A princess often embodies elegance, grace, and a rich cultural heritage that captivates many around the world. Understanding the historical and modern roles of a princess can reveal fascinating insights into royal traditions and influence. Explore the full article to discover the intriguing lives and legacies of princesses throughout history.
Table of Comparison
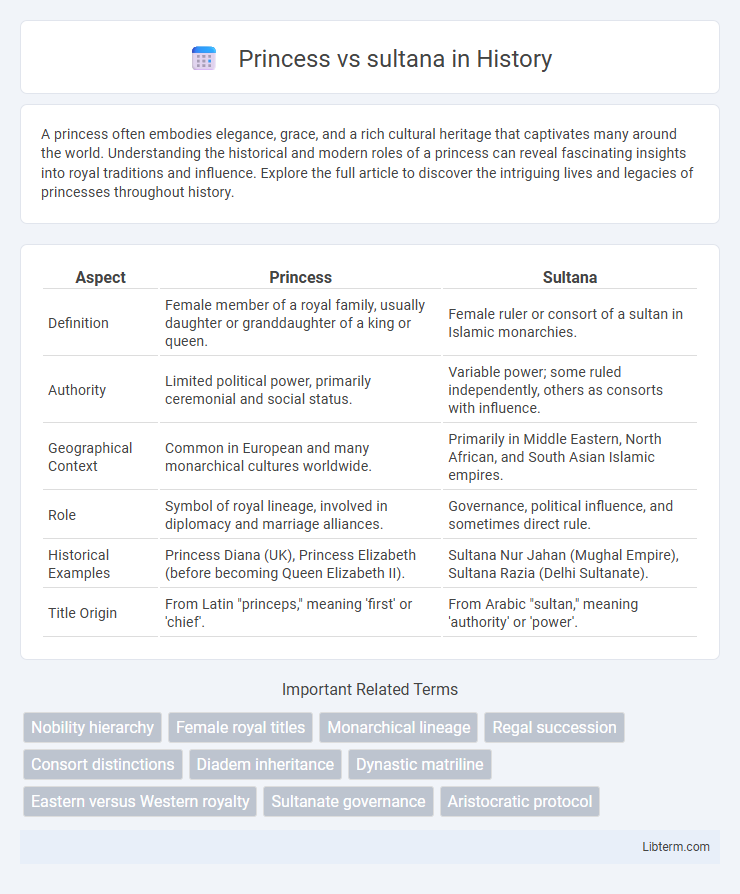
| Aspect | Princess | Sultana |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Female member of a royal family, usually daughter or granddaughter of a king or queen. | Female ruler or consort of a sultan in Islamic monarchies. |
| Authority | Limited political power, primarily ceremonial and social status. | Variable power; some ruled independently, others as consorts with influence. |
| Geographical Context | Common in European and many monarchical cultures worldwide. | Primarily in Middle Eastern, North African, and South Asian Islamic empires. |
| Role | Symbol of royal lineage, involved in diplomacy and marriage alliances. | Governance, political influence, and sometimes direct rule. |
| Historical Examples | Princess Diana (UK), Princess Elizabeth (before becoming Queen Elizabeth II). | Sultana Nur Jahan (Mughal Empire), Sultana Razia (Delhi Sultanate). |
| Title Origin | From Latin "princeps," meaning 'first' or 'chief'. | From Arabic "sultan," meaning 'authority' or 'power'. |
Introduction: Defining Princess and Sultana
A princess is typically a female royal family member, often the daughter or granddaughter of a king or queen, signifying nobility and direct lineage within a monarchy. A sultana refers specifically to a female ruler or consort in Islamic monarchies, with the title denoting power or status equivalent to a sultan. Both titles reflect elite status but differ culturally and historically, with sultana tied to Islamic governance and princess linked more broadly to hereditary royalty.
