Culturalism explores how culture shapes individuals' identities, behaviors, and social interactions within societies. This approach emphasizes the influence of shared beliefs, values, and customs on human development and social cohesion. Discover how understanding culturalism can enrich Your perspective by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
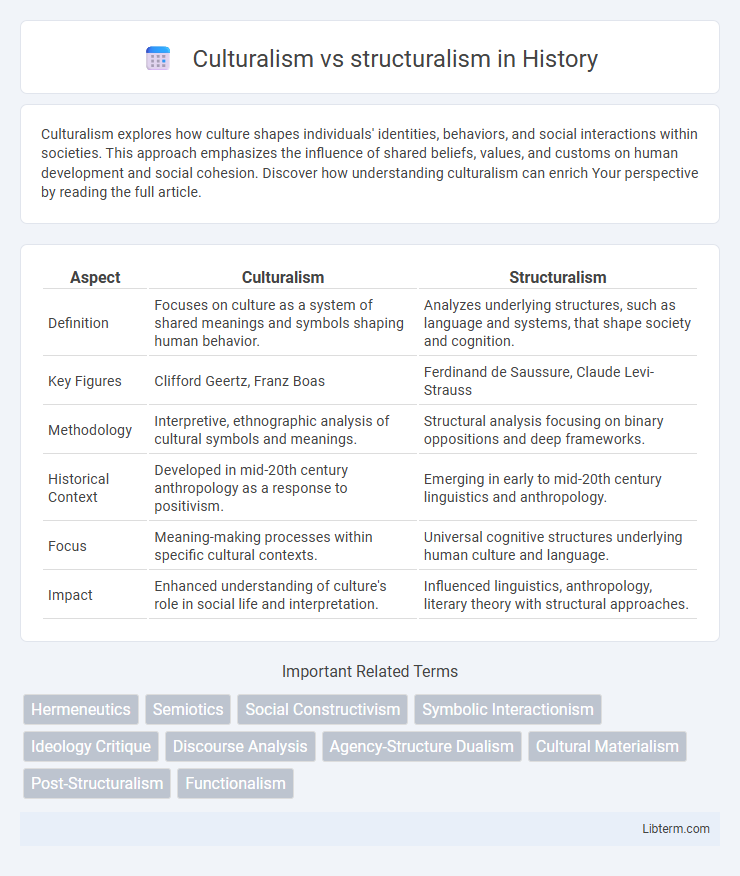
| Aspect | Culturalism | Structuralism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on culture as a system of shared meanings and symbols shaping human behavior. | Analyzes underlying structures, such as language and systems, that shape society and cognition. |
| Key Figures | Clifford Geertz, Franz Boas | Ferdinand de Saussure, Claude Levi-Strauss |
| Methodology | Interpretive, ethnographic analysis of cultural symbols and meanings. | Structural analysis focusing on binary oppositions and deep frameworks. |
| Historical Context | Developed in mid-20th century anthropology as a response to positivism. | Emerging in early to mid-20th century linguistics and anthropology. |
| Focus | Meaning-making processes within specific cultural contexts. | Universal cognitive structures underlying human culture and language. |
| Impact | Enhanced understanding of culture's role in social life and interpretation. | Influenced linguistics, anthropology, literary theory with structural approaches. |
Understanding Culturalism: Core Concepts
Culturalism emphasizes the role of culture, values, beliefs, and symbols in shaping human behavior and social structures, highlighting how cultural meanings influence individual and collective identities. This approach contrasts with structuralism, which analyzes underlying systems and patterns that govern social phenomena, focusing on universal structures rather than cultural variations. Understanding culturalism requires exploring how cultural narratives and practices construct social realities and guide interactions within specific historical and social contexts.
Foundations of Structuralism Explained
Structuralism is founded on the idea that human culture can be understood through the analysis of underlying structures, such as language, myths, and social institutions, which shape behavior and thought patterns. Key figures like Claude Levi-Strauss emphasized binary oppositions and universal mental structures that govern cultural phenomena across different societies. This approach contrasts with Culturalism, which focuses more on the meanings and values individuals and groups assign to cultural elements within specific historical and social contexts.
