Republicanism emphasizes the importance of a government by the people through elected representatives, promoting civic virtue and the common good over hereditary rule or autocracy. It advocates for a political system where laws and policies reflect the consent of the governed, ensuring individual rights and limiting the power of centralized authorities. Explore the article to understand how republicanism shapes modern democracy and impacts your role as a citizen.
Table of Comparison
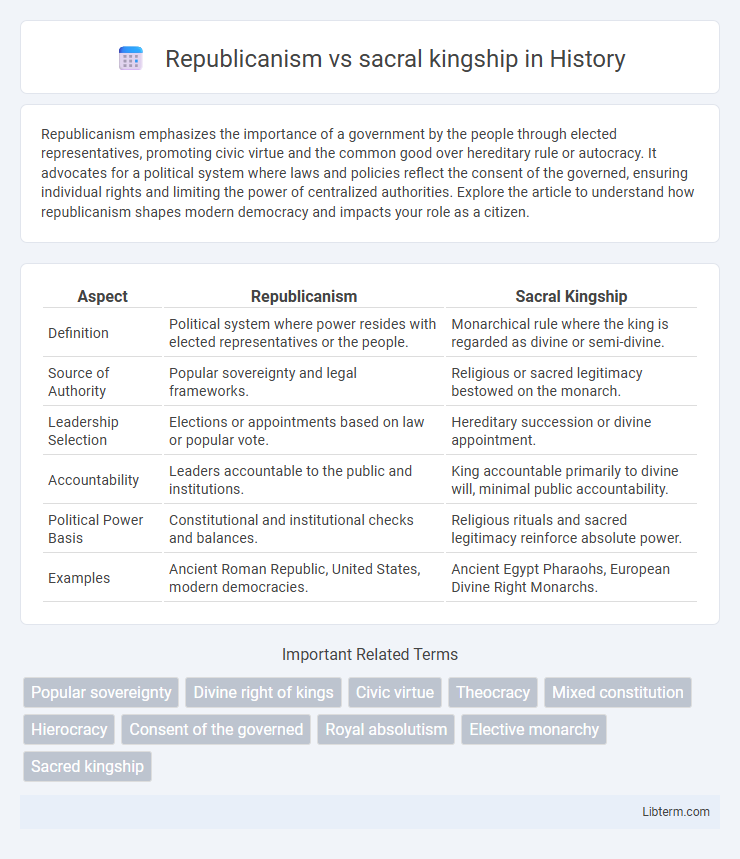
| Aspect | Republicanism | Sacral Kingship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political system where power resides with elected representatives or the people. | Monarchical rule where the king is regarded as divine or semi-divine. |
| Source of Authority | Popular sovereignty and legal frameworks. | Religious or sacred legitimacy bestowed on the monarch. |
| Leadership Selection | Elections or appointments based on law or popular vote. | Hereditary succession or divine appointment. |
| Accountability | Leaders accountable to the public and institutions. | King accountable primarily to divine will, minimal public accountability. |
| Political Power Basis | Constitutional and institutional checks and balances. | Religious rituals and sacred legitimacy reinforce absolute power. |
| Examples | Ancient Roman Republic, United States, modern democracies. | Ancient Egypt Pharaohs, European Divine Right Monarchs. |
Understanding Republicanism: Core Principles
Republicanism emphasizes the sovereignty of the people, advocating for a government based on popular consent, rule of law, and civic virtue, contrasting sharply with sacral kingship where authority is derived from divine right and religious legitimacy. Central to republican thought is the idea of a mixed government structure that prevents tyranny through checks and balances, promoting accountability and active citizen participation. This political philosophy prioritizes individual rights and collective governance over hereditary or autocratic rule rooted in sacred authority.
Defining Sacral Kingship: Divine Authority and Tradition
Sacral kingship is defined by its foundation in divine authority, where the ruler is seen as a holy figure or earthly representative of a deity, legitimizing their power through sacred tradition and religious rituals. This system contrasts with republicanism, which rejects divine right and emphasizes popular sovereignty, constitutional governance, and the rule of law. The sacral king's legitimacy is deeply intertwined with religious symbolism and ceremonial practices that reinforce the sacred nature of monarchy.
