Chamberlain offers advanced climate control solutions known for durability and innovative technology that enhance your home's comfort and efficiency. Their products blend seamless integration with smart home systems, ensuring reliable performance and ease of use. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Chamberlain can transform your living environment.
Table of Comparison
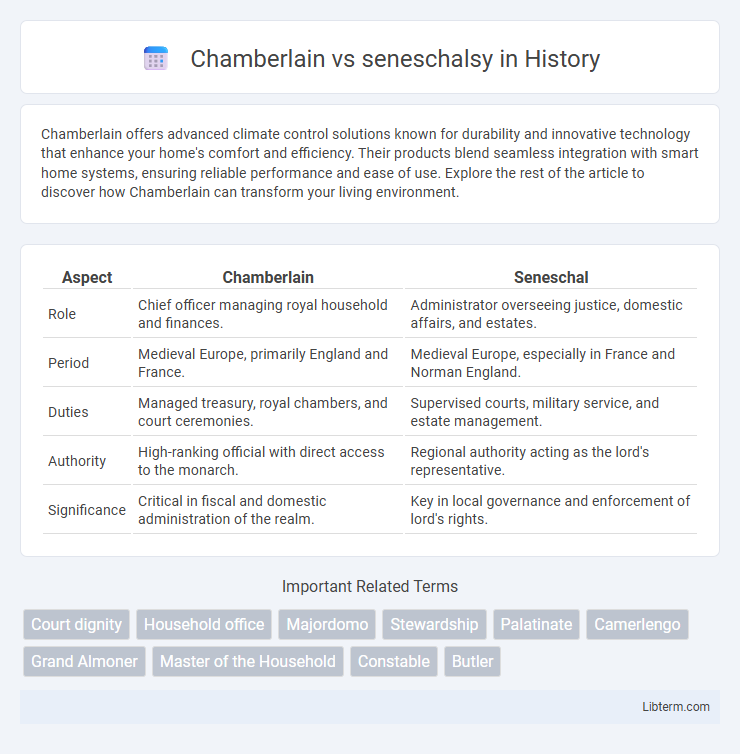
| Aspect | Chamberlain | Seneschal |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Chief officer managing royal household and finances. | Administrator overseeing justice, domestic affairs, and estates. |
| Period | Medieval Europe, primarily England and France. | Medieval Europe, especially in France and Norman England. |
| Duties | Managed treasury, royal chambers, and court ceremonies. | Supervised courts, military service, and estate management. |
| Authority | High-ranking official with direct access to the monarch. | Regional authority acting as the lord's representative. |
| Significance | Critical in fiscal and domestic administration of the realm. | Key in local governance and enforcement of lord's rights. |
Definition and Origins: Chamberlain vs Seneschal
The Chamberlain, originating from medieval European courts, was a high-ranking official responsible for managing the private chambers of a monarch, overseeing household affairs, and controlling access to the ruler. In contrast, the Seneschal served as a steward or chief administrative officer, primarily in noble or royal households in France and England, managing domestic staff and overseeing justice and administration in the lord's absence. While both roles involved household management, the Chamberlain focused on personal service and court protocol, whereas the Seneschal held broader administrative and judicial powers.
Historical Roles and Evolution
Chamberlains historically served as high-ranking royal household officers responsible for managing domestic affairs and overseeing the king's private chambers, evolving into key administrative and financial roles within medieval courts. Seneschals functioned primarily as stewards or chief administrators in noble households, supervising justice, managing estates, and coordinating feudal duties, especially in the Angevin Empire and French territories. The evolution of these roles reflects the shifting power structures and administrative complexities of medieval governance, with chamberlains often involved in court politics while seneschals emphasized regional governance and legal authority.
Key Responsibilities and Functions
Chamberlain, historically known as the chief officer of a royal or noble household, managed financial accounts, supervised domestic staff, and oversaw household operations to ensure efficiency and order. The seneschal held a broader administrative role, often responsible for justice administration, territorial management, and coordination of feudal duties within a lord's domain. Both positions were crucial in medieval governance, with the Chamberlain focusing more on household stewardship and the seneschal on estate and jurisdictional authority.
Geographic Variations in Duties
Chamberlain v. Seneschalsy highlights significant geographic variations in feudal duties, reflecting differing regional customs and obligations in medieval England. The case underscores how land tenure and associated services could vary drastically from one shire to another, influencing local governance and legal interpretations. These variations impacted the enforcement of duties, exemplifying the complexity of decentralized feudal systems across geographic boundaries.
Ranking within Noble Households
Chamberlains typically hold a higher rank than seneschals within noble households, often serving as chief officers responsible for managing the private chambers and overseeing domestic staff. Seneschals function primarily as stewards, administering the estate's daily operations and overseeing agricultural management. The distinction in ranking reflects the chamberlain's closer personal access to and influence over the lord or noble, while seneschals maintain broader administrative duties.
Influence in Royal Courts
Chamberlains held significant influence in royal courts by controlling access to the monarch and managing private chambers, thereby shaping political decisions and court dynamics. Seneschals oversaw administrative and judicial functions within the noble household or regional domains, affecting governance and local authority rather than direct royal policy. The balance of power between chamberlains and seneschals reflected broader tensions in medieval court politics, impacting the consolidation of royal authority.
Notable Chamberlains and Seneschals
Notable chamberlains, such as Thomas Chamberlain in medieval England, were responsible for managing the household finances and overseeing domestic affairs, often serving as key advisors to the monarchy. Prominent seneschals like Philip of Alsace in the County of Flanders acted as high-ranking officials charged with judicial authority, administration of justice, and managing estates on behalf of the nobility. Both roles, though differing in scope, symbolized significant power structures within feudal governance and estate management.
Comparison of Powers and Authority
Chamberlain historically held administrative control over town defenses, markets, and local justice, while the seneschal exercised broader authority in overseeing household management and regional judiciary functions. The seneschal's powers extended to supervising vassals, collecting revenues, and presiding over courts, reflecting a higher status in feudal hierarchy compared to the Chamberlain's more localized responsibilities. This distinction highlights the seneschal as a pivotal intermediary between the lord and his subjects, whereas the Chamberlain focused on operational duties within the lord's domain.
Modern Equivalents and Legacy
Chamberlain vs Seneschalsy highlights the historical role of a seneschal as a medieval steward or chief administrative officer managing estates and justice, which finds modern equivalents in corporate estate managers, chief operating officers, and judicial administrators. The legacy of the seneschals endures in the contemporary emphasis on centralized management of land, resources, and legal affairs within organizations or government bodies. This evolution demonstrates the transition from feudal oversight to professionalized management structures in modern administrative and legal systems.
Chamberlain vs Seneschal: Summary of Differences
Chamberlain and seneschal are distinct medieval offices with different responsibilities and hierarchical status. The Chamberlain primarily managed the royal household's financial affairs and private chambers, emphasizing domestic and fiscal duties. In contrast, the Seneschal acted as a chief administrative officer overseeing justice, military command, and governance within a lord's estate or region.
Chamberlain Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com