Trade associations represent the interests of businesses within specific industries, facilitating networking, advocacy, and the sharing of best practices. Membership offers access to valuable resources, industry insights, and opportunities to influence regulations affecting your sector. Explore the rest of the article to discover how joining a trade association can elevate your business success.
Table of Comparison
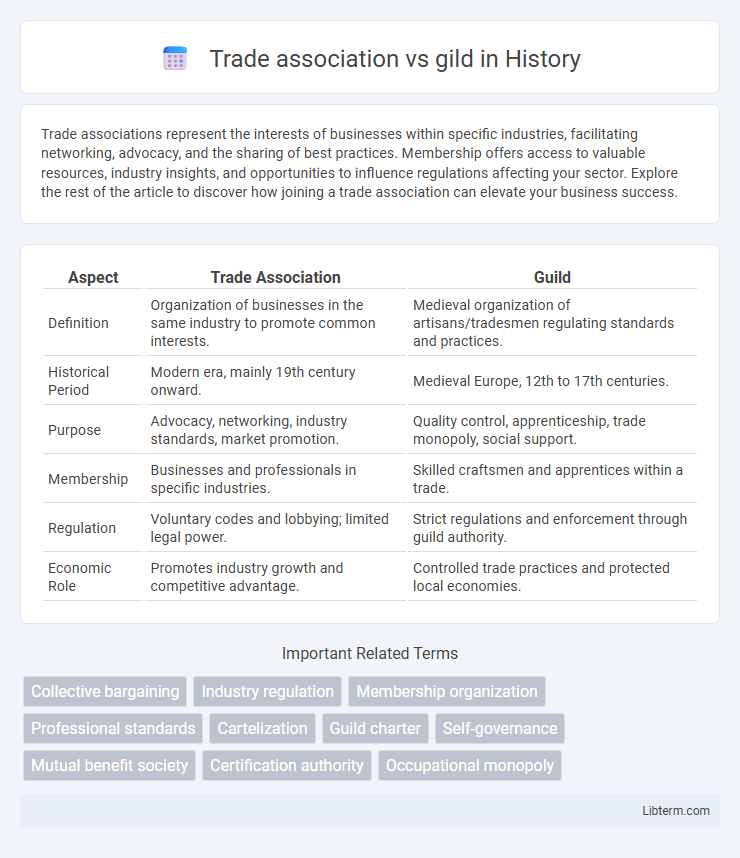
| Aspect | Trade Association | Guild |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organization of businesses in the same industry to promote common interests. | Medieval organization of artisans/tradesmen regulating standards and practices. |
| Historical Period | Modern era, mainly 19th century onward. | Medieval Europe, 12th to 17th centuries. |
| Purpose | Advocacy, networking, industry standards, market promotion. | Quality control, apprenticeship, trade monopoly, social support. |
| Membership | Businesses and professionals in specific industries. | Skilled craftsmen and apprentices within a trade. |
| Regulation | Voluntary codes and lobbying; limited legal power. | Strict regulations and enforcement through guild authority. |
| Economic Role | Promotes industry growth and competitive advantage. | Controlled trade practices and protected local economies. |
Understanding Trade Associations: Definition and Purpose
Trade associations are organizations formed by businesses within the same industry to promote common interests, enhance networking opportunities, and advocate for favorable regulations. Unlike guilds, which historically regulated trade practices and controlled membership, trade associations primarily focus on education, market research, and collective lobbying efforts. These associations help members stay competitive by providing industry insights, setting standards, and facilitating collaboration.
What Is a Guild? Historical and Modern Perspectives
A guild is a historical association of artisans or merchants who controlled the practice of their craft in a particular town, often regulating quality, training, and trade secrets to protect their members' interests. Historically, guilds maintained strict membership rules, monopolized local markets, and played significant social and political roles within medieval communities. Modern guilds have evolved into professional organizations that preserve traditional skills, provide networking opportunities, and advocate for members' rights, distinguishing them from trade associations that primarily focus on industry-wide lobbying and standards.
Key Differences Between Trade Associations and Guilds
Trade associations primarily represent businesses within a specific industry, focusing on advocacy, regulation, and promoting collective interests such as market growth and professional standards. Guilds, historically rooted in medieval craft and trade, emphasize controlling the quality, training, and membership within a particular craft or trade, often maintaining exclusive rights to practice. The key difference lies in trade associations' broader business-oriented goals versus guilds' emphasis on preserving craft traditions and member exclusivity.
Membership Structure: Who Joins Guilds vs. Trade Associations?
Guilds typically consist of skilled craftsmen or artisans within a specific trade, where membership is often restricted to practitioners who have completed rigorous apprenticeships or achieved mastery. Trade associations attract a broader membership, including businesses, suppliers, and professionals connected to an industry, emphasizing collective advocacy and networking. While guilds focus on maintaining quality and training standards within a craft, trade associations prioritize industry-wide representation and market development for their members.
Primary Functions: Advocacy, Training, and Certification
Trade associations primarily focus on advocacy by representing industry interests to government and regulatory bodies, while guilds emphasize maintaining professional standards through training and apprenticeship programs. Certification is a key function of trade associations, providing industry-recognized credentials to members, whereas guilds often control entry and skill verification within their specific craft. Both entities support member development, but trade associations concentrate on broad industry benefits and policy influence, while guilds preserve traditional practices and craftsmanship quality.
Regulatory Influence: Trade Associations vs. Guilds
Trade associations wield regulatory influence by lobbying government bodies to shape industry standards, advance legislation, and protect member interests across modern sectors. Guilds, historically rooted in medieval crafts, exercised regulatory control internally by setting strict entry qualifications, quality standards, and resolving disputes within their trade communities. While trade associations impact external regulatory frameworks on a broad scale, guilds maintained localized authority through direct management of skills and practices.
Industry Representation and Collective Bargaining
Trade associations primarily focus on industry representation by advocating for regulatory policies and standards that benefit multiple businesses within a sector, while guilds emphasize collective bargaining to protect the labor rights and working conditions of their members. Trade associations engage with government bodies and stakeholders to influence legislation, whereas guilds negotiate wages and contracts directly with employers on behalf of skilled workers. Together, these organizations enhance industry cohesion through distinct but complementary roles in representation and labor advocacy.
Professional Standards and Ethical Guidelines
Trade associations promote professional standards and ethical guidelines by developing industry-specific codes of conduct and providing member training to ensure compliance with legal and ethical business practices. Guilds historically emphasized skill mastery and craftsmanship ethics, often enforcing apprenticeship systems and internal rules to maintain quality and moral standards among members. Both entities serve to uphold professionalism, but trade associations are more formalized in codifying ethics for broader industry impact.
Modern Examples: Guilds and Trade Associations Today
Modern trade associations, such as the National Retail Federation and the American Medical Association, function as industry advocates, providing members with networking opportunities, policy influence, and standardized practices. Contemporary guilds, like the Screen Actors Guild-American Federation of Television and Radio Artists (SAG-AFTRA), primarily focus on protecting members' labor rights, negotiating contracts, and maintaining professional standards within specific trades. Both entities play crucial roles in their industries, but trade associations emphasize collective business interests, while guilds prioritize worker protections and skill certification.
Choosing the Right Organization: Which Suits Your Profession?
Trade associations specialize in representing businesses within specific industries, providing networking opportunities, advocacy, and industry standards support. Guilds traditionally focus on crafts or trades, emphasizing skill development, apprenticeship programs, and preserving quality and tradition within a profession. Choosing the right organization depends on whether your priority is industry-wide influence and business interests or craftsmanship, training, and historical legacy.
Trade association Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com