Leasehold property grants you the right to use a property for a specified period, often ranging from several years to decades, under the terms set by the freeholder. Understanding the implications of lease length, ground rent, and maintenance responsibilities is crucial for making informed decisions in leasehold agreements. Explore the detailed aspects of leasehold arrangements to protect your investment and ensure smooth property management.
Table of Comparison
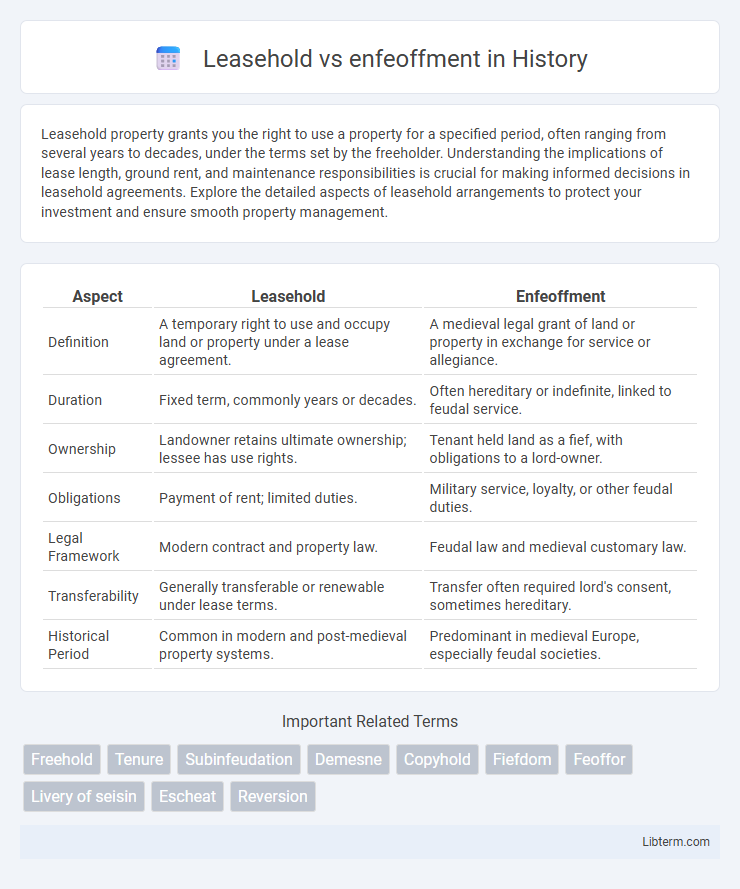
| Aspect | Leasehold | Enfeoffment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A temporary right to use and occupy land or property under a lease agreement. | A medieval legal grant of land or property in exchange for service or allegiance. |
| Duration | Fixed term, commonly years or decades. | Often hereditary or indefinite, linked to feudal service. |
| Ownership | Landowner retains ultimate ownership; lessee has use rights. | Tenant held land as a fief, with obligations to a lord-owner. |
| Obligations | Payment of rent; limited duties. | Military service, loyalty, or other feudal duties. |
| Legal Framework | Modern contract and property law. | Feudal law and medieval customary law. |
| Transferability | Generally transferable or renewable under lease terms. | Transfer often required lord's consent, sometimes hereditary. |
| Historical Period | Common in modern and post-medieval property systems. | Predominant in medieval Europe, especially feudal societies. |
Understanding Leasehold: Definition and Key Features
Leasehold refers to a legal arrangement where a tenant holds the right to use and occupy land or property for a specified period under a lease agreement, without owning the freehold title. Key features include a fixed-term duration, payment of rent to the freeholder, and obligations outlined in the lease contract, such as maintenance and land use restrictions. Unlike enfeoffment, which involves the transfer of land ownership under feudal law, leasehold grants temporary possession without transferring full legal ownership.
What is Enfeoffment? Historical Background and Meaning
Enfeoffment originated in medieval English feudal law as the formal transfer of land ownership through a symbolic act, often involving the delivery of a physical object like a clod of earth or a twig, to establish a lord-vassal relationship. This process created a tenure system where the enfeoffee received the land in exchange for services or rent, distinguishing it from modern leasehold arrangements which are contractual tenancy agreements without ownership transfer. Historically, enfeoffment formed the foundation of feudal land tenure, embedding social hierarchies and obligations within landholding practices in England and influenced property law evolution across Europe.