Historical Roots: From Ancient Republics to Sacred Monarchies
Republicanism traces its roots to ancient city-states like Rome and Athens, where power was vested in elected representatives and civic participation shaped governance. In contrast, sacral kingship emerged in early civilizations such as Egypt and Mesopotamia, where rulers were perceived as divine or semi-divine figures embodying religious authority and legitimizing their political power through sacred rites. These historically distinct frameworks illustrate the evolution from communal sovereignty to theocratic monarchy, reflecting differing views on legitimacy and the source of political authority.
Governance Structures: Republican Systems vs Divine Rule
Republicanism emphasizes governance through elected representatives and institutional checks and balances, ensuring power derives from the consent of the governed rather than hereditary or divine authority. Governance structures in republican systems prioritize codified laws and civic participation, contrasting sharply with sacral kingship, where rulers claim divine right and absolute authority based on religious legitimacy. This fundamental difference impacts political accountability, with republican governments promoting transparency and sacral kingships often centralizing power under a sacrosanct monarch.
Legitimacy and Power: Popular Sovereignty vs Divine Mandate
Republicanism bases legitimacy on popular sovereignty, where power is derived from the consent of the governed and authority is accountable to the people. Sacral kingship, in contrast, legitimizes power through a divine mandate, presenting the ruler as ordained or chosen by a deity, often justified by religious or sacred traditions. This fundamental difference impacts political structures, with republics emphasizing civic participation and sacral monarchies prioritizing religious sanctity and hierarchical obedience.
Political Stability: Checks and Balances vs Sacred Leadership
Republicanism promotes political stability through institutional checks and balances that prevent the concentration of power, ensuring accountability and the rule of law. In contrast, sacral kingship derives authority from divine sanction, centralizing power in a sacred ruler whose legitimacy is unquestioned, often leading to stability rooted in religious tradition rather than legal frameworks. The contrast lies in republican mechanisms fostering adaptability and citizen participation, while sacral kingship emphasizes continuity based on sacred legitimacy and hierarchical obedience.
Role of Religion in Governance
Republicanism emphasizes secular governance by separating religion from political authority, advocating for laws based on civic reason and popular sovereignty. In contrast, sacral kingship integrates religion deeply into governance, where monarchs derive their authority from divine sanction, often embodying both spiritual and political leadership. This fusion of religious legitimacy and political power in sacral kingship contrasts with republicanism's prioritization of legal-rational authority over divine right.
Evolution of Republicanism and Sacral Kingship Through History
Republicanism evolved from ancient city-states like Rome, emphasizing civic participation, rule of law, and separation of powers to prevent autocratic rule, while sacral kingship, seen in civilizations such as ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, intertwined political authority with divine sanction, legitimizing monarchs as gods or their earthly representatives. Over centuries, republican ideas influenced the decline of sacral monarchies, especially during the Enlightenment and revolutionary movements, promoting secular governance and popular sovereignty. Despite this, sacral kingship persisted in some cultures, highlighting the tension and transformation between sacred authority and emerging democratic principles throughout history.
Modern Implications: Republicanism and Monarchic Traditions Today
Modern republicanism emphasizes popular sovereignty, democratic governance, and the rule of law, contrasting with sacral kingship's foundation on divine right and ceremonial authority. Many contemporary states blend monarchic traditions with republican institutions, maintaining symbolic monarchs while upholding constitutional frameworks and elected governments. This hybrid approach reflects evolving political legitimacy rooted in both historical continuity and democratic principles.
Comparative Analysis: Societal Impacts of Both Systems
Republicanism promotes political participation, individual rights, and accountability through representative institutions, fostering societal equality and civic engagement. Sacral kingship centralizes power in a monarch considered divine or semi-divine, often legitimizing authority through religious or spiritual claims, which can limit political pluralism and concentrate social hierarchy. Societal impacts differ as republicanism encourages legal frameworks and collective governance, while sacral kingship reinforces traditional structures and cultural cohesion centered on sacred rulership.
Republicanism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com