Assembly language is a low-level programming language that provides direct control over a computer's hardware by translating machine code instructions into human-readable form. Mastering assembly allows you to optimize performance-critical applications and understand the inner workings of processors at a granular level. Explore the rest of this article to uncover how assembly programming can enhance your coding expertise and system efficiency.
Table of Comparison
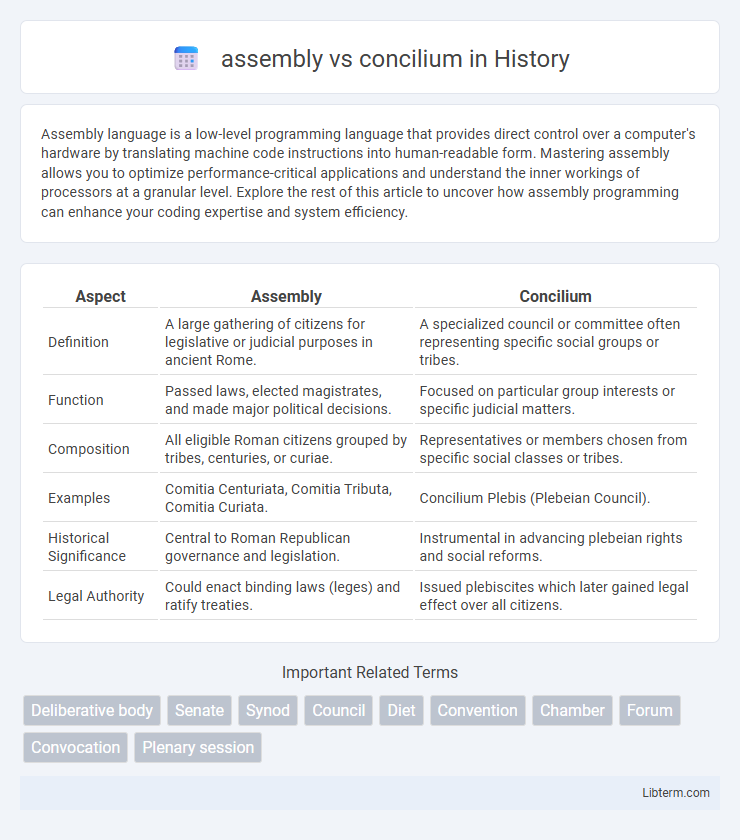
| Aspect | Assembly | Concilium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A large gathering of citizens for legislative or judicial purposes in ancient Rome. | A specialized council or committee often representing specific social groups or tribes. |
| Function | Passed laws, elected magistrates, and made major political decisions. | Focused on particular group interests or specific judicial matters. |
| Composition | All eligible Roman citizens grouped by tribes, centuries, or curiae. | Representatives or members chosen from specific social classes or tribes. |
| Examples | Comitia Centuriata, Comitia Tributa, Comitia Curiata. | Concilium Plebis (Plebeian Council). |
| Historical Significance | Central to Roman Republican governance and legislation. | Instrumental in advancing plebeian rights and social reforms. |
| Legal Authority | Could enact binding laws (leges) and ratify treaties. | Issued plebiscites which later gained legal effect over all citizens. |
Introduction to Assembly and Concilium
Assembly refers to a legislative or deliberative body where members convene to discuss, debate, and make decisions, often representing a specific constituency or region. Concilium denotes a smaller, more focused council or advisory group tasked with providing guidance and specialized input on particular issues. Both terms emphasize collective governance but differ in scale, function, and procedural formality within organizational or governmental contexts.
Defining Assembly: Functions and Structure
An assembly is a formal decision-making body typically composed of elected or appointed members representing various constituencies or interest groups, tasked with enacting legislation, debating policies, and overseeing governance functions. Its structure often includes specialized committees, leadership roles such as a speaker or chairperson, and procedural rules to manage debates and voting processes efficiently. The assembly's primary functions encompass lawmaking, budget approval, and holding the executive accountable through mechanisms like inquiries and motions.
Understanding Concilium: Roles and Organization
Concilium functions as a specialized legislative body with defined roles including policy formulation, strategic decision-making, and oversight. Its organization typically involves hierarchical committees and designated leaders to streamline governance and enhance accountability. Unlike a general assembly, Concilium emphasizes structured debate and expert participation to ensure informed resolutions.
Key Differences Between Assembly and Concilium
Assembly refers to a gathering of individuals typically for legislative, deliberative, or decision-making purposes, often characterized by a structured membership and formal procedures. Concilium, historically rooted in Roman contexts, denotes a council or advisory group with a focus on consultation and collective judgment rather than broad legislative authority. Key differences include the scope of power--assemblies usually possess formal decision-making authority, whereas concilia primarily serve advisory roles--and the composition, as assemblies often include a wider representation compared to more exclusive concilia.
Historical Origins and Development
Assembly and concilium share roots in ancient governance, with the assembly evolving from popular gatherings in Greek city-states and Roman comitia, while concilium originated as a council of notable figures advising rulers or magistrates. The assembly typically represented broader citizen participation in decision-making, reflecting early democratic principles, whereas the concilium functioned as a more exclusive advisory or deliberative body. Over time, assemblies institutionalized as legislative or popular forums, whereas concilia developed into formal councils or synods influencing political, religious, and social policies.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Assemblies involve direct participation of members in decision-making, enabling collective voting and debate, which fosters transparency and immediate consensus-building. In contrast, concilia (councils) consist of selected representatives or experts who deliberate and decide on behalf of a larger group, often allowing for specialized knowledge and structured discussion. The assembly's open approach promotes inclusivity while the concilium's focused framework enhances efficiency and depth in decision outcomes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Assembly
Assemblies offer direct participation and faster decision-making, enabling diverse viewpoints and immediate feedback, which enhances democratic legitimacy. However, assemblies can become inefficient with larger groups, prone to dominance by vocal minorities and potential disorganization. The informal nature may lead to ambiguous outcomes compared to the structured deliberations found in concilium settings.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Concilium
Concilium excels in fostering inclusive decision-making by enabling direct participation from diverse members, enhancing transparency and collective accountability. However, its effectiveness can be hampered by prolonged discussions and potential difficulties in reaching consensus, leading to slower decision-making processes compared to traditional assemblies. While assemblies often streamline decisions through hierarchical structures, Concilium's strength lies in collaborative deliberation but requires strong facilitation to prevent inefficiency.
Modern Applications of Assembly and Concilium
Assembly language remains crucial in modern embedded systems, firmware development, and performance-critical applications, enabling low-level hardware control and optimized execution speed. Concilium platforms, such as modern councils or advisory bodies, are integral in corporate governance, policy-making, and collaborative decision-making processes across industries. The fusion of assembly-level programming with concilium-driven strategies enhances technical efficiency and organizational responsiveness in contemporary technology and business environments.
Choosing Between Assembly and Concilium: Factors to Consider
Choosing between assembly and concilium depends on the size and purpose of the gathering, with assemblies suited for large, public decision-making and concilium ideal for smaller, specialized groups. Assemblies offer broad participation and democratic voting processes, while concilium allows for expert deliberation and focused discussions. Consider the complexity of issues and the desired level of inclusivity when determining the appropriate format for effective governance.
assembly Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com