Legal Framework: Leasehold vs Enfeoffment
Leasehold grants tenants a temporary right to use property based on a contractual agreement governed by modern property laws, often limiting duration and rights to transfer or modify the leased asset. Enfeoffment, rooted in medieval feudal systems, involves the transfer of land ownership or possession in exchange for services or duties under customary feudal obligations, creating a tenure that is hereditary or permanent. The legal framework for leasehold is codified in statutory landlord-tenant laws, whereas enfeoffment operates under historical feudal legal principles, which have largely been replaced or abolished in contemporary jurisdictions.
Duration and Terms: Comparing Lease Agreements and Enfeoffment Grants
Leasehold agreements typically grant property use rights for a fixed term ranging from months to several decades, with clearly defined renewal options and conditions. Enfeoffment grants often confer more permanent or hereditary rights, historically tied to feudal duties, with less formalized renewal but potentially lifelong tenure. Lease terms emphasize contractual obligations and periodic payments, whereas enfeoffment terms involve feudal allegiance and land tenure traditions.
Transferability and Rights: Leasehold vs Enfeoffment
Leasehold grants tenants the right to use property for a specified period, with limited transferability subject to landlord approval and lease terms. Enfeoffment involves the transfer of land ownership with feudal obligations, allowing more enduring rights and generally greater freedom to transfer ownership through inheritance or sale. Leasehold rights are temporary and contractual, while enfeoffment establishes a form of property ownership with accompanying duties and privileges.
Landowner and Tenant Responsibilities
Leasehold grants tenants the right to use land for a specified period under defined terms, requiring them to pay rent and maintain the property, while landowners retain ownership and are responsible for major structural repairs. Enfeoffment, historically involving the transfer of land ownership through feudal tenure, places more permanent obligations on the tenant, who assumes certain duties akin to ownership, including land improvement and defense, with the landowner's role often limited to oversight or receipt of customary services. Landowner responsibilities in leasehold primarily include ensuring legal title and property usability, whereas in enfeoffment, they may involve granting protection or rights tied to feudal hierarchy.
Financial Implications: Costs and Benefits
Leasehold arrangements typically require regular rent payments, which can lead to predictable long-term expenses but limited asset appreciation since ownership reverts to the lessor after the lease term. Enfeoffment, an ancient feudal tenure, involves transferring land ownership with associated obligations like service or fees, potentially resulting in upfront financial costs but offering greater control and investment value over time. Understanding these financial dynamics is crucial for investors prioritizing cash flow stability versus capital growth in property holdings.
Pros and Cons of Leasehold Ownership
Leasehold ownership allows tenants to use a property for a fixed term, often offering lower upfront costs and more flexibility compared to freehold or enfeoffment arrangements. However, leaseholders face limitations such as lease expiration, potential rent increases, and restrictions imposed by the freeholder, which can affect property value and long-term security. Despite these drawbacks, leasehold arrangements are beneficial for short-term usage and can provide access to prime locations otherwise unattainable through outright ownership.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Enfeoffment
Enfeoffment offers the advantage of transferring land ownership with full rights, often including hereditary succession, providing long-term security and control over the property. However, its disadvantages include complex legal formalities, potential difficulties in transferring ownership compared to leasehold, and a risk of disputes due to historical feudal obligations. Unlike leasehold, enfeoffment is less flexible in terms of revocability and duration, requiring careful consideration of legal and financial implications.
Choosing Between Leasehold and Enfeoffment: Factors to Consider
Choosing between leasehold and enfeoffment involves evaluating the duration of property interest, rights transferred, and associated obligations. Leasehold offers a temporary interest with defined terms and conditions, suitable for limited-time use without full ownership. Enfeoffment provides a more permanent transfer of land ownership, often accompanied by feudal duties or services, ideal for long-term possession and control.
Leasehold Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com