Purism prioritizes privacy, security, and ethical software practices by offering devices and services designed to protect user data from surveillance and exploitation. Their Linux-based laptops and smartphones come with open-source software, providing transparency and control over your digital environment. Explore the rest of this article to learn how Purism can empower your technology experience.
Table of Comparison
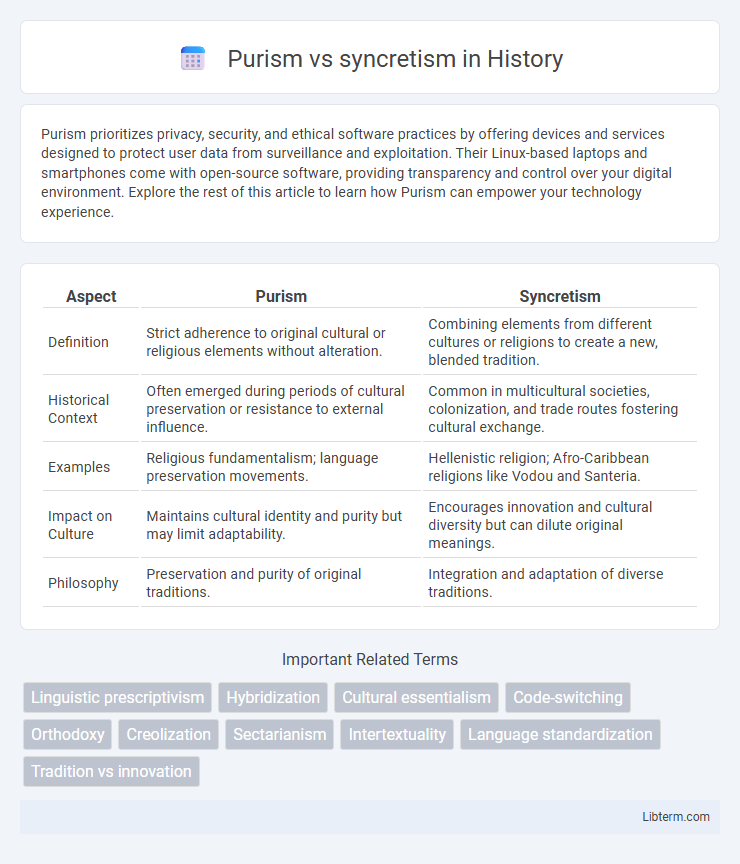
| Aspect | Purism | Syncretism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strict adherence to original cultural or religious elements without alteration. | Combining elements from different cultures or religions to create a new, blended tradition. |
| Historical Context | Often emerged during periods of cultural preservation or resistance to external influence. | Common in multicultural societies, colonization, and trade routes fostering cultural exchange. |
| Examples | Religious fundamentalism; language preservation movements. | Hellenistic religion; Afro-Caribbean religions like Vodou and Santeria. |
| Impact on Culture | Maintains cultural identity and purity but may limit adaptability. | Encourages innovation and cultural diversity but can dilute original meanings. |
| Philosophy | Preservation and purity of original traditions. | Integration and adaptation of diverse traditions. |
Understanding Purism: Definition and Origins
Purism refers to the linguistic or cultural approach that emphasizes maintaining strict adherence to original or "pure" forms, often resisting foreign influences or changes. Originating from a desire to preserve identity and authenticity, purism is commonly observed in language preservation movements aiming to protect vocabulary and grammar from loanwords and external modifications. This concept contrasts with syncretism, which encourages blending and merging diverse elements into a cohesive whole.
The Roots of Syncretism: Meaning and Historical Context
Syncretism originates from the Greek word "synkretismos," meaning the union of different groups or ideas, reflecting its historical context in ancient Crete where diverse cultures merged. It embodies the blending of religious, philosophical, or cultural beliefs, often emerging from intercultural contact and the need for social cohesion. Understanding the roots of syncretism reveals how religious and cultural identities evolve through synthesis rather than strict purity, contrasting sharply with the rigid boundaries emphasized in purism.
Key Differences Between Purism and Syncretism
Purism emphasizes strict adherence to original cultural or religious practices, seeking to preserve traditions without modification or external influence. Syncretism involves the blending of different cultural, religious, or philosophical elements into a new, unified system, often creating hybrid forms that integrate diverse beliefs. Key differences include purism's focus on preservation and exclusivity versus syncretism's emphasis on adaptation and inclusivity.
Cultural Identity: The Impact of Purism
Purism in cultural identity emphasizes preserving traditional practices and resisting external influences to maintain cultural authenticity. This approach can strengthen community bonds by fostering a clear, distinct cultural heritage but may also lead to exclusion of diverse perspectives and hinder cultural evolution. The impact of purism often results in rigid boundaries that prioritize ancestral customs over adaptive, syncretic cultural exchange.
Syncretism in Religion and Spirituality
Syncretism in religion and spirituality involves the blending of different beliefs, rituals, and traditions into a cohesive system, often fostering inclusivity and cultural exchange. This process can create new religious movements or hybrid practices that resonate with diverse communities, reflecting historical interactions and globalization. Syncretic religions like Vodou, Sikhism, and Baha'i exemplify the synthesis of elements from multiple faiths, promoting spiritual unity and innovation.
Language Evolution: Purist vs Syncretic Approaches
Purism in language evolution emphasizes maintaining linguistic purity by resisting foreign influences and preserving traditional grammar and vocabulary. Syncretism embraces the blending and integration of diverse linguistic elements, fostering language change through contact and cultural exchange. This dynamic interplay shapes the continuous transformation of languages, balancing preservation with innovation.
Art and Architecture: Merging Styles or Preserving Purity
Purism in art and architecture emphasizes maintaining traditional styles and techniques, prioritizing cultural authenticity and historical accuracy. Syncretism involves blending diverse artistic influences and architectural elements to create innovative, hybrid forms that reflect multicultural interactions. Both approaches impact identity expression, with purism preserving cultural heritage and syncretism fostering creative evolution through stylistic fusion.
Social Dynamics: Tensions Between Purist and Syncretic Views
Social dynamics reveal persistent tensions between purist and syncretic views, as purists advocate for maintaining cultural or ideological purity, resisting external influences to preserve traditional identity. Syncretism promotes blending diverse beliefs and practices, fostering adaptation and inclusivity within evolving social frameworks. These conflicting perspectives often lead to debates over authenticity, cultural preservation, and the acceptance of change in communities, shaping social cohesion and identity formation.
Globalization: Fueling Syncretism or Purism?
Globalization accelerates cultural exchange, often fueling syncretism by blending diverse traditions, beliefs, and practices into hybrid forms. However, it also provokes purism as communities may resist homogenization, striving to preserve distinct identities and authentic heritage. The dynamic interplay between syncretism and purism reflects globalization's dual impact on cultural evolution and identity preservation worldwide.
The Future of Cultural Expression: Purism vs Syncretism
The future of cultural expression hinges on the tension between purism, which seeks to preserve distinct cultural identities and traditions, and syncretism, which promotes blending and fusion of diverse cultural elements to create innovative forms. Purism emphasizes safeguarding authentic heritage by resisting external influences, while syncretism encourages adaptive evolution through cross-cultural interactions that reflect globalization and hybrid identities. Balancing these approaches shapes how societies maintain cultural integrity while embracing dynamic change in arts, language, and social practices.
Purism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com