Enactment refers to the process of officially making a law or regulation through legislative approval and formal declaration. It involves the translation of policy decisions into binding legal rules that govern behavior in society. Explore the rest of the article to understand how enactment shapes legal systems and impacts your daily life.
Table of Comparison
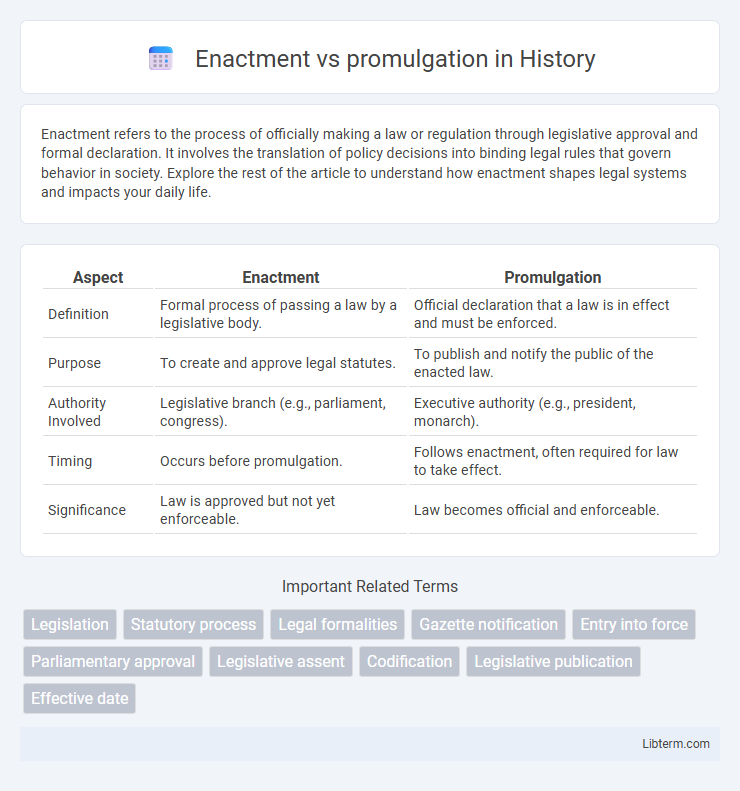
| Aspect | Enactment | Promulgation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal process of passing a law by a legislative body. | Official declaration that a law is in effect and must be enforced. |
| Purpose | To create and approve legal statutes. | To publish and notify the public of the enacted law. |
| Authority Involved | Legislative branch (e.g., parliament, congress). | Executive authority (e.g., president, monarch). |
| Timing | Occurs before promulgation. | Follows enactment, often required for law to take effect. |
| Significance | Law is approved but not yet enforceable. | Law becomes official and enforceable. |
Introduction to Enactment and Promulgation
Enactment refers to the formal process by which a legislative body approves a proposed law, making it an official statute. Promulgation is the subsequent act of formally declaring or announcing the enacted law to the public, often by an executive authority or government official. The distinction lies in enactment establishing the law's validity, while promulgation ensures its communication and implementation.
Defining Enactment in Legal Context
Enactment in the legal context refers to the formal process by which a legislative body adopts a new law or statute, giving it official legal force. It involves the proposal, consideration, approval, and signing of a bill to transform it into binding legislation. Enactment signifies the completion of the law-making procedure, distinguishing it from promulgation, which is the formal declaration or publication of the law for public knowledge and enforcement.
Understanding Promulgation: Meaning and Process
Promulgation refers to the formal proclamation or declaration that a new law or regulation has been officially enacted and is now in effect, typically made by a head of state or authorized official. The process involves publishing the law in an official gazette or legal journal, ensuring public awareness and legal enforceability. Understanding promulgation is crucial as it marks the transition from legislative approval to the law's practical application and compliance.
Key Differences Between Enactment and Promulgation
Enactment refers to the formal process whereby a legislative body passes a bill, making it a law, while promulgation involves the official public declaration and publication of that law, ensuring its enforceability. Key differences include the fact that enactment is concerned with legislative approval and creation, whereas promulgation focuses on notifying the public and setting the effective date. Enactment is a prerequisite for promulgation, which serves as the final step before a law becomes operational and binding on society.
Legal Procedures for Enactment
Legal procedures for enactment involve the formal process whereby a legislative body deliberates, drafts, and approves a bill through multiple readings and committee reviews. Enactment requires a majority vote or specific legislative approval according to jurisdictional rules before the bill becomes a law. This formal approval distinguishes enactment from promulgation, which is the official public announcement or publication of the newly enacted law.
Steps Involved in Promulgation
Promulgation involves formal steps such as the official publication of the law, issuance of a government decree or notification, and communication to the public or relevant authorities to ensure enforcement. This process guarantees that the enacted legislation is publicly accessible and legally binding from a specified date. The enactment phase, by contrast, is centered on legislative approval and formal adoption before promulgation occurs.
Importance of Enactment in Legislation
Enactment is the formal process by which a legislative body officially adopts a bill, transforming it into law, making it a crucial step in the legislative process. This stage ensures that proposed statutes undergo thorough debate, amendment, and approval, reflecting the collective will of elected representatives. Without enactment, legal frameworks would lack legitimacy and enforceability, rendering laws ineffective and undermining governance.
Significance of Promulgation in Law Implementation
Promulgation is the formal proclamation or declaration that a newly enacted law is officially valid and must be obeyed, ensuring legal certainty and public awareness. Unlike enactment, which is the process of drafting and passing the law, promulgation serves to notify the public and relevant authorities, triggering the law's effective implementation. This step is crucial for enforcing the law, preventing ignorance claims, and marking the commencement of its legal force.
Comparative Analysis: Global Practices
Enactment refers to the formal process by which a legislative body passes a law, while promulgation is the official announcement or publication of that law to make it effective. Global practices vary; for instance, in the United States, enactment occurs when both houses of Congress pass a bill and the President signs it, followed by promulgation through publication in the Federal Register. In contrast, some civil law countries like France formalize enactment during parliamentary approval, with promulgation handled by the head of state through official gazettes, illustrating distinct procedural roles in lawmaking across jurisdictions.
Conclusion: Enactment vs Promulgation in Modern Legal Systems
Enactment signifies the formal approval and adoption of a law by the legislature, whereas promulgation involves the official public announcement and publication to ensure legal enforceability. Modern legal systems distinguish these stages to maintain clarity in the legislative process, with enactment marking the creation and promulgation serving as the mechanism for public awareness. Understanding this separation is essential for legal compliance, as laws are only binding after promulgation despite prior enactment.
Enactment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com