Exogamy refers to the social practice of marrying outside one's own social group, clan, or community to promote genetic diversity and social alliances. This custom plays a crucial role in many cultures by preventing inbreeding and fostering broader social networks that can provide mutual support. Discover how exogamy influences societies worldwide and what it means for your understanding of cultural traditions in the full article.
Table of Comparison
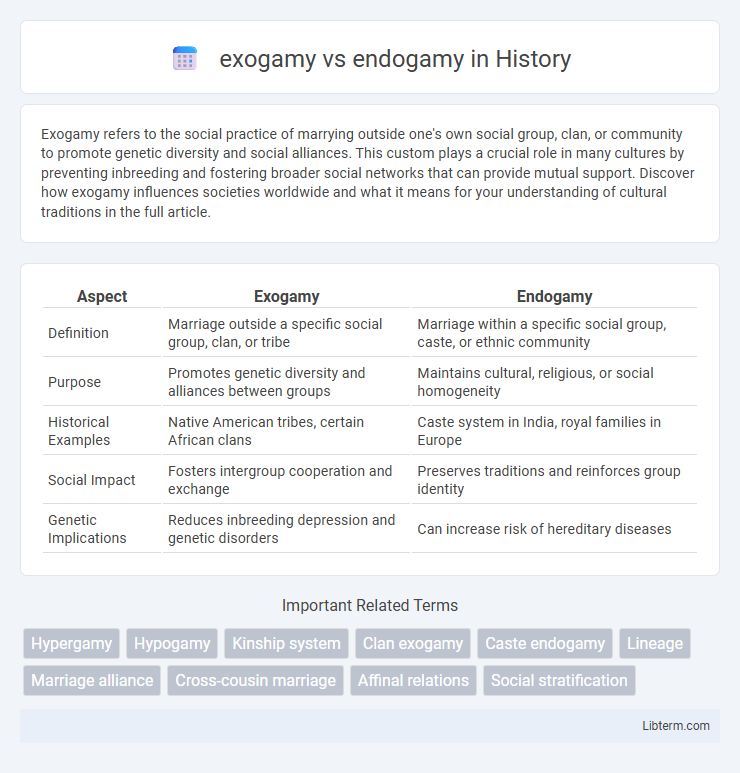
| Aspect | Exogamy | Endogamy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marriage outside a specific social group, clan, or tribe | Marriage within a specific social group, caste, or ethnic community |
| Purpose | Promotes genetic diversity and alliances between groups | Maintains cultural, religious, or social homogeneity |
| Historical Examples | Native American tribes, certain African clans | Caste system in India, royal families in Europe |
| Social Impact | Fosters intergroup cooperation and exchange | Preserves traditions and reinforces group identity |
| Genetic Implications | Reduces inbreeding depression and genetic disorders | Can increase risk of hereditary diseases |
Introduction to Exogamy and Endogamy
Exogamy involves marrying outside a specific social group, clan, or community, promoting genetic diversity and social alliances. Endogamy requires marrying within a defined group, such as a caste, tribe, or religious community, reinforcing social cohesion and cultural identity. These marriage practices shape kinship patterns and influence social structure across diverse cultures.
Defining Exogamy: Meaning and Origins
Exogamy refers to the custom of marrying outside one's social group, clan, or community, promoting genetic diversity and social alliances. Originating from anthropological studies, the term derives from the Greek words "exo" meaning outside and "gamos" meaning marriage. This practice contrasts with endogamy, which mandates marriage within a specific social group, reinforcing cultural cohesion and identity.
Understanding Endogamy: Concept and Significance
Endogamy refers to the social practice of marrying within a specific group, clan, or community, often based on shared ethnicity, religion, or social status. This practice reinforces cultural identity, preserves social cohesion, and maintains inherited wealth within the group. Understanding endogamy highlights its role in sustaining traditional values and regulating social structures in various societies.
Historical Perspectives on Marriage Practices
Historical perspectives on marriage practices reveal that exogamy and endogamy served distinct social functions: exogamy promoted alliances between different communities or clans, strengthening political and economic ties, while endogamy preserved cultural identities and maintained social hierarchies within homogeneous groups. In ancient societies such as those in Mesopotamia and India, endogamous marriage reinforced caste systems and lineage purity, whereas exogamous practices among Native American tribes facilitated inter-tribal cooperation and resource sharing. Anthropological evidence underscores how these opposing marriage strategies shaped social structures and influenced patterns of inheritance, kinship, and cultural continuity throughout history.
Cultural Variations in Exogamy and Endogamy
Cultural variations in exogamy and endogamy reflect diverse social structures and kinship systems across societies, with exogamy promoting alliances between different groups to enhance genetic diversity and social cohesion. In contrast, endogamy reinforces cultural identity and social boundaries by encouraging marriage within a specific community, caste, or ethnic group, often linked to religious or traditional norms. These practices influence social stratification, inheritance rules, and group solidarity, shaping the dynamics of cultural transmission and social organization worldwide.
Social Functions and Purposes of Exogamy
Exogamy promotes social cohesion and expands alliances by encouraging marriage outside one's social group, tribe, or community, thereby reducing inbreeding and fostering genetic diversity. It strengthens intergroup relationships, supports resource sharing, and enhances conflict resolution through kinship networks. This practice plays a crucial role in maintaining societal balance and facilitating cooperation across different social or ethnic groups.
Motivations Behind Endogamous Unions
Endogamous unions are primarily motivated by the desire to preserve cultural heritage, maintain social cohesion, and reinforce group identity within a community. These unions often aim to strengthen familial ties, ensure economic stability through inheritance and property consolidation, and protect religious or ethnic traditions. Such motivations are deeply rooted in societal norms that prioritize maintaining homogeneity and continuity within specific social groups.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Exogamy vs Endogamy
Exogamy promotes genetic diversity and reduces the risk of hereditary diseases by encouraging marriage outside one's social group, but it can challenge cultural cohesion and family acceptance. Endogamy strengthens social bonds and preserves cultural traditions within a community, yet it increases the likelihood of genetic disorders due to limited gene pools. Balancing these practices involves weighing the social benefits of cultural continuity against the biological advantages of genetic variation.
Modern Trends and Evolving Patterns
Modern trends reveal a rise in exogamy, driven by globalization and digital connectivity expanding social networks beyond traditional cultural and ethnic boundaries. Endogamy persists in certain communities prioritizing cultural preservation and social cohesion, reflecting ongoing resistance to assimilation. Changing patterns highlight a dynamic interplay between individual choice and collective identity in marriage practices worldwide.
Conclusion: The Future of Marriage Customs
Exogamy and endogamy reveal contrasting marriage customs shaped by cultural, social, and economic factors influencing partner selection within or outside specific groups. The future of marriage customs will likely embrace increased flexibility, blending traditional norms with globalized perspectives promoting diversity and inclusivity. Technological advancements and evolving social values are expected to further transform exogamous and endogamous practices to reflect modern identities and relationships.
exogamy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com