Diplomatics is the study of historical documents, focusing on their authenticity, origin, and meaning to ensure accurate interpretation. This discipline employs rigorous methods to analyze charters, letters, and official records, helping historians and archivists verify their legitimacy and context. Discover how mastering diplomatics can enhance your understanding of historical sources by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
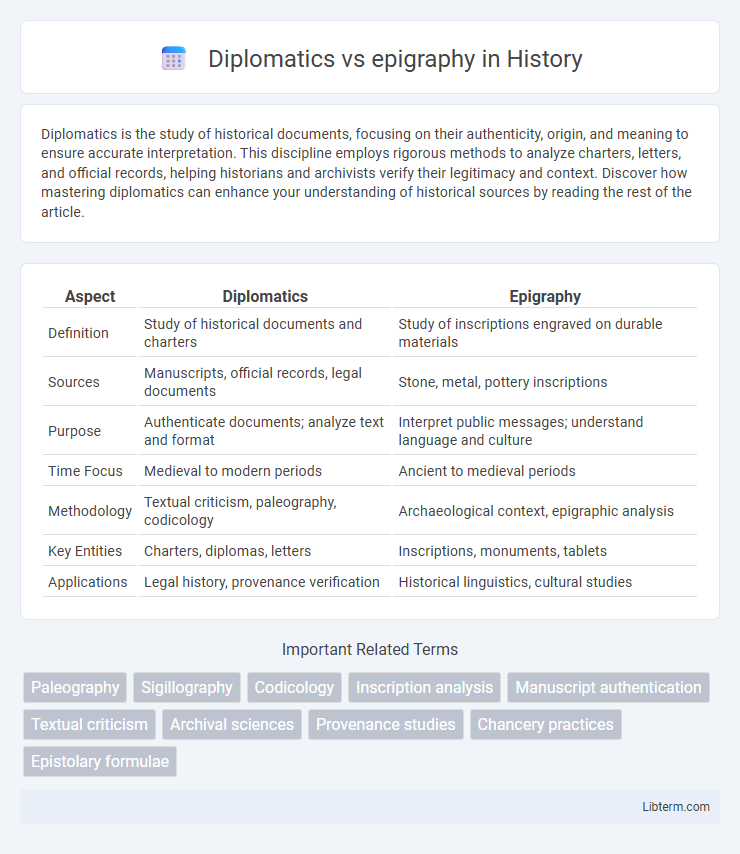
| Aspect | Diplomatics | Epigraphy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of historical documents and charters | Study of inscriptions engraved on durable materials |
| Sources | Manuscripts, official records, legal documents | Stone, metal, pottery inscriptions |
| Purpose | Authenticate documents; analyze text and format | Interpret public messages; understand language and culture |
| Time Focus | Medieval to modern periods | Ancient to medieval periods |
| Methodology | Textual criticism, paleography, codicology | Archaeological context, epigraphic analysis |
| Key Entities | Charters, diplomas, letters | Inscriptions, monuments, tablets |
| Applications | Legal history, provenance verification | Historical linguistics, cultural studies |
Introduction to Diplomatics and Epigraphy
Diplomatics studies historical documents to verify authenticity, analyze origin, and understand administrative context, focusing on charters, letters, and official records. Epigraphy examines inscriptions on durable materials like stone or metal, revealing linguistic, cultural, and chronological information from ancient civilizations. Both disciplines employ specialized methods to interpret and preserve historical evidence, contributing crucial insights to fields like archaeology and history.
Defining Diplomatics: Scope and Methods
Diplomatics is the critical study of historical documents, focusing on the authenticity, origin, and context of charters, letters, and official records from the Middle Ages to modern times. The discipline employs systematic methods such as analyzing language, handwriting, seals, and formulas to verify and date documents accurately. Unlike epigraphy, which studies inscriptions on durable materials like stone or metal, diplomatics concentrates on paper-based or parchment documents to reconstruct legal, administrative, and social history.
