Pragmatic approaches focus on practical solutions that yield tangible results in real-world situations rather than theoretical ideals. This mindset helps streamline decision-making processes and enhances efficiency by prioritizing what works best in practice. Explore the full article to discover how adopting a pragmatic perspective can transform your problem-solving skills.
Table of Comparison
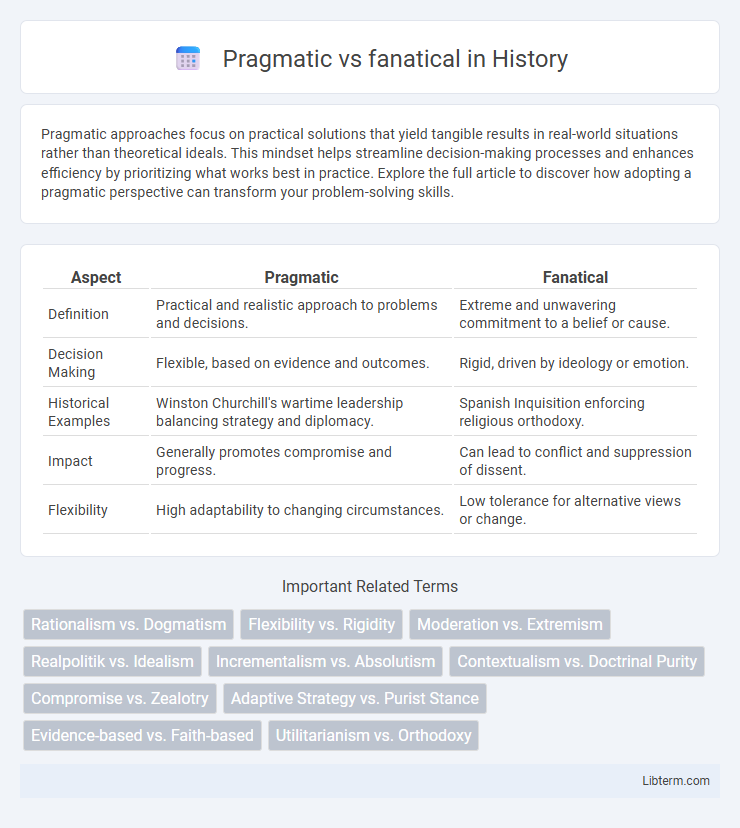
| Aspect | Pragmatic | Fanatical |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Practical and realistic approach to problems and decisions. | Extreme and unwavering commitment to a belief or cause. |
| Decision Making | Flexible, based on evidence and outcomes. | Rigid, driven by ideology or emotion. |
| Historical Examples | Winston Churchill's wartime leadership balancing strategy and diplomacy. | Spanish Inquisition enforcing religious orthodoxy. |
| Impact | Generally promotes compromise and progress. | Can lead to conflict and suppression of dissent. |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to changing circumstances. | Low tolerance for alternative views or change. |
Understanding Pragmatism: A Balanced Perspective
Pragmatism emphasizes practical solutions and adaptable strategies based on real-world outcomes rather than rigid ideology, fostering effective decision-making in complex situations. Unlike fanatical approaches, which often rely on unwavering beliefs and emotional intensity, pragmatism values flexibility, evidence, and compromise to achieve optimal results. This balanced perspective promotes collaboration and continuous learning, enhancing problem-solving across diverse fields such as business, politics, and interpersonal relationships.
Defining Fanaticism: Traits and Tendencies
Fanaticism is characterized by extreme, unwavering devotion to a cause or belief, often disregarding reason or opposing viewpoints. Traits include intolerance towards dissent, emotional rigidity, and a propensity for radical action without compromise. Such tendencies can lead to conflict and social division, contrasting sharply with pragmatic approaches that prioritize flexibility and evidence-based decision-making.
Origins of Pragmatic and Fanatical Mindsets
The pragmatic mindset originates from a focus on practical solutions and adaptable strategies rooted in empirical evidence and real-world experience. In contrast, the fanatical mindset stems from rigid belief systems often influenced by extreme ideology or unwavering commitment to a single doctrine. These divergent mentalities shape decision-making processes, with pragmatism emphasizing flexibility and results, while fanaticism prioritizes dogma and absolute conviction.
Key Differences: Pragmatic vs Fanatical Approaches
Pragmatic approaches emphasize practical solutions based on real-world evidence and adaptability, prioritizing efficiency and results over rigid adherence to ideology. Fanatical approaches are characterized by extreme, uncompromising beliefs that often ignore empirical data and resist flexibility, leading to polarized and dogmatic decision-making. The key difference lies in pragmatism's focus on balanced, outcome-driven methods versus fanaticism's insistence on unwavering commitment regardless of consequences.
The Impact on Decision-Making
Pragmatic decision-making emphasizes evidence-based solutions, flexibility, and adapting strategies to real-world outcomes, leading to more balanced and effective results. Fanatical approaches, driven by rigid beliefs or ideology, often result in biased judgments, resistance to alternative viewpoints, and poor adaptability to changing circumstances. The contrast between pragmatic and fanatical mindsets significantly shapes organizational and personal choices, influencing both success rates and long-term sustainability.
Pragmatic Solutions in Everyday Life
Pragmatic solutions in everyday life emphasize practical and realistic approaches to problem-solving, prioritizing efficiency and adaptability over rigid adherence to ideology. These solutions involve assessing situations based on tangible outcomes, using evidence-based methods that maximize results with minimal resources. By fostering flexibility and open-mindedness, pragmatic strategies enable individuals to navigate complexities and achieve goals effectively.
Dangers of Fanatical Beliefs
Fanatical beliefs can lead to extreme behaviors and intolerance, often resulting in social division, violence, and suppression of opposing viewpoints. Unlike pragmatic approaches grounded in rational thinking and adaptability, fanaticism disregards evidence and fosters dogmatism, increasing the risk of conflict and radicalization. The dangers of fanatical beliefs underscore the importance of critical thinking and open dialogue for healthy societal progress.
Navigating Conflicts: Pragmatism vs Fanaticism
Navigating conflicts requires balancing pragmatic solutions that emphasize compromise and adaptability with fanatical approaches driven by rigid ideologies and uncompromising stances. Pragmatism promotes dialogue, flexibility, and problem-solving to achieve mutually beneficial outcomes, while fanaticism often escalates tensions through intolerance and zero-sum thinking. Understanding these dynamics helps manage disputes effectively by prioritizing constructive communication over entrenched extremes.
Cultural and Historical Examples
Pragmatic approaches in history are exemplified by leaders like Abraham Lincoln, who sought practical solutions to unite a divided nation during the American Civil War, emphasizing compromise and reconciliation. In contrast, fanatical figures such as the French Revolution's Robespierre pushed radical ideological purity, leading to the Reign of Terror and widespread social upheaval. These cultural examples demonstrate how pragmatism often fosters stability and gradual progress, while fanaticism tends to result in conflict and societal disruption.
Striving for Balance: Embracing Pragmatism Over Fanaticism
Striving for balance involves embracing pragmatism by focusing on practical solutions and adapting to real-world constraints rather than rigid dogma. Pragmatic approaches prioritize flexibility, critical thinking, and problem-solving, which prevent the extremes and polarizing effects of fanaticism. This mindset fosters sustainable progress and constructive dialogue in complex situations.
Pragmatic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com