Open-mindedness fosters personal growth by encouraging you to embrace diverse perspectives and challenge your own beliefs. Cultivating this mindset enhances creativity, problem-solving, and relationships across various aspects of life. Discover practical strategies to develop and maintain open-mindedness throughout this article.
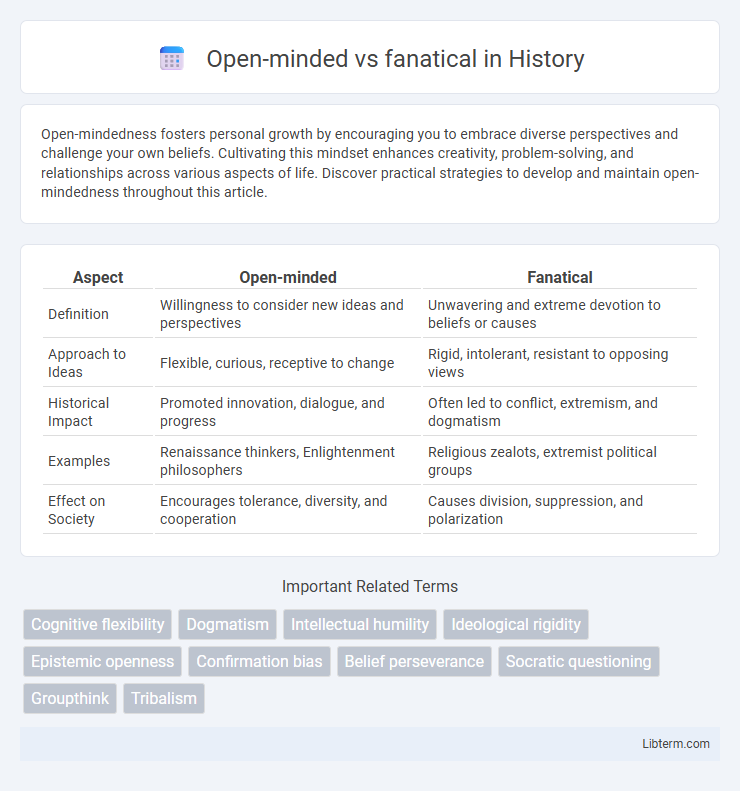
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Open-minded | Fanatical |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Willingness to consider new ideas and perspectives | Unwavering and extreme devotion to beliefs or causes |
| Approach to Ideas | Flexible, curious, receptive to change | Rigid, intolerant, resistant to opposing views |
| Historical Impact | Promoted innovation, dialogue, and progress | Often led to conflict, extremism, and dogmatism |
| Examples | Renaissance thinkers, Enlightenment philosophers | Religious zealots, extremist political groups |
| Effect on Society | Encourages tolerance, diversity, and cooperation | Causes division, suppression, and polarization |
Defining Open-Mindedness and Fanaticism
Open-mindedness involves a willingness to consider diverse perspectives and revise beliefs based on new evidence, promoting intellectual flexibility and tolerance. Fanaticism is characterized by an obsessive commitment to a particular ideology or cause, often resisting contrary information and fostering rigidity. Understanding these traits highlights the contrast between adaptive critical thinking and uncompromising dogmatism in cognitive attitudes.
Key Traits of Open-Minded Individuals
Open-minded individuals exhibit adaptability, curiosity, and a willingness to consider diverse perspectives, enhancing problem-solving and interpersonal relationships. They demonstrate cognitive flexibility by evaluating new information without bias and showing empathy towards differing opinions. In contrast to fanatical attitudes, open-mindedness fosters critical thinking and collaboration, promoting personal growth and informed decision-making.
Hallmarks of Fanatical Thinking
Fanatical thinking is characterized by rigid beliefs, intolerance to opposing viewpoints, and an unwavering conviction in one's ideals despite contradictory evidence. Hallmarks include cognitive inflexibility, black-and-white thinking, and an emotional attachment that overrides rational analysis. This mindset blocks open-mindedness by dismissing alternative perspectives and fostering polarized, extreme behaviors.
Psychological Roots of Open-Mindedness
Open-mindedness originates from psychological traits such as cognitive flexibility, tolerance for ambiguity, and a growth mindset, enabling individuals to consider diverse perspectives without rigid judgment. In contrast, fanatical thinking is often rooted in cognitive biases, emotional rigidity, and identity-protective cognition, leading to closed-mindedness and resistance to contradictory information. Neuroscientific studies link open-mindedness to enhanced activity in the prefrontal cortex, supporting critical thinking and adaptive decision-making processes.
What Drives Fanatical Behavior?
Fanatical behavior is driven by rigid beliefs and an intense emotional commitment to a specific ideology or cause, often fueled by fear, identity threats, or social group dynamics. This extremity limits openness to new information and reinforces black-and-white thinking, contrasting sharply with the flexibility and tolerance seen in open-minded individuals. Understanding these psychological and social drivers helps in addressing the root causes of fanaticism and promoting more adaptable, inclusive perspectives.
Impact of Open-Mindedness on Relationships
Open-mindedness fosters effective communication and empathy, enhancing trust and emotional connection in relationships. It allows individuals to consider diverse perspectives, reducing conflicts and encouraging mutual growth. In contrast, fanatical attitudes often create rigidity, leading to misunderstandings and strained interactions.
Dangers of Fanaticism in Society
Fanaticism poses significant dangers in society by fostering intolerance, suppressing critical thinking, and inciting conflict through rigid, unyielding beliefs. Unlike open-minded individuals who embrace diverse perspectives and encourage dialogue, fanatics often reject dissent, leading to social polarization and violent extremism. The escalation of fanaticism contributes to the breakdown of democratic values and undermines social cohesion essential for peaceful coexistence.
Open-Minded vs Fanatical Approaches to Conflict
Open-minded approaches to conflict emphasize active listening, empathy, and a willingness to consider diverse perspectives, fostering collaborative problem-solving and mutual understanding. Fanatical approaches often involve rigid beliefs, intolerance for opposing views, and an uncompromising stance, which escalate tensions and hinder resolution. Embracing open-mindedness in conflict encourages constructive dialogue and sustainable agreements, while fanaticism typically perpetuates division and impasse.
How to Cultivate Open-Mindedness
Cultivating open-mindedness involves actively seeking diverse perspectives and embracing curiosity about unfamiliar ideas, which enhances cognitive flexibility and empathy. Practicing critical thinking skills and questioning personal biases helps individuals evaluate information objectively without rigid adherence to preconceived beliefs. Engaging in meaningful dialogue with people holding different viewpoints fosters adaptability and reduces the risk of becoming fanatical or dogmatic.
Breaking Free from Fanatical Patterns
Breaking free from fanatical patterns involves cultivating an open-minded approach that embraces diverse perspectives and critical thinking. Open-minded individuals prioritize evidence-based reasoning and adaptability, avoiding rigid beliefs that restrict growth and social harmony. Conscious efforts to challenge dogmatic views foster intellectual freedom and emotional resilience, enabling balanced decision-making and inclusive dialogue.
Open-minded Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com