A balanced diet provides essential nutrients that support your body's overall health, improve energy levels, and strengthen the immune system. Incorporating a variety of whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains ensures optimal nutrient intake and aids in maintaining a healthy weight. Discover how to create a personalized diet plan that suits your lifestyle by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
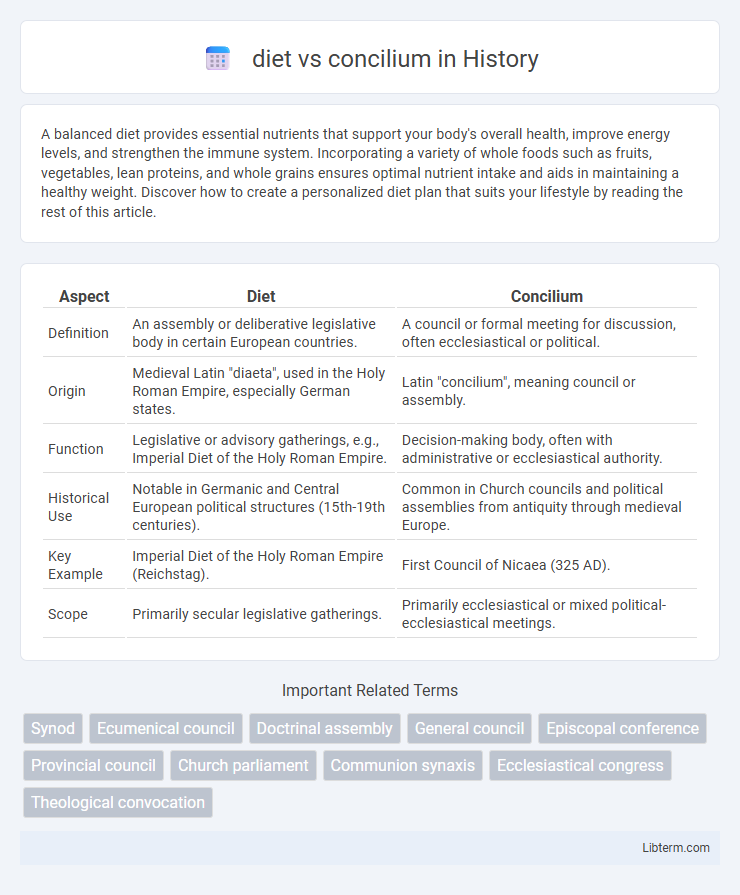
| Aspect | Diet | Concilium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An assembly or deliberative legislative body in certain European countries. | A council or formal meeting for discussion, often ecclesiastical or political. |
| Origin | Medieval Latin "diaeta", used in the Holy Roman Empire, especially German states. | Latin "concilium", meaning council or assembly. |
| Function | Legislative or advisory gatherings, e.g., Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire. | Decision-making body, often with administrative or ecclesiastical authority. |
| Historical Use | Notable in Germanic and Central European political structures (15th-19th centuries). | Common in Church councils and political assemblies from antiquity through medieval Europe. |
| Key Example | Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire (Reichstag). | First Council of Nicaea (325 AD). |
| Scope | Primarily secular legislative gatherings. | Primarily ecclesiastical or mixed political-ecclesiastical meetings. |
Understanding Diet: Definitions and Types
A diet refers to the sum of food consumed by a person or organism, structured to meet specific nutritional goals such as weight loss, muscle gain, or managing medical conditions. Common types of diets include ketogenic, Mediterranean, vegan, and intermittent fasting, each varying in macronutrient composition and food restrictions to optimize health outcomes. Understanding the definitions and variations of diets is essential for tailoring nutritional strategies to individual health needs and lifestyle preferences.
What Is a Concilium? Origins and Purpose
A concilium is a formal assembly or council primarily used in historical and ecclesiastical contexts to discuss and decide on important matters. Originating from Latin, the term 'concilium' denotes a gathering of leaders or experts aimed at achieving consensus or resolving disputes. Unlike a diet, which often refers to legislative bodies in specific regions, a concilium emphasizes advisory or decision-making roles in religious or organizational settings.
