Bioarchaeology studies human remains from archaeological sites to understand past health, diet, and lifestyle. It combines biological and cultural data to reconstruct ancient populations' life experiences and environmental interactions. Explore the full article to discover how bioarchaeology reveals secrets of your ancestors' lives.
Table of Comparison
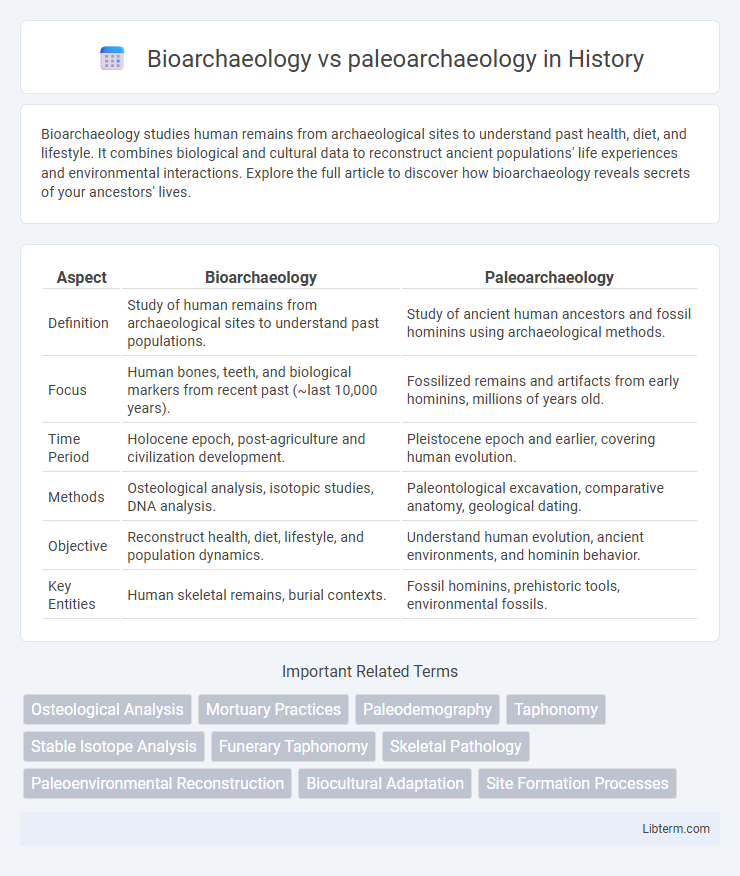
| Aspect | Bioarchaeology | Paleoarchaeology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of human remains from archaeological sites to understand past populations. | Study of ancient human ancestors and fossil hominins using archaeological methods. |
| Focus | Human bones, teeth, and biological markers from recent past (~last 10,000 years). | Fossilized remains and artifacts from early hominins, millions of years old. |
| Time Period | Holocene epoch, post-agriculture and civilization development. | Pleistocene epoch and earlier, covering human evolution. |
| Methods | Osteological analysis, isotopic studies, DNA analysis. | Paleontological excavation, comparative anatomy, geological dating. |
| Objective | Reconstruct health, diet, lifestyle, and population dynamics. | Understand human evolution, ancient environments, and hominin behavior. |
| Key Entities | Human skeletal remains, burial contexts. | Fossil hominins, prehistoric tools, environmental fossils. |
Introduction to Bioarchaeology and Paleoarchaeology
Bioarchaeology examines human remains from archaeological sites to understand past health, diet, and lifestyles, integrating biological and cultural data. Paleoarchaeology focuses on the study of ancient human ancestors and their tool use, often extending back to prehistoric periods far beyond recent historical contexts. Both disciplines provide critical insights into human evolution and cultural development through interdisciplinary methods combining anthropology, archaeology, and paleontology.
Defining Bioarchaeology: Focus and Methods
Bioarchaeology is the study of human remains from archaeological sites to understand health, diet, and lifestyle through bio-anthropological methods such as osteology, stable isotope analysis, and DNA sequencing. This discipline emphasizes the biological and cultural interactions of past populations by examining skeletal and mummified remains to reconstruct life histories and population dynamics. Unlike paleoarchaeology, which broadly studies ancient human cultures and environments, bioarchaeology specifically focuses on the biological aspects of human history integrated with archaeological context.
