The Teutonic Knights were a medieval military order known for their role in the Crusades and the Christianization of the Baltic region. Their influence extended through both military conquest and territorial governance, shaping much of medieval Eastern European history. Discover how the legacy of the Teutonic Knights continues to impact modern culture and regional politics in the full article.
Table of Comparison
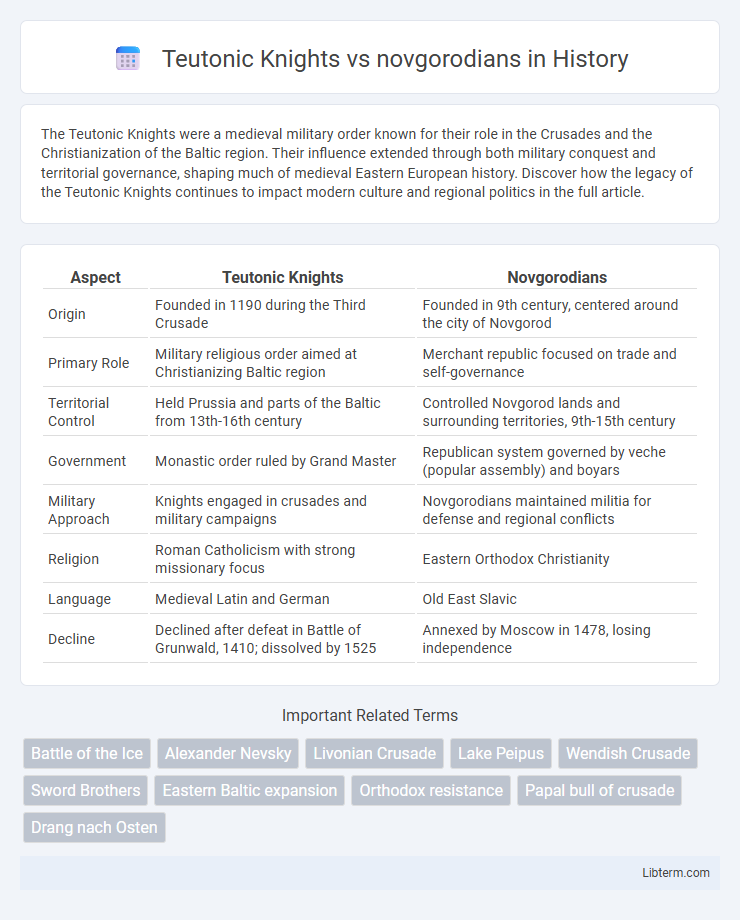
| Aspect | Teutonic Knights | Novgorodians |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Founded in 1190 during the Third Crusade | Founded in 9th century, centered around the city of Novgorod |
| Primary Role | Military religious order aimed at Christianizing Baltic region | Merchant republic focused on trade and self-governance |
| Territorial Control | Held Prussia and parts of the Baltic from 13th-16th century | Controlled Novgorod lands and surrounding territories, 9th-15th century |
| Government | Monastic order ruled by Grand Master | Republican system governed by veche (popular assembly) and boyars |
| Military Approach | Knights engaged in crusades and military campaigns | Novgorodians maintained militia for defense and regional conflicts |
| Religion | Roman Catholicism with strong missionary focus | Eastern Orthodox Christianity |
| Language | Medieval Latin and German | Old East Slavic |
| Decline | Declined after defeat in Battle of Grunwald, 1410; dissolved by 1525 | Annexed by Moscow in 1478, losing independence |
Origins of the Teutonic Knights and Novgorodians
The Teutonic Knights originated in the late 12th century during the Third Crusade as a German Catholic military order aimed at defending the Holy Land and converting pagan populations in the Baltic region. The Novgorodians were a medieval East Slavic people centered around the city of Novgorod, known for establishing the Novgorod Republic, which flourished from the 12th to 15th centuries as a major trading and political power in Northwestern Russia. The conflict between the Teutonic Knights and Novgorodians arose from territorial and religious expansion, with the Knights seeking to Christianize and control Baltic territories, while Novgorodians aimed to defend their lands and Orthodox Christian heritage.
