Moderate exercise offers numerous health benefits, including improved cardiovascular fitness, enhanced mood, and better weight management. Engaging in activities like brisk walking or cycling helps reduce the risk of chronic diseases while fitting seamlessly into your daily routine. Discover more about how moderate exercise can transform your lifestyle in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
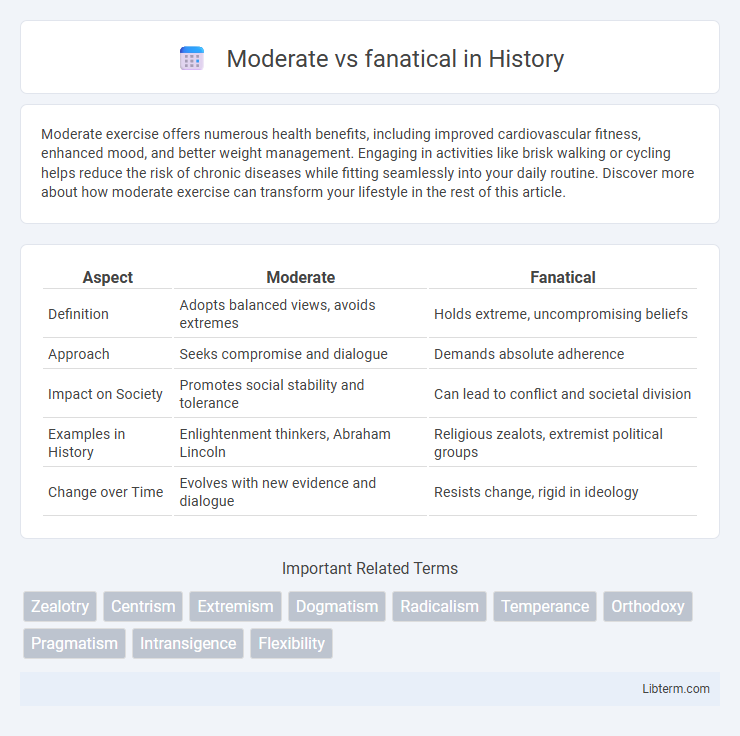
| Aspect | Moderate | Fanatical |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adopts balanced views, avoids extremes | Holds extreme, uncompromising beliefs |
| Approach | Seeks compromise and dialogue | Demands absolute adherence |
| Impact on Society | Promotes social stability and tolerance | Can lead to conflict and societal division |
| Examples in History | Enlightenment thinkers, Abraham Lincoln | Religious zealots, extremist political groups |
| Change over Time | Evolves with new evidence and dialogue | Resists change, rigid in ideology |
Defining Moderation and Fanaticism
Moderation refers to maintaining balanced, rational beliefs and actions without extreme behaviors or rigid ideologies, promoting openness and adaptability. Fanaticism involves an obsessive, uncompromising commitment to a cause or belief, often accompanied by intolerance and extreme behaviors. Understanding these definitions helps distinguish constructive engagement from harmful extremism in social and political contexts.
Psychological Drivers Behind Moderation and Fanaticism
Psychological drivers behind moderation often include empathy, cognitive flexibility, and a balanced perception of social and political issues, promoting open-mindedness and tolerance. In contrast, fanaticism is fueled by rigid cognitive schemas, identity protection mechanisms, and high in-group loyalty, leading to extreme, uncompromising beliefs. Understanding these cognitive and emotional differences helps explain why moderates seek common ground while fanatics pursue ideological purity.
Historical Examples of Moderates and Fanatics
Historical examples illustrate the stark contrast between moderates and fanatics in shaping societal outcomes. The moderate leadership of Abraham Lincoln during the American Civil War sought to preserve the Union through measured emancipation policies, avoiding radical upheaval. In contrast, fanatics like Robespierre during the French Revolution pursued extreme revolutionary measures, resulting in the Reign of Terror and widespread violence.
Social Impact of Moderate Versus Fanatical Behavior
Moderate behavior promotes social cohesion by encouraging open dialogue, tolerance, and constructive conflict resolution, which strengthens community bonds and fosters inclusive environments. Fanatical behavior often leads to polarization, social fragmentation, and increased conflict due to rigid ideologies and intolerance toward differing viewpoints. Studies show societies with predominant moderate attitudes experience lower rates of violence and greater political stability compared to those influenced by fanaticism.
Political Movements: Moderation vs Fanaticism
Political movements rooted in moderation prioritize compromise, incremental reform, and inclusivity to foster stability and broad-based support. Fanatical political movements, by contrast, often embrace uncompromising ideologies, radical actions, and polarized rhetoric, which can lead to social division and conflict. The balance between these approaches significantly influences democratic resilience and policy effectiveness.
Benefits of a Moderate Approach
A moderate approach fosters open-mindedness and balanced decision-making, reducing polarizing conflicts and promoting social harmony. Emphasizing compromise and empathy allows diverse perspectives to coexist, enhancing collaboration and long-term stability. This balanced mindset supports sustainable progress by avoiding the extremes that often lead to burnout or rigid dogmatism.
Risks Associated with Fanatical Mindsets
Fanatical mindsets pose significant risks including decreased critical thinking, increased susceptibility to misinformation, and heightened potential for social polarization and conflict. Such rigid perspectives often lead to intolerance, undermining constructive dialogue and collaboration in diverse environments. In contrast, moderate views foster open-mindedness and adaptability, reducing the likelihood of extremist behaviors and promoting societal stability.
How to Identify Moderate and Fanatical Rhetoric
Identifying moderate rhetoric involves recognizing language that emphasizes balance, reason, and openness to differing viewpoints, often using inclusive terms and avoiding absolute statements. Fanatical rhetoric typically features extreme, uncompromising language, frequently employing absolutes, emotional appeals, and demonization of opposing views to mobilize unwavering support. Key indicators include the use of nuanced arguments and evidence in moderation versus polarized, dogmatic phrases and repetition in fanatic discourse.
Strategies for Navigating Extremes in Communities
Navigating the dynamics between moderate and fanatical groups in communities requires strategic engagement that prioritizes dialogue and inclusive decision-making. Employing conflict resolution techniques and fostering mutual understanding can mitigate polarization and promote collaborative solutions. Empowering community leaders to act as mediators and utilizing evidence-based communication strategies enhances resilience against extremist influences.
Fostering Dialogue Between Moderates and Fanatics
Moderates seek constructive dialogue by emphasizing shared values and common goals, aiming to bridge divides without escalating conflict. Fanatics often hold rigid, uncompromising beliefs, making open communication challenging yet essential to reduce polarization. Fostering dialogue requires creating safe spaces for respectful exchange, encouraging empathy, and promoting understanding to transform extremism into collaborative problem-solving.
Moderate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com