Understanding Epigraphy: Nature and Techniques
Epigraphy is the study of inscriptions carved or engraved on durable materials such as stone, metal, or pottery, providing direct evidence of historical languages, scripts, and cultures. Techniques in epigraphy involve detailed recording, deciphering ancient scripts, and contextual analysis to interpret the content, style, and purpose of inscriptions. Unlike diplomatics, which focuses on the analysis of documentary forms and authenticity in manuscripts, epigraphy emphasizes the physical and material aspects of inscriptions as primary historical sources.
Historical Origins of Diplomatics
Diplomatics, originating in the Middle Ages, is the critical study of historical documents to verify their authenticity and understand administrative practices, contrasting with epigraphy which analyzes inscriptions primarily carved on durable materials like stone or metal. The discipline of diplomatics emerged from the need to authenticate charters, diplomas, and official records produced by medieval institutions such as monasteries and royal chancelleries. Its historical origins lie in the scholarly efforts of the 17th century, notably through figures like Jean Mabillon, who formalized methodologies that distinguished genuine documents from forgeries.
Evolution of Epigraphy Through the Ages
Epigraphy evolved from simple inscriptions on stone and metal in ancient civilizations to complex, multilingual records that document historical, political, and social changes. While diplomatics concentrates on analyzing official documents and charters' authenticity and provenance, epigraphy provides direct evidence of everyday language, public decrees, and monumental commemorations. The development of advanced dating techniques and digital imaging has revolutionized epigraphic studies, enabling precise reconstruction of inscriptions and deeper understanding of cultural evolution.
Key Differences Between Diplomatics and Epigraphy
Diplomatics focuses on the analysis and authentication of historical documents, emphasizing the study of charters, deeds, and official records to understand their origin, form, and function. In contrast, epigraphy concentrates on the interpretation of inscriptions engraved on durable materials such as stone, metal, or pottery, providing vital information on ancient languages, cultures, and chronologies. While diplomatics deals primarily with written texts in manuscript or codex form, epigraphy specializes in deciphering and contextualizing text embedded in physical artifacts.
Interdisciplinary Connections
Diplomatics and epigraphy intersect through their analysis of historical documents and inscriptions, offering complementary insights into administrative, legal, and societal contexts. Diplomatics emphasizes the authentication and interpretation of charters, letters, and official records, while epigraphy focuses on the study of inscriptions on durable materials like stone or metal. Their interdisciplinary connection enhances understanding of historical communication by integrating paleographical, archaeological, and linguistic methods.
Notable Case Studies in Diplomatics
Notable case studies in diplomatics include the analysis of medieval charters such as the Domesday Book, where experts authenticate documents to distinguish genuine royal decrees from forgeries. The study of papal bulls provides critical insights into the administrative practices of the Catholic Church and the evolution of bureaucratic protocols. In contrast, epigraphy focuses on inscriptions like the Rosetta Stone, offering direct evidence of historical languages and ancient civilizations through engraved texts on stone or metal.
Significant Epigraphic Discoveries
Significant epigraphic discoveries include the Rosetta Stone, which was crucial in deciphering Egyptian hieroglyphs, and the Behistun Inscription, pivotal for understanding Old Persian cuneiform. These artifacts provide direct, inscribed evidence of historical events, laws, and languages, enabling accurate reconstruction of ancient cultures. In contrast to diplomatics, which analyzes documentary authenticity and origin, epigraphy focuses on the study and interpretation of inscriptions carved or written on durable materials.
Future Directions in Document and Inscription Studies
Future directions in diplomatics and epigraphy emphasize integrating digital technologies such as AI-driven text analysis and 3D imaging to enhance the study of ancient manuscripts and inscriptions. Advances in machine learning enable automated decipherment and classification of scripts, improving accuracy in dating and provenance determination. Collaborative databases and virtual reconstructions are expanding access to rare documents and inscriptions, fostering interdisciplinary research and preservation efforts.
Diplomatics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com