Uncover the mysteries of past civilizations through the detailed study of artifacts, structures, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology reveals how ancient societies lived, adapted, and evolved, offering essential insights into human history and heritage. Explore the article to deepen your understanding of this fascinating discipline and its impact on our knowledge of the past.
Table of Comparison
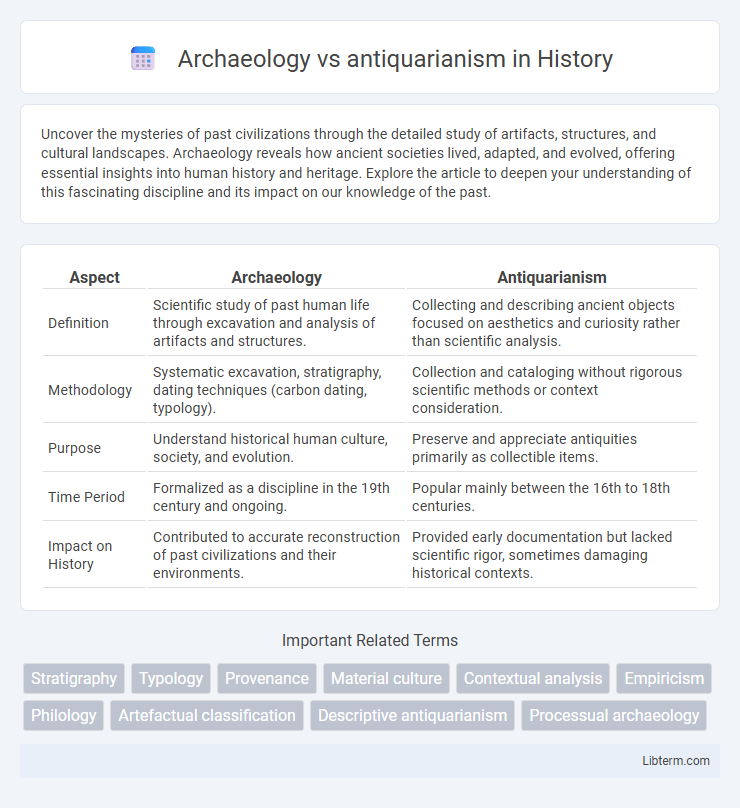
| Aspect | Archaeology | Antiquarianism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scientific study of past human life through excavation and analysis of artifacts and structures. | Collecting and describing ancient objects focused on aesthetics and curiosity rather than scientific analysis. |
| Methodology | Systematic excavation, stratigraphy, dating techniques (carbon dating, typology). | Collection and cataloging without rigorous scientific methods or context consideration. |
| Purpose | Understand historical human culture, society, and evolution. | Preserve and appreciate antiquities primarily as collectible items. |
| Time Period | Formalized as a discipline in the 19th century and ongoing. | Popular mainly between the 16th to 18th centuries. |
| Impact on History | Contributed to accurate reconstruction of past civilizations and their environments. | Provided early documentation but lacked scientific rigor, sometimes damaging historical contexts. |
Defining Archaeology and Antiquarianism
Archaeology is the systematic study of past human cultures through excavation, analysis, and interpretation of material remains, emphasizing scientific methods and context. Antiquarianism primarily focuses on the collection and description of ancient artifacts and curiosities without rigorous analysis of their cultural or historical significance. While archaeology aims to reconstruct past human behavior and societies, antiquarianism tends to prioritize preservation and documentation of antiquities as isolated objects.
Historical Origins of Antiquarianism
Antiquarianism originated in the Renaissance period as a scholarly pursuit dedicated to the collection and study of ancient artifacts, manuscripts, and inscriptions, primarily emphasizing description and preservation. Unlike archaeology, which applies systematic excavation and scientific methods to understand past human cultures, antiquarianism focused more on the accumulation of curiosities without rigorous contextual analysis. The historical roots of antiquarianism laid the groundwork for modern archaeological practices by prioritizing antiquities' documentation and appreciation, ultimately evolving into a more structured discipline.
