Calligraphy transforms ordinary writing into an art form, enhancing the visual appeal of letters through elegant strokes and balanced composition. Mastering calligraphy requires patience and practice, allowing you to express creativity and convey messages with distinctive style. Explore the full article to discover tips, tools, and techniques to elevate your calligraphy skills.
Table of Comparison
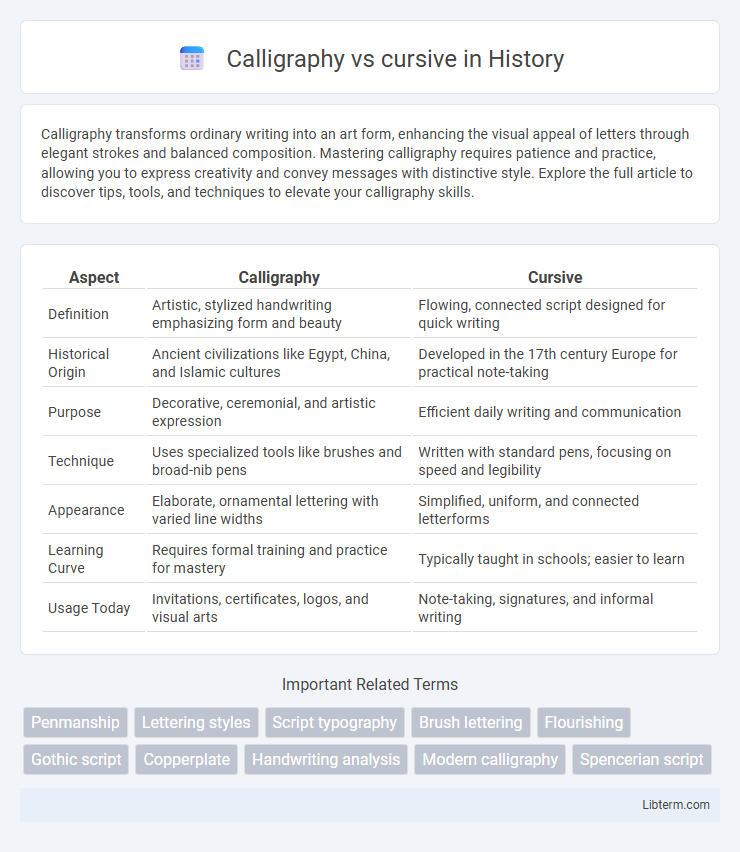
| Aspect | Calligraphy | Cursive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artistic, stylized handwriting emphasizing form and beauty | Flowing, connected script designed for quick writing |
| Historical Origin | Ancient civilizations like Egypt, China, and Islamic cultures | Developed in the 17th century Europe for practical note-taking |
| Purpose | Decorative, ceremonial, and artistic expression | Efficient daily writing and communication |
| Technique | Uses specialized tools like brushes and broad-nib pens | Written with standard pens, focusing on speed and legibility |
| Appearance | Elaborate, ornamental lettering with varied line widths | Simplified, uniform, and connected letterforms |
| Learning Curve | Requires formal training and practice for mastery | Typically taught in schools; easier to learn |
| Usage Today | Invitations, certificates, logos, and visual arts | Note-taking, signatures, and informal writing |
Understanding Calligraphy: An Art Form
Calligraphy is an artistic form that emphasizes decorative handwriting with precise strokes and carefully controlled variations in line thickness, distinguishing it from cursive, which prioritizes fluidity and speed in regular writing. The art of calligraphy combines traditional tools like broad-edged pens and brushes with techniques that enhance visual beauty, making it a discipline rooted deeply in cultural and historical significance. Mastery of calligraphy requires understanding letterforms, spacing, and rhythm to create visually harmonious compositions that elevate writing to an expressive and aesthetic experience.
What is Cursive Writing?
Cursive writing is a style of penmanship where letters are connected in a flowing manner to enhance writing speed and efficiency. It features continuous strokes that allow for seamless transitions between characters, distinguishing it from print or block lettering. Commonly taught in schools, cursive improves handwriting fluency and can vary significantly in formality compared to calligraphy.
Historical Roots: Calligraphy vs Cursive
Calligraphy and cursive both trace their historical roots to ancient writing systems but evolved for different purposes: calligraphy originated as an art form emphasizing decorative, stylized handwriting, often associated with religious texts in cultures like China and medieval Europe. Cursive developed primarily to increase writing speed and efficiency, emerging in Renaissance Europe as a practical script for everyday communication and record-keeping. While calligraphy maintains a focus on aesthetic form and meticulous strokes, cursive prioritizes fluid motion and legibility in continuous handwriting.
Visual Differences Between Calligraphy and Cursive
Calligraphy features ornate, deliberate strokes with varied line thickness achieved through specialized brushes or pens, creating an artistic and decorative appearance. Cursive handwriting consists of smooth, fluid, and connected letterforms designed for speed and legibility, typically displaying uniform line weight. The visual contrast lies in calligraphy's emphasis on stylization and embellishment versus cursive's practical, continuous flow.
Tools and Materials: Calligraphy vs Cursive
Calligraphy requires specialized tools such as dip pens, brushes, and ink to create varying line widths and artistic strokes, emphasizing precision and fluidity. Cursive writing typically uses standard ballpoint or gel pens and pencils designed for quick, continuous handwriting without the need for special materials. High-quality calligraphy paper or parchment enhances ink absorption, while cursive can be practiced on regular notebook or lined paper.
Learning Curves: Which Is Easier?
Cursive writing typically has a gentler learning curve than calligraphy due to its practical use in everyday handwriting and simpler strokes. Calligraphy demands precise control and mastery of specialized tools like dip pens or brush pens, making it more challenging for beginners. For those seeking quicker proficiency, cursive offers a more accessible entry point, while calligraphy requires dedicated practice to achieve artistic skill.
Popular Uses Today: Calligraphy and Cursive
Calligraphy is widely used in artistic projects such as wedding invitations, logos, and decorative signage, where the focus is on aesthetic appeal and intricate design. Cursive remains popular for everyday handwriting, note-taking, and educational purposes, emphasizing speed and fluidity. Both styles continue to influence digital fonts and personalized stationery, reflecting their enduring cultural and practical significance.
Artistic Expression and Personal Style
Calligraphy emphasizes artistic expression through structured, deliberate strokes that create visually stunning letterforms, often used in formal designs and traditional art. Cursive writing prioritizes fluidity and speed, reflecting personal style through individual variations in connected letters and handwriting quirks. Both calligraphy and cursive capture unique artistic identities, with calligraphy serving as an art form and cursive embodying personal, everyday expression.
Calligraphy and Cursive in Modern Education
Calligraphy in modern education emphasizes artistic expression and fine motor skills, often incorporated into art and design curriculums to enhance creativity and cultural appreciation. Cursive writing remains a practical skill taught to improve handwriting fluency and cognitive development, supporting reading and writing proficiency in early education. Both calligraphy and cursive contribute uniquely to student engagement, with calligraphy fostering aesthetic appreciation and cursive facilitating everyday writing efficiency.
Choosing the Right Style for Your Needs
Calligraphy emphasizes artistic, stylized letterforms ideal for invitations, logo design, and decorative projects, while cursive offers a faster, connected handwriting style suited for everyday note-taking and personal correspondence. Selecting between calligraphy and cursive depends on the purpose: choose calligraphy for formal, visually impactful presentations, and cursive for efficient, legible writing. Consider legibility, speed, and aesthetic requirements to match the style with your specific communication needs.
Calligraphy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com