Historical Origins of Both Theories
Culturalism emerged in the early 20th century, rooted in anthropological studies emphasizing the importance of culture in shaping human behavior and social structures, with key figures like Franz Boas promoting cultural relativism. Structuralism originated in the mid-20th century, largely influenced by linguist Ferdinand de Saussure's work on structural linguistics and later developed by Claude Levi-Strauss, who analyzed cultural phenomena through binary oppositions and underlying structures. Both theories responded to earlier social sciences by shifting focus: culturalism prioritized individual meanings and cultural context, while structuralism emphasized universal patterns and cognitive frameworks.
Key Differences: Culturalism vs Structuralism
Culturalism emphasizes the role of culture, values, and shared meanings in shaping social behavior, while structuralism focuses on underlying structures, such as language and social systems, that determine human actions. Culturalism prioritizes interpretive analysis and the subjective experience of individuals within a cultural context, whereas structuralism relies on identifying universal patterns and binary oppositions embedded in cultural phenomena. Key differences also include culturalism's focus on historical context and change versus structuralism's search for timeless, invariant structures.
Major Proponents and Their Perspectives
Culturalism is championed by Clifford Geertz, who emphasizes interpretive anthropology and the importance of symbols and meanings in understanding culture. Structuralism, advocated by Claude Levi-Strauss, focuses on uncovering the underlying structures of human thought through binary oppositions in myths, language, and social practices. While Geertz prioritizes thick description and cultural context, Levi-Strauss seeks universal cognitive patterns shaping societies.
Culturalism in Contemporary Society
Culturalism in contemporary society emphasizes the role of cultural practices, symbols, and meanings in shaping social life, highlighting how identity and power are constructed through shared beliefs and rituals. It focuses on the fluidity of culture and rejects deterministic views of social structures, promoting an understanding of social dynamics through interpretive analysis of cultural narratives. This approach contrasts with structuralism by prioritizing human agency and the dynamic nature of cultural expression in everyday interactions and institutional frameworks.
Structuralism’s Influence on Modern Thought
Structuralism's influence on modern thought reshaped disciplines such as linguistics, anthropology, and psychology by emphasizing underlying structures shaping human culture and cognition. Pioneers like Claude Levi-Strauss and Ferdinand de Saussure highlighted binary oppositions and sign systems, which became foundational in analyzing myths, language, and social practices. This paradigm shifted focus from individual agency to systemic frameworks, impacting contemporary theory in literary criticism and social sciences.
Real-world Applications and Case Studies
Culturalism emphasizes the role of cultural context and symbolic meaning in shaping social behavior, evident in case studies like Clifford Geertz's analysis of Balinese cockfighting, which highlights interpretive meanings within local rituals. Structuralism focuses on underlying structures and binary oppositions in human thought, as demonstrated by Claude Levi-Strauss's work on myths and kinship systems that reveal universal cognitive patterns across cultures. Real-world applications include culturalism's use in anthropology and media studies to understand cultural narratives, while structuralism informs linguistics, psychology, and literary criticism through its analysis of deep structural codes.
Critiques and Limitations of Each Approach
Culturalism often faces critiques for its tendency to overemphasize symbols and meanings, potentially neglecting underlying social structures that shape cultural expressions. Structuralism is criticized for its rigid framework that may overlook individual agency and historical context, leading to an overly deterministic analysis of social phenomena. Both approaches exhibit limitations in addressing the complexity of human behavior, as culturalism may ignore power relations inherent in structures, while structuralism can disregard the fluidity and diversity of cultural meanings.
Future Directions: Integrating Culturalism and Structuralism
Future directions in the study of Culturalism vs Structuralism emphasize the integration of both approaches to better understand social phenomena. Combining Culturalism's focus on values, symbols, and meanings with Structuralism's emphasis on underlying systems and institutions fosters a comprehensive analysis of human behavior. Advanced interdisciplinary methodologies and digital humanities tools facilitate this synthesis, promoting nuanced insights into culture-structure interactions.
Culturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com