Historical Origins of Princesses and Sultanas
Princesses historically emerged from European monarchies as daughters of kings or queens, symbolizing nobility and often used to forge alliances through marriage. Sultanas, in contrast, originated within Islamic empires, particularly the Ottoman Empire, either as wives or female relatives of sultans, holding various degrees of political influence and power. The distinction lies in their cultural and political contexts: princesses aligned with hereditary European royalty, while sultanas were integral to the dynastic and administrative frameworks of Middle Eastern and South Asian Islamic states.
Cultural Differences: East vs. West
The title "Princess" in Western cultures typically denotes a royal daughter or a noblewoman with formal rank, often associated with European monarchies and rooted in Christian traditions. In contrast, "Sultana" in Eastern cultures, particularly in Middle Eastern and Islamic contexts, refers to a female ruler or consort linked to a sultan, embodying both political power and cultural influence. These titles reflect distinct historical roles and societal structures, highlighting key cultural differences between Western aristocratic lineage and Eastern Islamic governance.
Roles and Duties in Royal Courts
Princesses often serve as diplomatic envoys and cultural ambassadors within royal courts, responsible for fostering alliances through marriage and representation. Sultanas hold significant political influence, sometimes acting as advisors or regents with authority over state affairs and court administration. Both roles encompass ceremonial duties, yet sultanas typically wield more direct power in governance compared to the primarily symbolic and social responsibilities of princesses.
Symbolism and Representation
Princess symbolizes nobility, youth, and innocence within royal hierarchies, often representing potential and future leadership in Western and global cultures. Sultana signifies power, authority, and sovereignty in Islamic and Middle Eastern contexts, embodying both political influence and cultural heritage. The distinction reflects differing cultural frameworks: princess emphasizes lineage and grace, while sultana embodies rulership and active governance.
Notable Princesses in World History
Notable princesses in world history include Princess Diana of Wales, known for her humanitarian work and influence on the British monarchy, and Princess Elizabeth, who became Queen Elizabeth II, the longest-reigning British monarch. Unlike sultanas, who typically held power in Islamic empires such as the Ottoman Empire, princesses often played significant roles in European dynasties and diplomacy. Their legacies reflect the political and cultural impact of royal women across different regions and historical periods.
Famous Sultanas and Their Influence
Famous sultanas such as Hurrem Sultan, Roxelana of the Ottoman Empire, exerted immense political and cultural influence, shaping imperial policies and patronizing the arts. Sultanas held powerful positions within royal courts, often acting as advisors, regents, or key diplomatic figures, which distinguished their roles from princesses who typically had limited political authority. Unlike princesses, sultanas' influence extended beyond ceremonial duties, directly impacting governance and historical legacies in Islamic empires.
Attire and Regalia: Dress Codes Compared
Princess attire often features elegant gowns crafted from luxurious fabrics like silk and velvet, adorned with intricate embroidery and delicate pearls symbolizing nobility. Sultana dress codes emphasize grand, opulent garments such as elaborately decorated kaftans with gold thread and gemstones, reflecting their sovereign status and cultural heritage. Regalia for princesses typically includes tiaras and subtle jewelry, whereas sultanas wear more prominent crowns, heavy necklaces, and ceremonial sashes signifying power and authority.
Media Portrayal: Myths vs. Reality
Media often portrays princesses as passive figures focused on beauty and romance, while sultanas are depicted as mysterious and power-driven, creating a stark contrast that oversimplifies their real roles. Historically, many princesses and sultanas have exercised significant political influence and leadership, challenging these stereotypes. Accurate representation requires recognizing their diverse contributions beyond traditional myths perpetuated by films and literature.
Legacy and Modern Interpretation
Princess titles historically signified noble lineage within royal families, while Sultana denoted a female ruler or consort in Islamic monarchies, emphasizing political and religious authority. In modern interpretations, Princess often represents ceremonial and symbolic status in constitutional monarchies, whereas Sultana symbolizes female empowerment and leadership in cultural and political contexts. Both titles reflect evolving legacies influenced by regional traditions and contemporary gender roles in governance.
Princess Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com