seals date back to ancient Mesopotamia around 3500 BCE, while bullae became prominent during the Roman Republic and Empire periods as tools of administrative control and legal authority.
Key Differences Between Seal and Bulla
A seal is an engraved emblem or device used to authenticate documents, typically made of metal or stone, while a bulla is a clay or lead lump impressed with a seal to secure and verify the closure of a document or container. Seals often serve as a signature of authority or identity, whereas bullae function as tamper-evident evidence preserving the document's integrity. The key difference lies in seals being the original engraved design, while bullae are the physical impressions created by pressing seals into soft material.
Materials and Methods of Production
Seals were typically made from durable materials such as stone, metal, or clay, and crafted through carving or engraving techniques to create detailed impressions. Bullae were usually formed from soft clay or wax and produced by molding or pressing seals onto the material to secure documents or goods. Both artifacts demonstrate varying production methods reflecting their distinct functional purposes in ancient administrative and legal processes.
Purposes and Functions in Ancient Societies
Seals and bullae served critical administrative and security purposes in ancient societies, with seals used primarily to imprint unique symbols or insignias onto documents or goods, ensuring authentication and authority. Bullae, typically clay or metal lumps, functioned as tamper-evident devices to secure containers or documents sealed by these imprints, protecting contents from unauthorized access and validating the transaction or message's integrity. Both tools facilitated governance, commerce, and legal processes by guaranteeing the origin and authenticity of materials in Mesopotamian, Egyptian, and other early civilizations.
Geographic and Cultural Variations
Seal and bulla exhibit significant geographic and cultural variations reflecting their distinct historical contexts. In ancient Mesopotamia, seals were primarily cylinder-shaped and intricately engraved for administrative purposes, while in the Roman world, bullae served as protective amulets worn by children, often made of metal or leather. East Asian cultures, such as China and Japan, emphasize personal seals or stamps called "chops," used for authentication in documents, starkly contrasting the Western use of bullae as symbolic jewelry or official tokens.
Iconography and Symbolism
Seals and bullae both function as ancient authentication devices but differ significantly in iconography and symbolism; seals often bear intricate engraved images representing authority, identity, or divine protection, while bullae, typically clay or metal enclosures, feature impressed seal designs symbolizing security and official endorsement. Seal iconography frequently includes gods, animals, or royal insignias, conveying power and legitimacy, whereas bullae emphasize the safeguarding of documents or goods, reinforcing trust and authenticity. The symbolic hierarchy reflected in seal motifs contrasts with the functional symbolism of bullae as physical proof of tampering prevention.
Archaeological Significance
Seals and bullae play crucial roles in archaeological studies by providing insights into ancient administrative systems and socio-political structures. Seals, often engraved stones or metals used to imprint designs, served as markers of authenticity and ownership, while bullae, typically clay or wax impressions enclosing documents, functioned as secure transaction records. Their discovery at excavation sites helps reconstruct historical trade networks, legal practices, and cultural interactions in civilizations such as Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley, and ancient Egypt.
Notable Discoveries and Case Studies
Notable discoveries in the study of seals versus bullae include the 7th-century BCE administrative bullae found in ancient Mesopotamian archives, which provide detailed records of economic transactions, contrasting with seals used as personal identification marks in various ancient civilizations. The Nimrud Seal case study reveals how cylinder seals served both as artistic expressions and symbols of authority in Assyrian culture, while bullae from the same period functioned primarily as security devices to authenticate documents or goods. Comparative analysis of these artifacts sheds light on their distinct roles in communication, trade verification, and legal practices across early urban societies.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Seals and Bullae
Seals and bullae serve as critical artifacts for understanding ancient administrative and legal practices, reflecting the evolution of authentication methods in historical societies. Their legacy endures in modern security techniques, highlighting the persistent need for verifying identity and authority. These objects offer invaluable insights into cultural, political, and economic interactions across civilizations.
Seal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com