Critique involves evaluating a subject by analyzing its strengths and weaknesses to provide balanced feedback. It requires objective observation, constructive comments, and clear reasoning to help improve the work or deepen understanding. Discover how effective critique techniques can enhance your skills by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
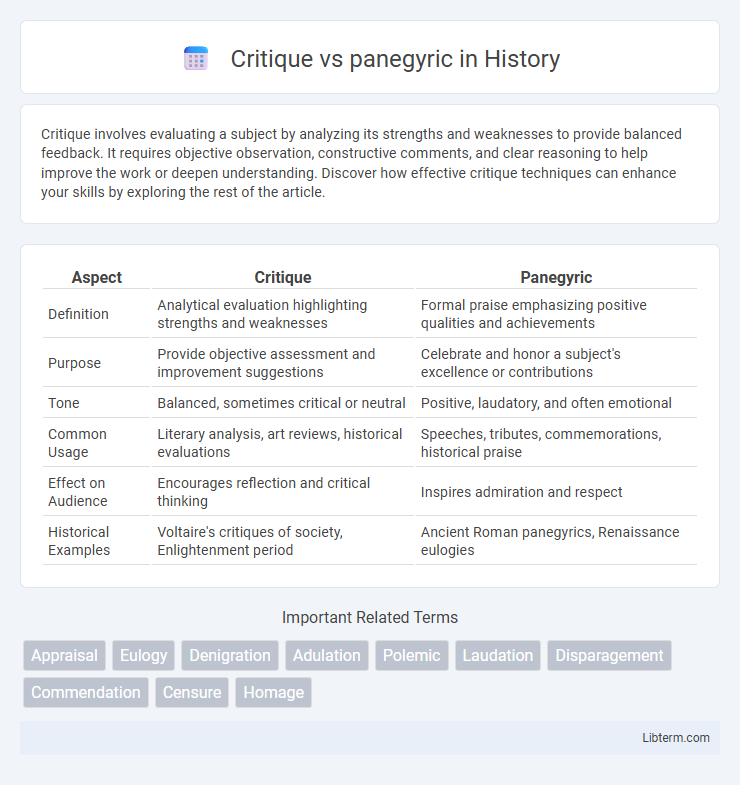
| Aspect | Critique | Panegyric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analytical evaluation highlighting strengths and weaknesses | Formal praise emphasizing positive qualities and achievements |
| Purpose | Provide objective assessment and improvement suggestions | Celebrate and honor a subject's excellence or contributions |
| Tone | Balanced, sometimes critical or neutral | Positive, laudatory, and often emotional |
| Common Usage | Literary analysis, art reviews, historical evaluations | Speeches, tributes, commemorations, historical praise |
| Effect on Audience | Encourages reflection and critical thinking | Inspires admiration and respect |
| Historical Examples | Voltaire's critiques of society, Enlightenment period | Ancient Roman panegyrics, Renaissance eulogies |
Understanding Critique and Panegyric
Understanding critique involves analyzing a subject with the aim of identifying strengths and weaknesses to provide balanced feedback. Panegyric, in contrast, is a form of praise that highlights only the positive attributes, often celebrating achievements or virtues. Mastery of both allows for nuanced communication that can guide improvement while also recognizing excellence.
Historical Origins of Critique and Panegyric
Critique and panegyric have their historical origins in ancient rhetoric and literature, where critique emerged as a disciplined evaluation or judgment of art, literature, and ideas, often rooted in Greek philosophical traditions like those of Aristotle. Panegyric originated as formal public speeches or written encomiums praising individuals, deities, or events, common in Roman and medieval cultures to celebrate virtues and achievements. These practices evolved to shape contemporary modes of critical analysis and laudatory expression, reflecting distinct functions within the history of communication and intellectual discourse.
Key Differences Between Critique and Panegyric
Critique involves objective evaluation highlighting both strengths and weaknesses of a subject, aiming for balanced judgment and improvement, whereas panegyric is a formal expression of high praise, often idealizing the subject without acknowledging flaws. Critiques rely on analytical reasoning and evidence, while panegyrics emphasize admiration and celebration. The key difference lies in critique's critical appraisal versus panegyric's laudatory tone.
The Role of Critique in Intellectual Discourse
Critique serves as a fundamental mechanism in intellectual discourse by rigorously evaluating ideas, arguments, and theories to foster clarity and truth. Unlike panegyric, which offers uncritical praise, critique promotes critical thinking and intellectual growth, challenging assumptions and encouraging deeper analysis. This process ensures that knowledge evolves through constructive scrutiny rather than mere affirmation.
The Importance of Panegyric in Cultural Narratives
Panegyric plays a crucial role in cultural narratives by celebrating and preserving the virtues, achievements, and ideals of individuals or communities, thus reinforcing shared values and collective identity. Unlike critique, which dissects flaws and promotes improvement through critical analysis, panegyric elevates subjects through praise, fostering inspiration and cultural continuity. This positive reinforcement supports societal cohesion and nurtures historical memory by highlighting exemplary models worth emulating.
Positive and Negative Impacts of Critique
Critique plays a vital role in refining ideas, fostering growth, and enhancing the quality of creative and intellectual work by identifying flaws and areas for improvement. Negative impacts may include discouragement, diminished confidence, and resistance when feedback is perceived as overly harsh or unfair. Balancing constructive criticism with sensitivity maximizes positive outcomes and mitigates emotional or professional setbacks.
Panegyric: Benefits and Potential Pitfalls
Panegyric delivers powerful praise that can boost morale, inspire excellence, and solidify reputations by highlighting achievements and virtues with compelling language. It enhances motivation and fosters positive relationships, yet excessive or uncritical panegyric risks fostering complacency, obscuring flaws, and reducing opportunities for growth. Balancing panegyric with objective feedback ensures recognition remains constructive while avoiding the pitfalls of sycophancy or inflated self-perception.
Critique and Panegyric in Modern Media
Critique in modern media serves as a crucial tool for analyzing and evaluating content, offering balanced perspectives that highlight both strengths and weaknesses, thereby guiding audience interpretation and cultural discourse. Panegyric in contemporary media often manifests as uncritical praise, typically found in promotional content or influencer endorsements, which can skew public perception by emphasizing positive attributes while downplaying flaws. Both critique and panegyric shape media narratives, influencing consumer opinions and the broader cultural landscape by either fostering critical engagement or reinforcing idealized portrayals.
Balancing Critique and Panegyric for Constructive Dialogue
Balancing critique and panegyric is essential for fostering constructive dialogue that encourages growth and mutual understanding. Effective communication integrates honest criticism with genuine praise, highlighting both areas for improvement and accomplishments to maintain motivation and respect. This approach builds trust and collaboration by ensuring feedback is perceived as supportive rather than adversarial.
The Future of Critique and Panegyric in Society
Critique and panegyric serve distinct roles in shaping societal discourse, with critique fostering critical thinking and accountability, while panegyric promotes admiration and collective identity. The future of these forms depends on balancing constructive criticism with sincere praise to cultivate informed yet motivated communities. Emerging digital platforms amplify both voices, necessitating careful curation to prevent polarization and maintain meaningful dialogue.
Critique Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com