Religious Motivations and Crusading Zeal
The Teutonic Knights, driven by their Catholic mission, sought to Christianize the pagan Novgorodians, viewing the conflict as a holy crusade sanctioned by the Pope. Their religious motivations were intertwined with crusading zeal, aiming to expand Christendom's borders through military conquest and forced conversion. The Novgorodians, firmly rooted in Eastern Orthodox Christianity, resisted these incursions, defending their faith and territories against the Teutonic Order's aggressive attempts at religious domination.
Military Strategies and Tactics Compared
The Teutonic Knights employed heavily armored cavalry and disciplined infantry brigades, leveraging fortified castles and siege warfare to dominate open battlefields. The Novgorodians utilized agile, lightly armored forces adept at guerrilla tactics, swift riverine movements, and fortified wooden strongholds to counter the Knights' heavy armor and siege capabilities. The contrasting strategies highlight the Teutonic reliance on direct confrontation and fortifications, opposed by Novgorod's flexible defense and mobility in dense forests and river networks.
Key Leaders and Influential Figures
The Teutonic Knights were led by Grand Master Hermann von Salza, whose strategic leadership expanded the Order's influence across the Baltic region. On the Novgorodian side, Alexander Nevsky emerged as a pivotal figure, renowned for his military prowess and diplomatic acumen in resisting Teutonic advances. Both leaders significantly shaped the power dynamics during the Northern Crusades, with Nevsky celebrated for his victory at the Battle of the Ice in 1242.
Major Battles: Lake Peipus and Beyond
The Battle of Lake Peipus in 1242 marked a decisive victory for the Novgorodians under Prince Alexander Nevsky against the Teutonic Knights, halting their eastward expansion into Russian territories. The heavily armored Teutonic cavalry faced devastating losses due to Novgorodians' strategic use of the lake's icy conditions, which caused the knights' formations to collapse. Subsequent skirmishes reinforced Novgorod's dominance in the region, preventing further Teutonic incursions and consolidating Russia's northwest borders.
Weapons, Armor, and Technological Differences
The Teutonic Knights employed advanced crossbows, longswords, and heavy plate armor, reflecting Western Europe's technological edge in metallurgy and combat gear during the 13th century. Novgorodians favored lighter chainmail, lamellar armor, and composite bows, allowing greater mobility and adaptability in the dense forests and harsh climates of Northern Rus'. The technological disparity between the heavily armored Teutonic Knights and the more agile Novgorodian forces significantly influenced their battlefield tactics and engagement outcomes.
Political Alliances and External Influences
The Teutonic Knights forged alliances with various Western European powers, leveraging papal support to legitimize their military campaigns against the Novgorodians, who in turn sought backing from the Byzantine Empire and neighboring Rus' principalities to resist crusader expansion. Diplomatic alignments were heavily influenced by religious affiliations, with the Catholic Teutonic Order receiving aid from the Holy Roman Empire, while the Orthodox Novgorodians consolidated ties through trade agreements with the Hanseatic League. These political alliances and external influences intensified the regional power struggle, shaping the geopolitical landscape of the Baltic region during the 13th and 14th centuries.
Impact on Local Populations and Territories
The Teutonic Knights' campaigns against the Novgorodians significantly disrupted local populations, leading to widespread displacement and economic hardship. Territorial control shifted frequently, with fortified settlements and strategic locations contested, severely altering demographic and trade patterns in the region. Persistent warfare inflicted cultural and social fragmentation, impacting both indigenous livelihoods and regional political stability.
Cultural Legacy and Historical Narratives
The conflict between the Teutonic Knights and Novgorodians significantly shaped the cultural legacy and historical narratives of the Baltic region, intertwining Christian militarism with Orthodox Slavic traditions. The Battle of the Ice in 1242 remains a seminal event, celebrated in Russian historiography as a symbol of resistance against Western crusading forces, reinforcing national identity and Orthodox resilience. This clash influenced medieval art, literature, and folklore, embedding the Teutonic Knights as antagonists in Slavic cultural memory while highlighting Novgorod's role as a defender of Eastern Orthodoxy and regional autonomy.
Lasting Effects on Eastern European History
The Teutonic Knights' conflicts with the Novgorodians shaped Eastern European political boundaries by halting the Knights' eastward expansion and preserving Novgorod's territorial integrity. This prolonged rivalry influenced the region's religious landscape, reinforcing Eastern Orthodoxy in Novgorod while curbing Catholic dominance. The resulting balance of power contributed to the development of distinct national identities and set the stage for future state formations in the Baltics and Russia.
Teutonic Knights Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com