Diet vs Concilium: Key Differences Explained
The Diet and Concilium both function as legislative bodies but differ significantly in structure and scope; the Diet typically refers to national parliaments like the Japanese Diet, consisting of two houses responsible for enacting laws and approving budgets. Concilium, often seen in historical or religious contexts such as the Concilium lateranense, serves as council gatherings focusing on ecclesiastical decisions and doctrinal clarifications rather than legislative governance. Understanding these distinctions highlights the Diet's role in political lawmaking compared to the Concilium's deliberative and consultative functions within religious or advisory institutions.
Historical Significance of Diets and Conciliums
Diets and conciliums played pivotal roles in shaping political, religious, and social history across Europe, especially during the Middle Ages and Renaissance. The Imperial Diets of the Holy Roman Empire, such as the Diet of Worms (1521), influenced major religious reforms and political decisions, while church conciliums like the Council of Trent (1545-1563) were instrumental in defining Catholic doctrine and countering Protestant movements. Both assemblies served as crucial platforms for negotiation, policy-making, and conflict resolution, leaving lasting impacts on governance and religious practices.
Political Impact: Diets and Conciliums Through Time
Diets and conciliums have played pivotal roles in shaping political landscapes by facilitating governance and decision-making among rulers and representatives across centuries. Historic diets, such as the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire, centralized legislative power and influenced state policies, while ecclesiastical conciliums convened to address doctrinal disputes, indirectly affecting political alliances and power balances in medieval Europe. Both institutions exemplify how assemblies functioned as instruments of political authority and social order, impacting governance structures and political stability through formal deliberations.
Decision-Making Processes: Comparing Functions
The diet functions as a legislative body responsible for enacting laws and setting policy agendas, while the concilium primarily serves as an advisory council influencing executive decisions. Decision-making in the diet involves formal voting procedures and majority rule, ensuring democratic legitimacy, whereas the concilium relies on consensus-building and expert consultation to guide leadership strategies. Understanding these distinct operational frameworks highlights their complementary roles in governance and policy formulation.
Notable Examples: Famous Diets in History
Notable famous diets in history include the Paleolithic diet, which emphasizes whole foods based on presumed ancient human eating patterns, and the Atkins diet, popularized for low-carbohydrate intake focused on weight loss. The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, olive oil, and fish, is renowned for cardiovascular benefits supported by numerous studies. The Concilium model contrasts with these traditional diets by promoting collective decision-making in dietary guidelines, integrating diverse nutritional perspectives for public health policy.
Prominent Conciliums: Case Studies
The Diet of Worms (1521) exemplifies a prominent concilium, where Martin Luther was summoned to recant his teachings, shaping the Protestant Reformation's trajectory. The Council of Nicaea (325) stands as a landmark case, establishing foundational Christian doctrines and addressing Arianism, significantly influencing ecclesiastical unity. The Council of Trent (1545-1563) served as a decisive concilium that reformed Catholic doctrine in response to the Reformation, reinforcing church authority and clarifying dogma through extensive decrees.
Modern Relevance: Diets and Conciliums Today
Modern diets prioritize tailored nutrition plans that address individual health needs, while conciliums continue to serve as pivotal forums for collective decision-making in political, religious, and social contexts. Advances in nutritional science have transformed dietetics into a dynamic field promoting wellness and disease prevention. Conciliums remain relevant by facilitating dialogue and consensus among diverse groups in rapidly changing global landscapes.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Diet and Concilium
Selecting between Diet and Concilium depends heavily on individual health goals, dietary preferences, and specific medical conditions. Diet emphasizes personalized nutrition plans to improve metabolic health, while Concilium integrates expert medical advice with tailored lifestyle modifications for holistic wellness. Evaluating long-term sustainability and evidence-based outcomes is crucial for making an informed decision.
diet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com