Quaestiones disputatae represent a pivotal method in medieval scholastic philosophy, where complex theological and philosophical questions were systematically debated to clarify and resolve intricate issues. This structured form of inquiry influenced the intellectual rigor of medieval universities and laid the foundation for modern academic discourse. Explore the rest of this article to understand how Quaestiones disputatae shaped scholarly debates and the development of critical thinking.
Table of Comparison
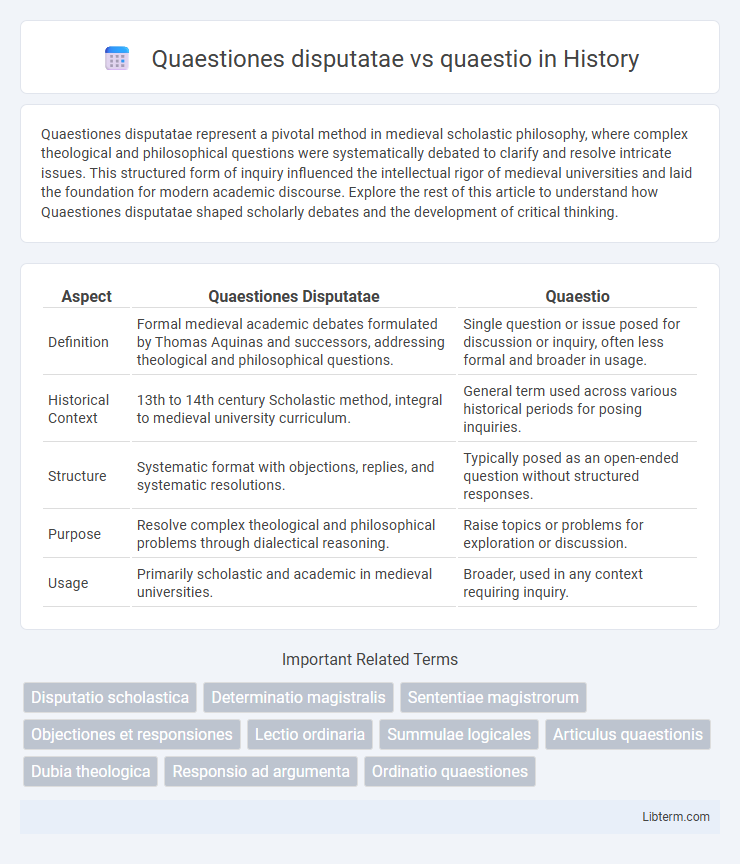
| Aspect | Quaestiones Disputatae | Quaestio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal medieval academic debates formulated by Thomas Aquinas and successors, addressing theological and philosophical questions. | Single question or issue posed for discussion or inquiry, often less formal and broader in usage. |
| Historical Context | 13th to 14th century Scholastic method, integral to medieval university curriculum. | General term used across various historical periods for posing inquiries. |
| Structure | Systematic format with objections, replies, and systematic resolutions. | Typically posed as an open-ended question without structured responses. |
| Purpose | Resolve complex theological and philosophical problems through dialectical reasoning. | Raise topics or problems for exploration or discussion. |
| Usage | Primarily scholastic and academic in medieval universities. | Broader, used in any context requiring inquiry. |
Introduction to Quaestiones Disputatae
Quaestiones Disputatae refers to a structured method of scholastic debate used primarily in medieval universities to explore complex theological and philosophical questions through formal disputation. The Introduction to Quaestiones Disputatae typically outlines the precise question (quaestio) to be examined, the objections raised against a particular thesis, and the responses that form the basis of intellectual inquiry. This method emphasizes systematic reasoning and dialectical argumentation to clarify and resolve nuanced scholastic issues.
Defining the Term: Quaestio
Quaestio, in medieval scholastic tradition, refers to a specific question posed for detailed philosophical or theological analysis, forming the foundation for scholarly debate. It serves as the starting point for the systematic inquiry undertaken in Quaestiones disputatae, where multiple arguments for and against the quaestio are rigorously examined. Defining quaestio precisely is crucial for understanding how complex doctrinal issues were methodically explored in scholastic settings.
