Legal precedent establishes the foundation for consistent judicial decisions by relying on past rulings to guide the interpretation of laws in current cases. Understanding how precedents influence court outcomes can empower your ability to navigate complex legal issues more effectively. Explore the rest of this article to discover how legal precedents shape the justice system and impact your rights.
Table of Comparison
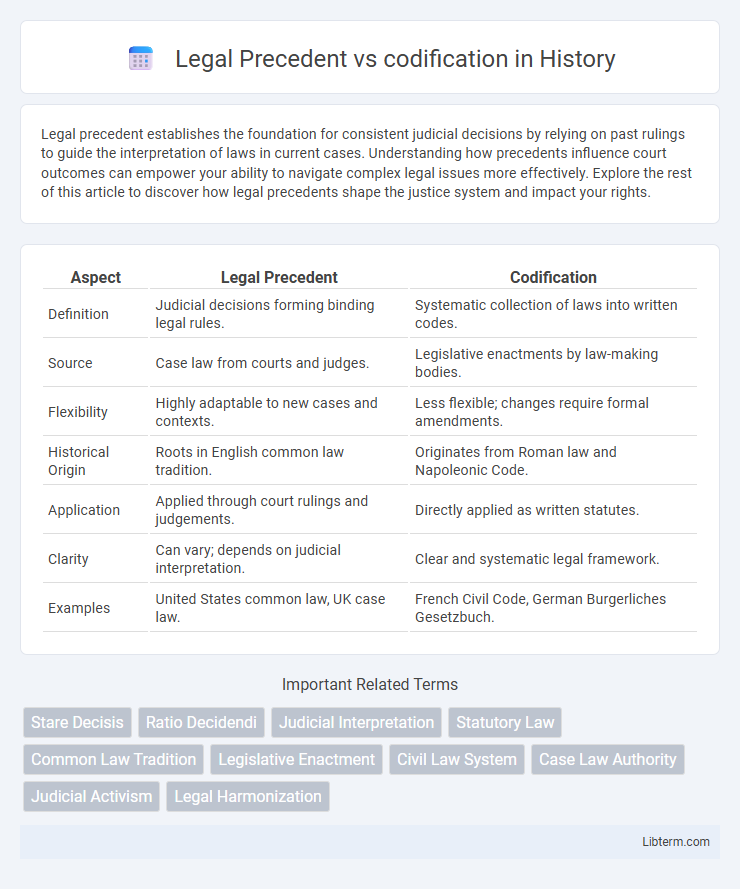
| Aspect | Legal Precedent | Codification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicial decisions forming binding legal rules. | Systematic collection of laws into written codes. |
| Source | Case law from courts and judges. | Legislative enactments by law-making bodies. |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to new cases and contexts. | Less flexible; changes require formal amendments. |
| Historical Origin | Roots in English common law tradition. | Originates from Roman law and Napoleonic Code. |
| Application | Applied through court rulings and judgements. | Directly applied as written statutes. |
| Clarity | Can vary; depends on judicial interpretation. | Clear and systematic legal framework. |
| Examples | United States common law, UK case law. | French Civil Code, German Burgerliches Gesetzbuch. |
Definition of Legal Precedent
Legal precedent, also known as case law, refers to judicial decisions that establish a rule or principle to be followed in future cases with similar facts. It is based on the doctrine of stare decisis, ensuring consistency and predictability within the legal system by relying on past rulings. Unlike codification, which involves systematically organizing and writing down laws into statutes, legal precedent evolves through court judgments and interpretations.
Understanding Codification in Law
Codification in law refers to the systematic compilation and organization of statutes and legal principles into comprehensive codes, enhancing clarity and accessibility for legal practitioners and the public. Unlike legal precedent, which relies on judicial decisions to interpret and apply laws, codification provides a fixed, authoritative legal framework that reduces ambiguity and inconsistency. Examples such as the Napoleonic Code illustrate how codification streamlines legal systems by consolidating diverse laws into coherent, written statutes.
Historical Development of Legal Precedent
Legal precedent, originating from the English common law system, evolved through centuries of judicial decisions that established binding rules for future cases, emphasizing the principle of stare decisis. This historical development contrasts with codification, which systematically organizes and consolidates laws into written statutes, as seen in the Napoleonic Code of 1804. The reliance on legal precedent allowed common law to adapt dynamically to societal changes, whereas codification aimed to provide clarity and uniformity in legal interpretation.
Evolution of Legal Codification
Legal codification has evolved as a systematic process to consolidate and organize laws into comprehensive codes, enhancing clarity and accessibility compared to the case-by-case development of legal precedents. Early examples like the Code of Hammurabi demonstrated the shift towards written statutes, while modern civil law systems, such as the Napoleonic Code, embody this evolution by providing structured legal frameworks. This progression reflects a move from reliance on judicial decisions to formal legislative enactments, promoting consistency and predictability in legal interpretation.
Key Differences Between Precedent and Codification
Legal precedent relies on past judicial decisions to guide future case rulings, emphasizing case-by-case analysis and flexibility. Codification consolidates laws into systematic, written statutes, promoting clarity, consistency, and accessibility in legal rules. The key difference lies in precedent's adaptability through evolving case law versus codification's fixed and structured legislative enactments.
Advantages of Relying on Legal Precedent
Relying on legal precedent ensures consistency and predictability in judicial decisions, allowing courts to follow established interpretations of laws. It provides flexibility by enabling judges to adapt prior rulings to new and evolving circumstances without awaiting legislative changes. Legal precedent also promotes judicial efficiency by reducing the need for exhaustive analysis in every case, drawing upon authoritative past judgments to guide current rulings.
Benefits of Legal Codification
Legal codification provides clear, organized statutes that simplify legal interpretation and enhance consistency across judicial decisions, reducing ambiguity inherent in case law derived from legal precedent. Codified laws improve accessibility for lawmakers, legal professionals, and the public, facilitating transparency and predictability in legal processes. The systematic nature of legal codification supports efficient legislative updates and reforms, promoting adaptability to social changes while maintaining legal stability.
Challenges of Integrating Precedent and Codification
Integrating legal precedent with codification presents challenges such as reconciling the dynamic, case-specific nature of precedent with the static, systematically organized statutes found in codes. Conflicts arise when judicial decisions interpret laws in ways that diverge from the literal wording of codified statutes, creating ambiguity for legal practitioners. Ensuring consistency and predictability in legal outcomes requires sophisticated mechanisms for harmonizing evolving case law with fixed codified provisions.
Impact on Judicial Decision-Making
Legal precedent shapes judicial decision-making by relying on past court rulings to ensure consistency and predictability in interpreting laws. Codification provides a comprehensive and systematic collection of statutes that judges apply directly, reducing reliance on previous judgments and emphasizing statutory interpretation. The balance between precedent and codification impacts how judges navigate ambiguity and evolve legal principles within a structured framework.
Future Trends in Legal Precedent and Codification
Emerging AI technologies and data analytics are transforming legal precedent by enabling more efficient case law analysis and prediction of judicial outcomes. Codification trends show a global move towards comprehensive digital statutes and automated legal updates to enhance accessibility and uniformity in law enforcement. Integration of blockchain for immutable legal records promises increased transparency and reliability in both precedent and codified law frameworks.
Legal Precedent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com