Gender egalitarianism promotes equal rights, responsibilities, and opportunities regardless of gender, challenging traditional stereotypes and systemic inequalities. It fosters inclusive societies where diverse talents and perspectives contribute to social and economic progress. Discover how embracing gender egalitarianism can transform your environment and empower everyone by reading the rest of the article.
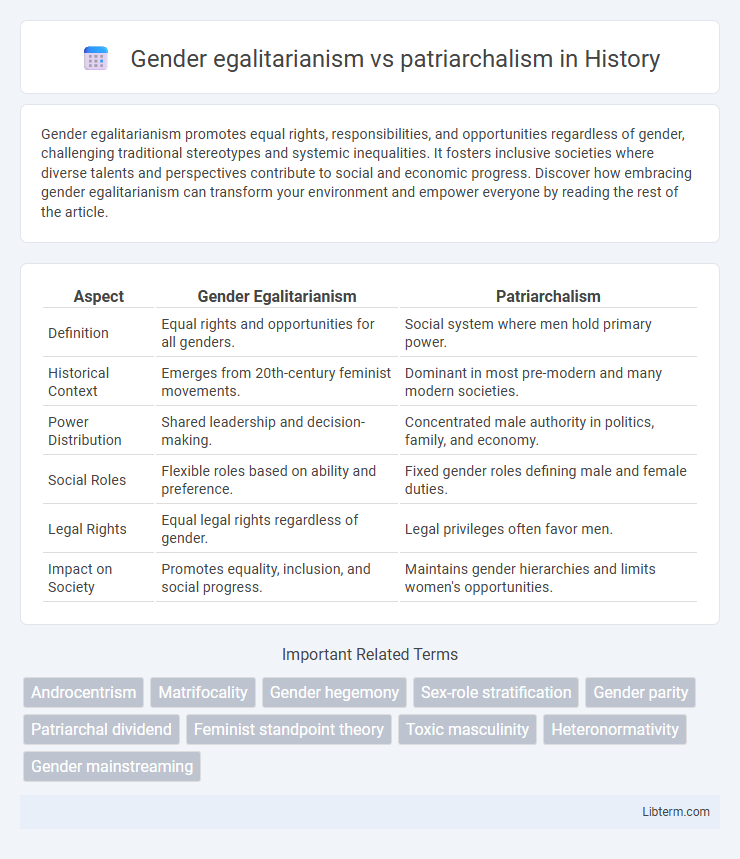
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Gender Egalitarianism | Patriarchalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Equal rights and opportunities for all genders. | Social system where men hold primary power. |
| Historical Context | Emerges from 20th-century feminist movements. | Dominant in most pre-modern and many modern societies. |
| Power Distribution | Shared leadership and decision-making. | Concentrated male authority in politics, family, and economy. |
| Social Roles | Flexible roles based on ability and preference. | Fixed gender roles defining male and female duties. |
| Legal Rights | Equal legal rights regardless of gender. | Legal privileges often favor men. |
| Impact on Society | Promotes equality, inclusion, and social progress. | Maintains gender hierarchies and limits women's opportunities. |
Defining Gender Egalitarianism and Patriarchalism
Gender egalitarianism advocates for equal rights, responsibilities, and opportunities regardless of gender, promoting social structures where power and resources are distributed without gender bias. Patriarchalism, in contrast, is a social system in which men hold primary power, dominating roles in political leadership, moral authority, social privilege, and control of property. Understanding these concepts is crucial for analyzing gender dynamics, as gender egalitarianism challenges the entrenched hierarchies inherent in patriarchal societies.
Historical Roots of Patriarchal Societies
Patriarchal societies have historical roots tracing back to early agrarian civilizations where male dominance emerged due to physical labor roles and inheritance systems favoring men. Ancient legal codes, such as Hammurabi's Code, institutionalized male authority, reinforcing gender hierarchies over generations. These patriarchal frameworks influenced social, political, and economic structures, limiting gender egalitarianism throughout history.
Evolution of Gender Roles Across Cultures
Gender egalitarianism emphasizes equal rights and responsibilities across genders, reflecting a shift from traditional patriarchalism rooted in male dominance. Across cultures, the evolution of gender roles reveals a dynamic process influenced by social, economic, and political changes, with many societies increasingly adopting more inclusive and flexible gender norms. Anthropological studies show that while patriarchal structures persist in some regions, global movements toward gender equality continue to reshape cultural expectations and institutional frameworks.
Social Impacts of Gender Egalitarianism
Gender egalitarianism promotes equal opportunities and rights across all genders, significantly reducing social inequalities and fostering inclusive communities. This approach improves social cohesion by challenging traditional gender norms that often limit individual potential and perpetuate discrimination. Societies embracing gender egalitarianism experience higher economic productivity, better health outcomes, and enhanced educational attainment for all genders.
Economic Outcomes in Egalitarian vs Patriarchal Systems
Gender egalitarianism promotes equitable access to education, employment, and leadership roles for all genders, resulting in higher overall economic growth and increased labor productivity. Patriarchal systems often restrict opportunities for women, leading to underutilization of human capital and slower economic development. Studies show that countries with higher gender equality report greater GDP per capita and more inclusive economic participation across sectors.
Influence on Legal Rights and Policy-Making
Gender egalitarianism promotes equal legal rights and inclusive policy-making, ensuring that women and men have equivalent access to education, employment, and political participation. Patriarchalism reinforces male dominance in law and policy, often resulting in discriminatory legislation that limits women's rights and representation. Countries with strong gender egalitarian principles tend to implement progressive policies such as gender quotas and anti-discrimination laws, enhancing legal equity and social justice.
Gender Equality in Education and Workplace
Gender egalitarianism promotes equal access to education and workplace opportunities, reducing disparities in enrollment rates and career advancement between men and women. Patriarchalism often restricts educational attainment and professional growth for women, reinforcing gender pay gaps and underrepresentation in leadership roles. Enhanced gender equality in education and the workplace fosters economic growth and social inclusivity by leveraging diverse talents and perspectives.
Family Dynamics and Power Structures
Gender egalitarianism in family dynamics promotes shared decision-making and equal distribution of household responsibilities, fostering mutual respect between partners. Patriarchalism often centers power within male authority, reinforcing traditional gender roles that limit women's autonomy and influence within the family. These contrasting power structures significantly shape emotional bonds, resource allocation, and conflict resolution in familial relationships.
Challenges to Achieving Gender Equality
Challenges to achieving gender equality arise from deeply rooted patriarchal structures that prioritize male authority and limit women's access to education, employment, and political participation. Gender egalitarianism faces resistance through institutional biases, cultural norms, and legal frameworks that perpetuate discrimination and gender-based violence. Overcoming these obstacles requires comprehensive policy reforms, community engagement, and increased awareness to dismantle systemic inequalities and promote equal rights for all genders.
The Future of Gender Relations: Toward Egalitarianism
The future of gender relations increasingly favors gender egalitarianism, emphasizing equal rights, responsibilities, and opportunities irrespective of gender. Societies embracing egalitarian values demonstrate higher economic growth, improved social cohesion, and enhanced well-being for all genders. Transitioning from patriarchalism to egalitarianism involves dismantling systemic biases, promoting inclusive policies, and advancing education on gender equity.
Gender egalitarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com