Silver is a precious metal known for its exceptional conductivity, reflectivity, and antimicrobial properties, making it valuable in industries ranging from electronics to jewelry. Its ability to withstand corrosion and its lustrous appearance contribute to its widespread use in coins, silverware, and solar panels. Discover how silver's unique characteristics can enhance your investments and applications by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
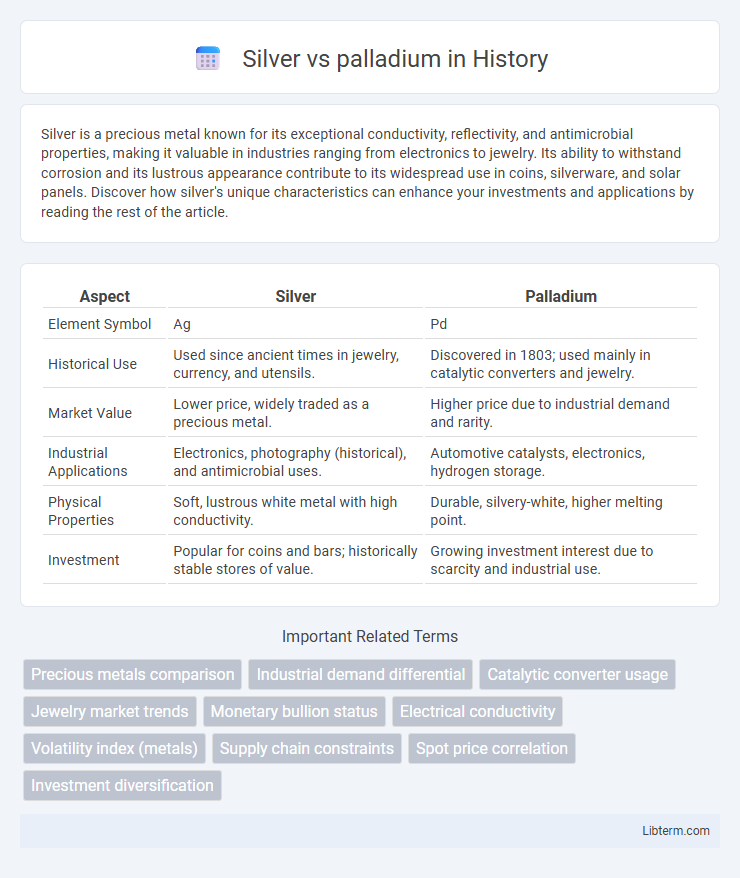
| Aspect | Silver | Palladium |
|---|---|---|
| Element Symbol | Ag | Pd |
| Historical Use | Used since ancient times in jewelry, currency, and utensils. | Discovered in 1803; used mainly in catalytic converters and jewelry. |
| Market Value | Lower price, widely traded as a precious metal. | Higher price due to industrial demand and rarity. |
| Industrial Applications | Electronics, photography (historical), and antimicrobial uses. | Automotive catalysts, electronics, hydrogen storage. |
| Physical Properties | Soft, lustrous white metal with high conductivity. | Durable, silvery-white, higher melting point. |
| Investment | Popular for coins and bars; historically stable stores of value. | Growing investment interest due to scarcity and industrial use. |
Introduction to Silver and Palladium
Silver and palladium are both precious metals valued for their unique properties and diverse industrial applications. Silver, known for its high electrical conductivity and antibacterial qualities, is widely used in electronics, jewelry, and medical instruments. Palladium is prized in the automotive industry for its catalytic properties in emission control systems and has become increasingly important in investment portfolios due to its rarity and industrial demand.
Chemical Properties and Characteristics
Silver exhibits high electrical conductivity, a melting point of 961.8degC, and excellent resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for electrical applications. Palladium, part of the platinum group, has a melting point of 1554.9degC, exceptional catalytic properties, and the unique ability to absorb hydrogen up to 900 times its volume. Both metals maintain good corrosion resistance, but palladium's chemical inertness and higher thermal stability differentiate it in industrial uses.
Occurrence and Mining Sources
Silver primarily occurs in native form and as ores like argentite, found abundantly in countries such as Mexico, Peru, and China, which lead global silver mining production. Palladium, a rare platinum-group metal, is mainly extracted as a byproduct from nickel and copper mines in Russia, South Africa, and Canada, with the Norilsk and Sudbury basins as significant sources. While silver deposits are more widespread, palladium's occurrence is closely tied to specific geologic settings involving ultramafic and mafic intrusions.
Industrial and Technological Applications
Silver and palladium are critical in industrial and technological applications due to their unique physical and chemical properties. Silver excels in electrical conductivity, making it indispensable for electronics, solar panels, and conductive inks. Palladium is vital in catalytic converters for reducing vehicle emissions, as well as in hydrogen purification and fuel cell technologies, thanks to its exceptional catalytic efficiency and resistance to poisoning.
Investment Potential and Market Trends
Silver offers greater liquidity and lower entry costs for investors, making it accessible for both retail and institutional portfolios, while palladium typically commands higher prices due to its rarity and industrial demand, particularly in automotive catalytic converters. Market trends reveal growing interest in palladium driven by tightening emission regulations and supply constraints in key mining regions like Russia and South Africa, whereas silver benefits from its dual role as an industrial metal and a traditional store of value. Investment potential in palladium may yield higher returns amid supply deficits, but silver provides diversification with its established market infrastructure and historical performance as a hedge against inflation.
Price Volatility and Historical Performance
Silver exhibits higher price volatility compared to palladium due to its greater industrial demand sensitivity and larger market size. Palladium's historical performance shows more pronounced price spikes, driven by automotive catalytic converter demand and supply constraints, leading to sharp but less frequent fluctuations. Both metals serve as valuable investment assets, but silver's price movements are typically more stable over long-term cycles.
Advantages of Investing in Silver
Silver offers excellent affordability compared to palladium, allowing investors to acquire larger quantities for the same investment capital. Known for its high industrial demand in electronics, solar panels, and medical applications, silver maintains strong intrinsic value and potential price growth. Unlike palladium, silver provides greater liquidity and accessibility in global markets, making it a preferred choice for both short-term trading and long-term wealth preservation.
Benefits of Choosing Palladium
Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher catalytic efficiency compared to silver, making it ideal for industrial applications such as automotive catalytic converters. Its lighter weight and hypoallergenic properties also provide advantages in jewelry, offering comfort and durability without tarnishing. Furthermore, palladium's growing demand in green technology and electronics enhances its investment potential over silver, which is more susceptible to environmental degradation.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
Silver mining generates significant environmental impacts, including habitat destruction, water contamination, and high energy consumption, raising concerns about ecosystem disruption. Palladium extraction also poses environmental challenges but is often associated with lower greenhouse gas emissions per ounce compared to silver. Ethically, both metals face scrutiny over labor practices in mining regions, with increasing demand for responsibly sourced certifications to ensure fair labor conditions and reduced environmental harm.
Conclusion: Which Metal Is Right for You?
Silver offers affordability, excellent conductivity, and classic aesthetics, making it ideal for budget-conscious buyers and everyday use. Palladium provides superior durability, tarnish resistance, and a modern, hypoallergenic alternative, suited for long-term investment and those with sensitive skin. Choosing between silver and palladium depends on your priorities: cost-effectiveness and traditional appeal versus longevity and premium quality.
Silver Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com