Evolution of Archaeological Practice
The evolution of archaeological practice reflects a shift from antiquarianism's focus on collecting curiosities to systematic investigation aimed at understanding past human cultures. Archaeology developed rigorous scientific methods such as stratigraphy, typology, and carbon dating to analyze artifacts within their historical context, enhancing accuracy and reliability. This transformation established archaeology as an academic discipline committed to reconstructing chronological narratives and cultural developments rather than merely amassing relics.
Key Differences in Methodology
Archaeology employs systematic excavation, scientific analysis, and contextual interpretation to uncover and understand past human activities, while antiquarianism primarily focuses on collecting artifacts and historical objects without rigorous stratigraphic or contextual study. Archaeologists utilize techniques such as carbon dating, GIS mapping, and interdisciplinary research, contrasting with antiquarians who rely more on descriptive cataloging and aesthetic appreciation. The methodological emphasis in archaeology on empirical evidence and chronological frameworks distinguishes it from the often anecdotal and less structured approach characteristic of antiquarianism.
The Role of Evidence and Documentation
Archaeology relies on systematic evidence collection and rigorous documentation to reconstruct past human activities with scientific accuracy. Antiquarianism often emphasized the collection of artifacts based on aesthetic or historical interest, lacking standardized methods for context recording and analysis. The evolution from antiquarianism to archaeology marked a shift towards evidence-based interpretation, ensuring reliability through stratigraphic excavation and precise documentation practices.
Influential Figures in Both Fields
Influential figures in archaeology include Heinrich Schliemann, who pioneered systematic excavation techniques at Troy, and Flinders Petrie, renowned for developing stratigraphic analysis and ceramic typology. In antiquarianism, figures like John Aubrey and Sir Robert Cotton played crucial roles by collecting and preserving historical artifacts and manuscripts, laying foundational work for later archaeological methodology. The transition from antiquarianism to archaeology marked a shift from mere collection to scientific inquiry, shaped by these key individuals' contributions.
Impact on Cultural Heritage Preservation
Archaeology employs systematic excavation and scientific analysis to uncover and preserve artifacts, significantly enhancing cultural heritage conservation through accurate context and documentation. Antiquarianism, often characterized by collection without rigorous methodology, risks fragmenting historical records and diminishing the integrity of cultural sites. The transition from antiquarian practices to archaeological standards has enabled more sustainable preservation and interpretation of cultural heritage worldwide.
Shifts in Public Perception
Archaeology transformed public perception by emphasizing scientific methods and systematic excavation, distinguishing itself from antiquarianism's primarily collection-focused approach. The rise of archaeology promoted understanding of cultural context and chronological framework, shifting interest from mere artifact accumulation to historical narratives. Public engagement increased as museums and educational institutions showcased findings within interpretative frameworks, enhancing appreciation for ancient civilizations beyond curiosity or aesthetic value.
Contemporary Relevance and Criticisms
Archaeology today emphasizes scientific methods and cultural context to interpret past human activities, distinguishing itself from antiquarianism, which focused primarily on collecting artifacts without analytical frameworks. Contemporary relevance lies in archaeology's contributions to heritage preservation, education, and understanding societal development, while antiquarianism is often critiqued for its lack of systematic methodology and contextual awareness. Criticisms of modern archaeology include issues of cultural bias, excavation ethics, and the potential destruction of sites, highlighting the ongoing need for responsible and inclusive research practices.
Future Directions: Merging Perspectives
Future directions in archaeology and antiquarianism emphasize integrating scientific methodologies with historical passion to create holistic research approaches. Emerging technologies like 3D scanning, AI-driven data analysis, and enhanced stratigraphic techniques bridge the gap between empirical excavation and artifact appreciation. Collaborative frameworks encourage interdisciplinary teams to preserve cultural heritage while advancing interpretive accuracy and public engagement.
Archaeology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com