The term "Eyalet" referred to a major administrative division within the Ottoman Empire, functioning similarly to a province governed by a Beylerbey. These regions played a crucial role in the empire's political and military organization, influencing the management of local affairs and taxation systems. Explore the detailed history and significance of Eyalets throughout the Ottoman period in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
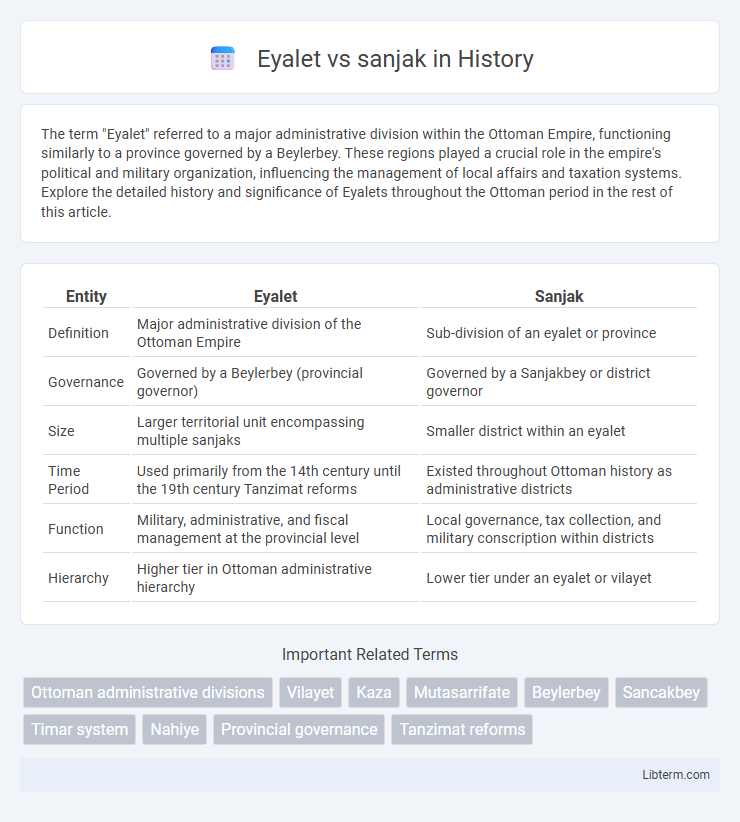
| Entity | Eyalet | Sanjak |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Major administrative division of the Ottoman Empire | Sub-division of an eyalet or province |
| Governance | Governed by a Beylerbey (provincial governor) | Governed by a Sanjakbey or district governor |
| Size | Larger territorial unit encompassing multiple sanjaks | Smaller district within an eyalet |
| Time Period | Used primarily from the 14th century until the 19th century Tanzimat reforms | Existed throughout Ottoman history as administrative districts |
| Function | Military, administrative, and fiscal management at the provincial level | Local governance, tax collection, and military conscription within districts |
| Hierarchy | Higher tier in Ottoman administrative hierarchy | Lower tier under an eyalet or vilayet |
Understanding the Ottoman Administrative Structure
The Ottoman administrative structure was divided into large provinces called eyalets, each governed by a beylerbey responsible for military and fiscal duties. Within eyalets, sanjaks served as smaller districts managed by sanjakbeys who oversaw local administration and collected taxes. This hierarchical system allowed the empire to maintain centralized control while efficiently managing diverse regions through delegated authority.
Defining Eyalet: The Provincial Unit
An Eyalet was a primary administrative division of the Ottoman Empire, serving as a large provincial unit governed by a Pasha or Beylerbey with considerable military and fiscal authority. Each Eyalet was subdivided into smaller districts called Sanjaks, which were overseen by Sanjakbeys responsible for local administration and tax collection. The Eyalet structure centralized imperial control while allowing regional governance through Sanjak authorities, forming the backbone of Ottoman provincial organization.
