The Star Chamber was a notorious English court that operated from the late 15th century to the mid-17th century, known for its secretive and often ruthless proceedings. It handled cases involving powerful individuals, using procedures that bypassed common law protections, which led to its reputation for injustice and abuse of power. Discover how the Star Chamber shaped legal history and explore its lasting impact throughout the article.
Table of Comparison
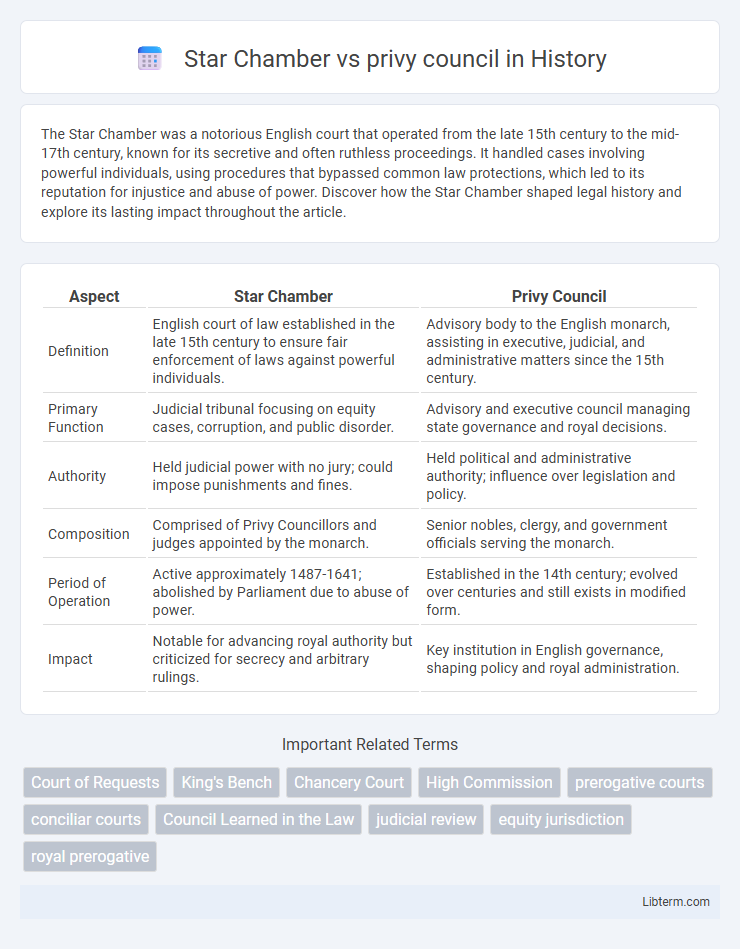
| Aspect | Star Chamber | Privy Council |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | English court of law established in the late 15th century to ensure fair enforcement of laws against powerful individuals. | Advisory body to the English monarch, assisting in executive, judicial, and administrative matters since the 15th century. |
| Primary Function | Judicial tribunal focusing on equity cases, corruption, and public disorder. | Advisory and executive council managing state governance and royal decisions. |
| Authority | Held judicial power with no jury; could impose punishments and fines. | Held political and administrative authority; influence over legislation and policy. |
| Composition | Comprised of Privy Councillors and judges appointed by the monarch. | Senior nobles, clergy, and government officials serving the monarch. |
| Period of Operation | Active approximately 1487-1641; abolished by Parliament due to abuse of power. | Established in the 14th century; evolved over centuries and still exists in modified form. |
| Impact | Notable for advancing royal authority but criticized for secrecy and arbitrary rulings. | Key institution in English governance, shaping policy and royal administration. |
Introduction to the Star Chamber and Privy Council
The Star Chamber, established in the late 15th century, served as a royal court in England designed to ensure the enforcement of laws against powerful nobles who might otherwise evade conventional legal processes. The Privy Council functioned as an advisory body to the monarch, wielding both administrative and judicial powers to implement royal policies and maintain political order. Both institutions played crucial roles in the governance and legal framework of Tudor and early Stuart England, with the Star Chamber focusing more on judicial matters and the Privy Council on broader executive functions.
