Traditional narrative history presents a chronological account of events, focusing on key figures, dates, and significant occurrences to provide a coherent story of the past. This method emphasizes cause and effect relationships, helping readers understand how historical developments unfold over time. Discover how this approach shapes our understanding of history and why it remains influential in historical studies by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
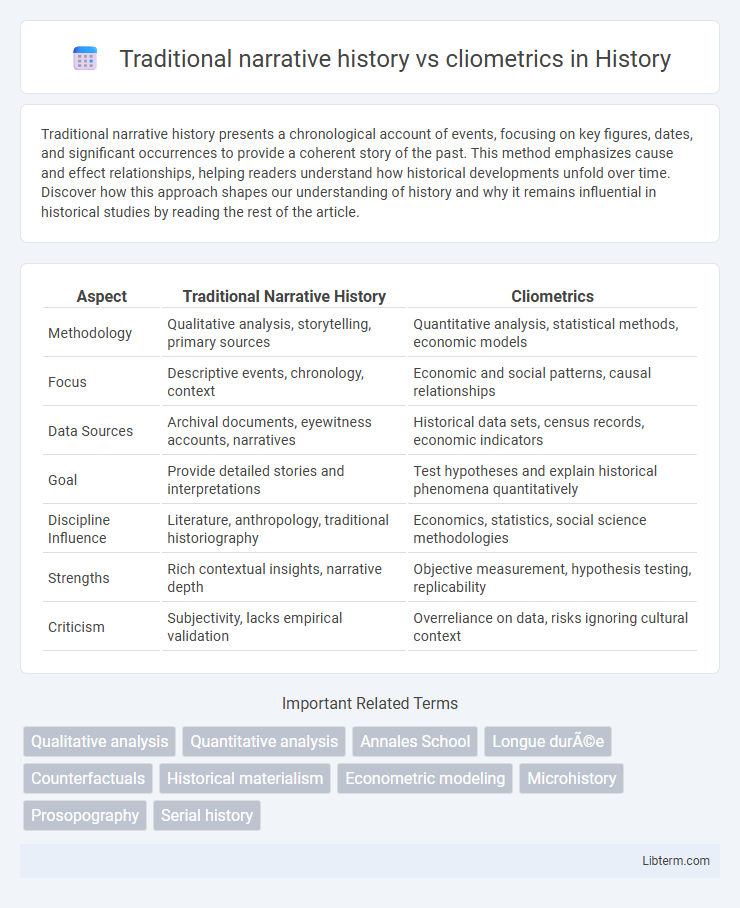
| Aspect | Traditional Narrative History | Cliometrics |
|---|---|---|
| Methodology | Qualitative analysis, storytelling, primary sources | Quantitative analysis, statistical methods, economic models |
| Focus | Descriptive events, chronology, context | Economic and social patterns, causal relationships |
| Data Sources | Archival documents, eyewitness accounts, narratives | Historical data sets, census records, economic indicators |
| Goal | Provide detailed stories and interpretations | Test hypotheses and explain historical phenomena quantitatively |
| Discipline Influence | Literature, anthropology, traditional historiography | Economics, statistics, social science methodologies |
| Strengths | Rich contextual insights, narrative depth | Objective measurement, hypothesis testing, replicability |
| Criticism | Subjectivity, lacks empirical validation | Overreliance on data, risks ignoring cultural context |
Introduction to Historical Methodologies
Traditional narrative history emphasizes chronological storytelling and qualitative analysis of primary sources, focusing on context and human experience to interpret past events. Cliometrics employs quantitative methods, such as econometric models and statistical data, to analyze economic and social patterns in history objectively. Introduction to historical methodologies reveals a shift from descriptive narratives toward data-driven analysis, improving precision and testing historical hypotheses systematically.
Defining Traditional Narrative History
Traditional narrative history emphasizes chronological storytelling based on qualitative sources such as letters, diaries, and eyewitness accounts to provide a detailed, human-centered perspective on past events. This approach prioritizes context, causality, and the interpretation of motives, often relying on primary documents and expert judgment. In contrast, cliometrics applies quantitative methods and economic theories to analyze historical data statistically, offering a more empirical and model-driven understanding of historical phenomena.
Understanding Cliometrics
Cliometrics applies quantitative methods and economic theory to historical data, revolutionizing the analysis of economic and social history by emphasizing statistical evidence over anecdotal accounts. This approach allows researchers to test hypotheses about historical events, patterns, and behaviors using econometric models and large datasets. Understanding cliometrics requires familiarity with advanced statistical techniques and an appreciation for how economic principles illuminate historical causation and trends.
Core Differences Between the Approaches
Traditional narrative history emphasizes descriptive storytelling and qualitative analysis based on primary sources, focusing on the experiences and perspectives of historical actors. Cliometrics employs quantitative methods, statistical models, and economic theory to analyze historical events, seeking patterns and causal relationships through data-driven evidence. The core difference lies in narrative history's reliance on subjective interpretation versus cliometrics' foundation in empirical and mathematical analysis.
Methodological Strengths of Narrative History
Traditional narrative history excels in providing rich, contextualized accounts of past events by integrating qualitative sources such as letters, diaries, and official documents. It emphasizes causality, culture, and human experience, offering a nuanced understanding that quantitative methods like cliometrics may overlook. This approach allows historians to interpret complex social dynamics and individual motivations beyond mere statistical correlations.
Advantages of Quantitative Analysis in Cliometrics
Quantitative analysis in cliometrics offers precise measurement of historical economic trends through statistical methods, enhancing objectivity compared to traditional narrative history. It enables the use of large datasets to identify patterns and test hypotheses rigorously, improving the reliability of conclusions. By applying econometric models, cliometrics provides deeper insights into causal relationships and economic impact over time.
Criticisms Faced by Traditional Narrative Historians
Traditional narrative historians face criticism for relying heavily on qualitative descriptions and anecdotal evidence, which can introduce subjective interpretations and limit analytical rigor. Their approach often lacks the quantitative methods employed by cliometrics, resulting in less precise economic and social trend analysis. This traditional method is also criticized for insufficiently addressing causality and failing to incorporate statistical data that enhance empirical validation.
Debates on the Objectivity of Cliometric Methods
Traditional narrative history relies on qualitative analysis and descriptive storytelling to interpret past events, often emphasizing cultural and social contexts. Cliometrics employs statistical and econometric techniques to quantify historical phenomena, aiming for empirical objectivity through data-driven analysis. Debates on the objectivity of cliometric methods center on challenges like the selection bias of historical data, the limitations of quantitative models to capture complex human behavior, and the potential reductionism in translating rich narratives into numerical datasets.
Case Studies: Applications of Both Approaches
Traditional narrative history uses rich, qualitative case studies to explore complex social and cultural contexts in historical events, providing detailed storytelling and nuanced perspectives. Cliometrics applies quantitative methods and economic models to historical data, allowing for statistical analysis and testing of hypotheses in case studies like demographic changes or economic impacts during specific time periods. Combining both approaches enriches historical understanding by integrating in-depth narrative insights with rigorous empirical evidence.
Future Directions in Historical Research
Future directions in historical research emphasize integrating cliometrics with traditional narrative history to enhance analytical rigor and contextual depth. Advances in data science and digitization facilitate large-scale quantitative analysis while preserving rich narratives that capture cultural and social complexities. This hybrid approach aims to produce more nuanced historical interpretations and predictive models, reshaping how historians understand and explain past events.
Traditional narrative history Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com