The Role and Function of Sanjak
A sanjak served as a key administrative subdivision within an Eyalet, functioning as a district governed by a Sanjakbey responsible for local tax collection, law enforcement, and military conscription. Its role was to implement central Ottoman policies at the district level while maintaining regional order and facilitating communication between the provincial governor and smaller communities. Sanjaks thus acted as essential units for political control and fiscal management, ensuring efficient governance within the larger Eyalet framework.
Hierarchical Differences: Eyalet vs Sanjak
Eyalets were large administrative provinces in the Ottoman Empire, governed by a beylerbey, overseeing several sanjaks. Sanjaks served as smaller districts within an eyalet, managed by a sanjakbey, responsible for local administration and tax collection. The hierarchical structure placed eyalets at a higher level with broader authority, while sanjaks operated as subordinate units focusing on regional governance.
Governance and Leadership in Eyalets
Eyalets were large administrative provinces in the Ottoman Empire governed by a Beylerbey or Pasha who held significant military and civil authority, overseeing multiple Sanjaks. Each Sanjak, a smaller district within the Eyalet, was administered by a Sanjak-bey responsible for local governance, tax collection, and maintaining order under the Eyalet's centralized control. The hierarchical leadership structure allowed the Ottoman Empire to efficiently manage vast territories by delegating authority through Eyalet governors while maintaining strict oversight over Sanjak officials.
Administration and Duties of Sanjak Beys
Sanjak bey was the administrative and military governor of a sanjak, a district within an Eyalet, responsible for tax collection, maintaining law and order, and mobilizing troops for the Ottoman army. Unlike the higher-ranking Eyalet governor (vali), the sanjak bey exercised localized authority, overseeing rural development and ensuring the implementation of central government policies. The sanjak bey's duties included managing timar lands, resolving disputes, and coordinating with janissary commanders to secure the region's stability and loyalty to the empire.
Territorial Scope: Comparing Size and Influence
Eyalets were large administrative divisions in the Ottoman Empire, typically consisting of multiple sanjaks, which were smaller districts within an eyalet. The territorial scope of an eyalet often covered vast regions with significant political and military influence, whereas sanjaks represented localized governance units with limited administrative authority. The hierarchical structure granted eyalets broader control over resources, taxation, and military recruitment compared to the relatively narrower jurisdiction of sanjaks.
Fiscal Responsibilities and Tax Collection
Eyalets, as large administrative divisions in the Ottoman Empire, held overarching fiscal responsibilities including the collection of taxes from sanjaks under their jurisdiction. Sanjaks, smaller districts within eyalets, managed localized tax collection, ensuring revenues from agriculture, trade, and artisanship were gathered efficiently. The eyalet authorities coordinated the allocation and forwarding of these collected taxes, maintaining fiscal order and funding imperial expenditures.
Evolution of the Eyalet and Sanjak System
The evolution of the Eyalet and Sanjak system in the Ottoman Empire marked a shift from loosely governed territories to a more centralized administrative structure, with Eyalets serving as large provinces headed by Beylerbeys and Sanjaks functioning as smaller districts overseen by Sanjakbeys. Over time, reforms, especially during the Tanzimat period, intensified central control by redefining the roles and boundaries of Eyalets and Sanjaks, incorporating modern administrative practices to improve tax collection and military conscription. This transformation laid the groundwork for the later Vilayet system, which aimed to further streamline governance and enhance bureaucratic efficiency across the empire.
Legacy and Influence on Modern Administrative Divisions
Eyalets and sanjaks were fundamental administrative units in the Ottoman Empire, with eyalets representing larger provinces governed by beylerbeys and sanjaks serving as smaller districts overseen by sanjakbeys. Their organizational structure laid the groundwork for modern regional administration in countries that once formed part of the empire, influencing contemporary provincial boundaries and local governance systems. This legacy persists in nations like Turkey and the Balkans, where present-day administrative divisions reflect the historical Ottoman model of hierarchical territorial management.
Eyalet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com