Historical Origins and Development
The Star Chamber, established in the late 15th century under King Henry VII, evolved as a judicial body to supplement common law courts by addressing cases of corruption and abuses by powerful individuals, emphasizing secrecy and equitable justice. The Privy Council, originating from the medieval Royal Council, functioned as the monarch's advisory body and executive arm, gradually expanding its judicial and administrative roles throughout the Tudor and Stuart periods. Both institutions played critical roles in the governance and legal system of England, with the Star Chamber focusing on equity and control over nobility, while the Privy Council combined political counsel, executive decisions, and judicial authority.
Composition and Membership
The Star Chamber was composed mainly of Privy Councillors and judges appointed by the monarch, often including influential nobles and royal officials who handled cases of political or high-profile nature. In contrast, the Privy Council consisted of a broader group of advisors to the sovereign, encompassing nobles, clergy, and senior government officers who provided counsel on administrative and judicial matters. Membership in the Star Chamber was more exclusive and focused on legal adjudication, while the Privy Council had a wider advisory role extending beyond judicial functions.
Jurisdiction and Scope of Authority
The Star Chamber exercised jurisdiction primarily over cases involving public disorder, corruption, and offenses against the state, extending its authority beyond common law courts to deliver swift and often secretive justice. The Privy Council, conversely, held a broader scope including advisory roles to the monarch, overseeing colonial governance, and acting as the highest appellate court, with authority spanning both judicial and executive functions. While the Star Chamber's jurisdiction was largely criminal and punitive within England, the Privy Council's influence was more expansive, encompassing legislative, administrative, and judicial matters across the British Empire.
Key Functions and Responsibilities
The Star Chamber primarily functioned as a judicial body handling cases involving public disorder, corruption, and abuses of power, ensuring enforcement of royal authority through secretive and often arbitrary proceedings. The Privy Council served as an advisory group to the monarch, overseeing administration, policy decisions, and high-level governance, coordinating state affairs and implementing the king's directives. While the Star Chamber exercised judicial authority with punitive measures, the Privy Council focused on executive governance and decision-making within the realm.
Procedures and Methods of Operation
The Star Chamber employed secretive procedures with no jury, relying on the judges' discretion and written evidence, often using coercion and torture to extract confessions. The Privy Council operated through a collective body of advisors providing counsel to the monarch, utilizing more formalized council meetings and recorded deliberations without the same degree of secrecy or judicial enforcement powers. While the Star Chamber was a judicial court focusing on criminal and civil cases, the Privy Council served primarily as an executive and advisory institution with broader administrative functions.
Influence on English Legal and Political Systems
The Star Chamber significantly shaped the English legal system by introducing centralized judicial authority that curbed powerful nobles and reinforced royal prerogative, while the Privy Council evolved to balance governance by advising the monarch and administering both legal and political affairs. The Star Chamber's legacy includes the enhancement of procedural fairness and prevention of corruption, influencing the development of equity courts. The Privy Council's influence extended into policymaking and administrative oversight, becoming a cornerstone for modern executive government and judicial appeal processes in England.
Major Cases and Decisions
The Star Chamber adjudicated high-profile cases involving political corruption, sedition, and abuses of power, notably the trials of Earl of Strafford and the Five Knights where it exercised extensive judicial authority without juries. The Privy Council primarily handled advisory and administrative functions but also dealt with significant legal matters such as colonial governance and disputes involving the Crown's prerogative. Major decisions in the Star Chamber often set precedents on royal authority and suppression of dissent, while Privy Council rulings shaped the development of imperial law and administrative governance.
Decline and Abolition
The Star Chamber declined in influence during the early 17th century due to widespread criticism of its arbitrary rulings and secretive procedures, leading to its abolition by the Long Parliament in 1641. The privy council, although also facing scrutiny and diminished power, persisted as a central executive body but gradually shifted towards advisory roles and lost its judicial authority. The abolishment of the Star Chamber marked a significant limitation on royal prerogative and expansion of parliamentary sovereignty in England.
Legacy and Impact on Modern Governance
The Star Chamber established precedents for centralized judicial authority and limitations on arbitrary power, influencing the development of constitutional checks and balances. The Privy Council evolved into a key advisory body with legislative and judicial roles, shaping modern executive governance through its function as a bridge between the monarchy and Parliament. Both institutions laid foundational frameworks for accountability, the rule of law, and institutional oversight evident in contemporary legal and political systems.
Star Chamber Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com