Duke University stands as a prestigious institution renowned for its rigorous academics, cutting-edge research, and vibrant campus life. With a strong emphasis on innovation and leadership, it offers diverse programs that prepare students for impactful careers. Discover how Duke can transform your educational journey by exploring the benefits detailed in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
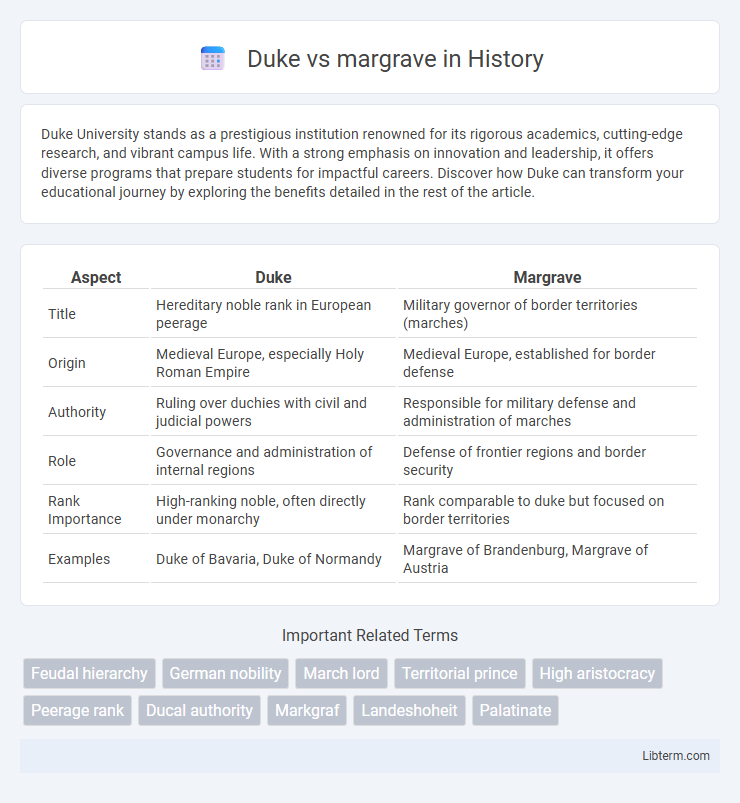
| Aspect | Duke | Margrave |
|---|---|---|
| Title | Hereditary noble rank in European peerage | Military governor of border territories (marches) |
| Origin | Medieval Europe, especially Holy Roman Empire | Medieval Europe, established for border defense |
| Authority | Ruling over duchies with civil and judicial powers | Responsible for military defense and administration of marches |
| Role | Governance and administration of internal regions | Defense of frontier regions and border security |
| Rank Importance | High-ranking noble, often directly under monarchy | Rank comparable to duke but focused on border territories |
| Examples | Duke of Bavaria, Duke of Normandy | Margrave of Brandenburg, Margrave of Austria |
Introduction to Dukes and Margraves
Dukes historically ruled large territorial regions within a kingdom, wielding significant military and administrative power as prominent nobles. Margraves served as frontier commanders tasked with defending border provinces, often granted additional authority to manage and fortify these strategic areas. Both titles reflect high-ranking positions in feudal Europe, with dukes typically overseeing established central regions and margraves focusing on peripheral borderlands.
Historical Origins of the Titles
The titles Duke and Margrave both originated in medieval Europe, with Duke deriving from the Latin "dux," meaning leader or commander, primarily denoting a noble ruling over a duchy. Margrave, from the German "Markgraf," combined "Mark" (border region) and "Graf" (count), designating nobles appointed to guard frontier territories called marches. These distinctions reflect the evolution of feudal hierarchy, where dukes held extensive territorial authority while margraves specialized in military defense of borderlands.
Duties and Responsibilities
Dukes historically commanded large territories and held military authority, overseeing defense, justice, and administration within their duchies. Margraves governed border regions known as marches, with duties centered on fortifying frontiers, defending against invasions, and maintaining regional security. Both titles required managing local nobility and ensuring loyalty to the crown, but margraves had heightened military obligations due to their strategically vulnerable positions.
Territorial Authority and Jurisdiction
Dukes traditionally held extensive territorial authority, often governing large regions with semi-autonomous power granted by the monarch, which included military command, law enforcement, and tax collection within their duchies. Margraves, originally appointed to defend border provinces called marchlands, wielded jurisdiction primarily focused on frontier defense and administration, balancing military responsibilities with civil governance. While both titles conferred noble status and regional authority, dukes typically exercised broader civil jurisdiction, whereas margraves combined territorial control with strategic military oversight in border territories.
Rank and Precedence in Nobility
A duke ranks above a margrave in the hierarchy of European nobility, typically holding one of the highest titles below the monarch. Dukes governed significant territories called duchies and often possessed greater political influence and precedence in court ceremonies. Margraves, originally military governors of border provinces known as marches, held a noble rank equivalent to counts but with strategic importance, positioned below dukes in both rank and precedence.
Power and Influence in the Feudal System
Dukes held significant power in the feudal system as high-ranking nobles often governing large duchies with military and judicial authority directly granted by the monarch. Margraves, on the other hand, were frontier lords responsible for defending border territories, combining military leadership with administrative duties to maintain regional security and influence. While dukes wielded broader political power within established regions, margraves possessed specialized authority crucial for expanding and protecting the realm's edges.
Differences in Military Roles
Dukes historically commanded large, semi-autonomous military forces within their duchies, often leading troops in major battles and defending extensive territorial borders. Margraves held command primarily over border provinces called marches, tasked with guarding frontiers against invasions and managing smaller but strategically critical garrisons. The military role of a margrave emphasized frontier defense and rapid response, whereas a duke's military responsibilities included broader regional control and the ability to muster large armies.
Symbolism and Heraldry
Dukes often bear coats of arms featuring crowns or coronets with specific jewel arrangements symbolizing their high rank and territorial authority, while margraves typically use a mural crown or a distinct border called a "bordure" to signify their role as frontier guardians. Heraldic symbols for dukes emphasize sovereignty and noble lineage, with lions, eagles, and fleur-de-lis commonly incorporated, whereas margraves' heraldry tends to highlight defense and boundary protection through imagery like fortifications or crosses. The differences in their heraldic elements reflect the historical responsibilities and prestige associated with each title in medieval European nobility.
Evolution of the Titles Over Time
The titles of Duke and Margrave originated in the medieval feudal system, with Dukes often governing large, semi-autonomous regions within a kingdom while Margraves initially served as military commanders of border territories known as marches. Over time, the role of Margraves evolved from defensive guardians of frontier zones to significant hereditary nobility with political influence comparable to that of Dukes. This transformation reflected broader changes in medieval governance and territorial administration, as earlier military functions gave way to more complex feudal and dynastic responsibilities.
Modern Relevance and Legacy
Dukes and margraves hold distinct historical titles that continue to influence modern European nobility and regional governance structures, especially within Germany and the UK. The title of duke remains prominent in contemporary British peerage, often associated with significant social and cultural roles, while margraves historically governed frontier regions, impacting territorial administration and defense strategies. Their legacies persist in place names, cultural heritage, and ceremonial functions, underscoring the enduring relevance of medieval nobility in shaping modern identity and governance.
Duke Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com