Understanding Paleoarchaeology: Scope and Techniques
Paleoarchaeology focuses on studying ancient human fossils and their environments to reconstruct early human evolution and behavior. Techniques include excavations, radiometric dating, and paleoenvironmental analysis to understand hominin adaptations and migration patterns. This field integrates data from geology, paleoanthropology, and archaeology to trace the origins and development of prehistoric populations.
Key Differences Between Bioarchaeology and Paleoarchaeology
Bioarchaeology primarily studies human skeletal remains to understand past populations' health, diet, and lifestyle, emphasizing biological and cultural interactions. Paleoarchaeology focuses on the examination of ancient hominins and their environments, integrating fossil records and stone tools to trace human evolution over millions of years. Key differences lie in their temporal scope--bioarchaeology deals mostly with recent centuries to millennia, while paleoarchaeology spans deep prehistory to early human origins.
Overlapping Areas and Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Bioarchaeology and paleoarchaeology share overlapping areas in the study of ancient human remains and environmental contexts, where bioarchaeology emphasizes human skeletal analysis and paleoarchaeology combines archaeological data with paleoenvironmental reconstructions. Interdisciplinary collaboration between these fields enhances understanding of past human health, diet, and migration patterns through integrating osteological evidence with paleoecological and geological data. This synergy supports comprehensive interpretations of human evolution and adaptation within ancient ecosystems.
Major Discoveries: Bioarchaeological Insights
Bioarchaeological insights have revealed critical information about ancient health, diet, and social structures through the analysis of human skeletal remains. Major discoveries include evidence of nutritional deficiencies, trauma patterns, and disease evolution, offering a nuanced understanding of past populations' lifestyles. These findings distinctively complement paleoarchaeological studies, which primarily focus on early human evolution and prehistoric sites.
Pioneering Finds: Contributions of Paleoarchaeology
Paleoarchaeology has pioneered significant discoveries by uncovering early human fossils and artifacts that illuminate hominin evolution and ancient behaviors. Key finds such as the Australopithecus afarensis "Lucy" and Homo erectus fossils have reshaped understanding of human ancestry and migration patterns. These contributions provide critical context for interpreting archaeological data within the broader framework of human biological and cultural development.
Analytical Tools and Technologies in Both Fields
Bioarchaeology employs advanced techniques such as stable isotope analysis, DNA sequencing, and radiocarbon dating to study human remains within archaeological contexts, providing insights into ancient diets, health, and migration patterns. Paleoarchaeology utilizes lithic analysis, paleoenvironmental reconstruction, and geochronological methods like optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating to investigate early hominin artifacts and their environmental adaptations. Both fields integrate high-resolution imaging and geospatial technologies, enhancing data accuracy and contextual interpretation of past human activity across different time scales.
Career Paths in Bioarchaeology vs Paleoarchaeology
Careers in bioarchaeology focus on analyzing human remains to understand health, diet, and lifestyle in past populations, often leading to roles in forensic anthropology, museum curation, or academic research. Paleoarchaeology career paths emphasize studying ancient human ancestors and prehistoric cultures through fossil records and artifact analysis, with opportunities in field excavation, paleoanthropology, and heritage conservation. Both fields require expertise in archaeological methods, but bioarchaeology prioritizes biological and osteological analysis, while paleoarchaeology centers on evolutionary and cultural context.
Future Trends and Challenges in Human Past Research
Future trends in bioarchaeology emphasize integrating advanced biomolecular techniques such as ancient DNA analysis and isotope geochemistry to reconstruct detailed human life histories, health patterns, and migration routes. Paleoarchaeology faces challenges in distinguishing early human behaviors within complex paleoenvironmental contexts, driving innovation in high-resolution dating methods and computational modeling to better interpret artifact functions and site formation processes. Collaboration between these disciplines promises comprehensive insights into human evolution and cultural development, while ethical considerations in handling ancient remains demand evolving protocols and stakeholder engagement.
Bioarchaeology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com