Historical Context of Medieval Scholasticism
Quaestiones disputatae and quaestio are key components of medieval scholastic methodology, with the former referring to formalized disputed questions debated by scholars to clarify theological and philosophical issues. Quaestio represents a structured question or problem posed for investigation, often serving as the basis for systematic analysis in medieval universities. These methods emerged prominently in the 13th century, exemplified by figures like Thomas Aquinas, facilitating rigorous dialectical reasoning essential to scholasticism's intellectual tradition.
Structural Differences: Quaestiones Disputatae vs Quaestio
Quaestiones disputatae feature a formal, structured format comprising a specific question, disputed arguments (objections), a main response (sed contra and respondeo), and replies to objections, promoting rigorous dialectical examination. In contrast, a quaestio is generally a singular question or issue posed for consideration without the elaborate argumentative framework characteristic of the quaestiones disputatae. This structural difference allows quaestiones disputatae to serve as comprehensive scholastic exercises in resolving complex theological or philosophical problems systematically.
Purpose and Function in Academic Discourse
Quaestiones disputatae serve as structured, formal debates designed to examine complex theological or philosophical issues through systematic argumentation and counterargument, promoting critical analysis and intellectual rigor. Quaestio functions as a broader inquiry or question that frames the discussion but may not inherently involve the detailed disputation process characteristic of quaestiones disputatae. In academic discourse, quaestiones disputatae facilitate deeper exploration and resolution of specific doctrinal controversies, while quaestio establishes the foundational query guiding scholarly investigation.
Methodologies Employed in Each Form
Quaestiones disputatae utilizes a structured dialectical method where a question is posed, objections and counterarguments are systematically examined, and a conclusive resolution is provided. The methodology emphasizes rigorous logical analysis, incorporating authoritative texts to resolve theological or philosophical issues. In contrast, the quaestio method is broader and more flexible, often involving open-ended inquiry or debate without strict procedural constraints, allowing for exploratory discussion rather than definitive answers.
Key Figures and Notable Examples
Thomas Aquinas stands as a key figure in Quaestiones Disputatae, where he systematically explored theological and philosophical questions through structured debate. Notable examples include the "Quaestiones Disputatae de Veritate," which thoroughly examined the nature of truth, and "Quaestiones Disputatae de Potentia Dei," focusing on divine power. In contrast, the term quaestio refers more generally to a single question or issue addressed without the extensive disputation format characteristic of Aquinas's works.
Evolution through the Medieval Period
Quaestiones disputatae and quaestio represent distinct scholarly methods in medieval philosophy, with quaestio initially used to pose specific, often theological, questions for exploration. Quaestiones disputatae evolved as a more structured academic exercise, featuring systematic debate and resolution of questions, prominently practiced in medieval universities like the University of Paris. This evolution highlights the shift from isolated inquiry in quaestio to collective dialectical reasoning in quaestiones disputatae, reflecting medieval scholasticism's emphasis on rigorous discussion and consensus-building.
Impact on Later Philosophical Traditions
Quaestiones disputatae, medieval scholastic debates structured as rigorous question-and-answer discussions, shaped the methodology and rigor of later philosophical traditions, especially in Thomism and Jesuit education. The formalized dialectical process encouraged critical analysis and systematic exploration of theological and philosophical issues, influencing early modern thinkers like Descartes and Spinoza. Quaestio, as a broader inquiry or problem, underpinned this tradition by fostering analytical precision and dialectical engagement foundational to Western intellectual history.
Contemporary Relevance and Legacy
Quaestiones disputatae represent a structured method of scholastic inquiry that shaped medieval academic discourse, influencing contemporary theological and philosophical debate frameworks. Quaestio, as a singular question or issue, serves as the foundational element of this method, facilitating focused analysis and critical examination within modern interdisciplinary research. The legacy of these techniques persists in contemporary legal and academic practices, emphasizing rigorous dialectical reasoning and structured argumentation.
Quaestiones disputatae Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com