Vassalage was a cornerstone of medieval feudal society, defining the relationship between lords and their subordinate vassals through mutual obligations of service and protection. This system structured political power, land ownership, and military support, shaping the social hierarchy and governance of the time. Discover how vassalage influenced historical developments and your understanding of medieval politics in the full article.
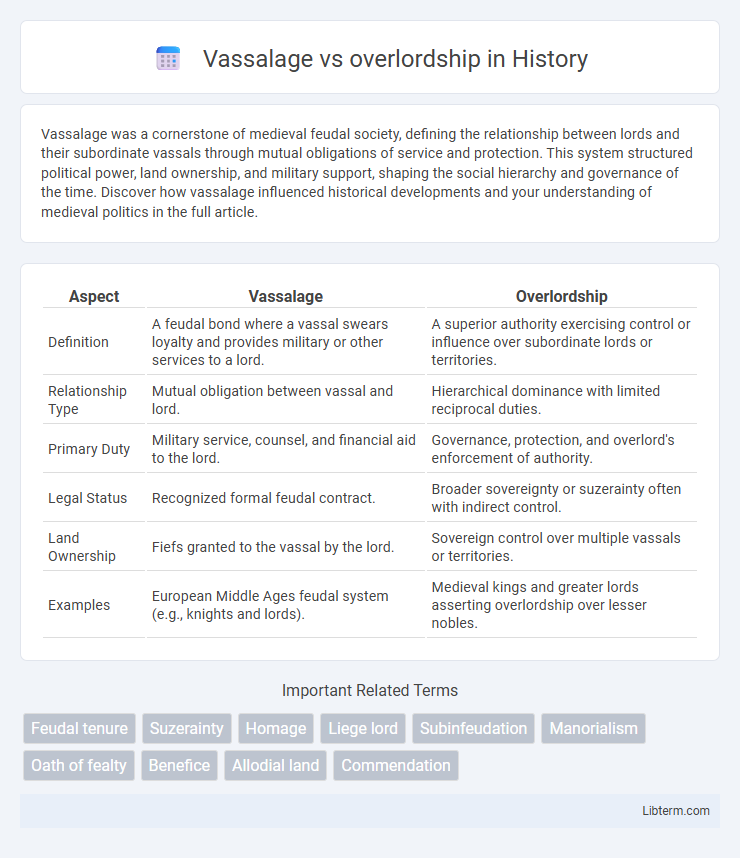
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Vassalage | Overlordship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A feudal bond where a vassal swears loyalty and provides military or other services to a lord. | A superior authority exercising control or influence over subordinate lords or territories. |
| Relationship Type | Mutual obligation between vassal and lord. | Hierarchical dominance with limited reciprocal duties. |
| Primary Duty | Military service, counsel, and financial aid to the lord. | Governance, protection, and overlord's enforcement of authority. |
| Legal Status | Recognized formal feudal contract. | Broader sovereignty or suzerainty often with indirect control. |
| Land Ownership | Fiefs granted to the vassal by the lord. | Sovereign control over multiple vassals or territories. |
| Examples | European Middle Ages feudal system (e.g., knights and lords). | Medieval kings and greater lords asserting overlordship over lesser nobles. |
Understanding Vassalage: Definition and Origins
Vassalage originated in medieval Europe as a system defining the mutual obligations between a vassal and their lord, where the vassal pledged loyalty and service in exchange for protection and land tenure. This feudal relationship involved the vassal providing military support or other services while the overlord granted fiefs, solidifying a hierarchical structure essential to governance and societal order. Understanding vassalage requires recognizing its role in establishing decentralized political authority distinct from the broader concept of overlordship, which emphasizes the dominance and control exerted by the superior lord over multiple vassals.
Overlordship Explained: Structure and Authority
Overlordship establishes a hierarchical framework where the overlord wields supreme authority over subordinate vassals, binding them through oaths of loyalty and service. This system centralizes power, allowing the overlord to exercise legal, military, and economic control within a defined territory. Authority under overlordship extends to adjudicating disputes, demanding tribute, and mobilizing vassal forces, reinforcing a structured network of dependence and governance.
Historical Contexts of Vassalage and Overlordship
Vassalage in medieval Europe involved a personal, reciprocal relationship where a vassal pledged loyalty and military service to a lord in exchange for land or protection, deeply rooted in feudal systems from the 9th to 15th centuries. Overlordship described a hierarchical superiority where an overlord exercised indirect control over subordinate rulers or territories, often reflected in the suzerainty of kings over lesser nobility or tributary states across various cultures including medieval England, the Byzantine Empire, and feudal Japan. The historical context highlights how vassalage focused on mutual obligations within a localized lord-vassal bond, while overlordship emphasized broader political dominance and systemic control beyond personal ties.
Key Differences Between Vassalage and Overlordship
Vassalage involves a mutual obligation between a vassal and a lord, where the vassal pledges loyalty and military service in exchange for protection and land tenure. Overlordship, on the other hand, denotes a hierarchical authority where the overlord exercises supreme control over subordinate lords without the reciprocal responsibilities characteristic of vassal relationships. The key difference lies in vassalage being a contractual bond based on fealty and service, whereas overlordship emphasizes dominance and command over weaker rulers or territories.
Social Hierarchy: Vassals vs Overlords
Vassalage and overlordship define distinct roles within medieval social hierarchy, where vassals held lands granted by overlords in exchange for military service or loyalty. Vassals operated under the jurisdiction and protection of overlords, who possessed superior authority and control over multiple vassals and territories. This hierarchical relationship cemented feudal power structures by intertwining landholding with personal allegiance and governance.
Obligations and Responsibilities: Tribute, Loyalty, and Service
Vassalage involves a reciprocal relationship where the vassal owes tribute, loyalty, and military or administrative service to the overlord, ensuring protection and governance. Obligations typically include regular payment of tribute or taxes, personal loyalty expressed through oaths, and active participation in the overlord's military campaigns or court duties. Overlordship emphasizes authority and control, requiring subjects to provide consistent tribute and support while enforcing loyalty to maintain dominance over vassals or subordinate leaders.
Legal Frameworks Governing Vassalage and Overlordship
Legal frameworks governing vassalage and overlordship were rooted in medieval feudal law, which defined distinct rights and obligations between a vassal and an overlord. Vassalage entailed a personal bond formalized through homage and fealty, obligating military service and counsel to the overlord, while overlordship established hierarchical authority with rights to jurisdiction and feudal dues. These legal relationships were enforceable through oaths and charters, creating a system of mutual loyalty and obligations integral to medieval governance and land tenure.
Economic Impact of Feudal Relationships
Vassalage in feudal societies involved land granted by a lord to a vassal in exchange for military service and loyalty, establishing economic dependencies through the allocation of productive estates and the extraction of rents or labor. Overlordship expanded this dynamic by placing multiple vassals under a higher authority who collected tributes or taxes, thereby concentrating economic resources and controlling regional trade routes. These hierarchical relationships shaped the medieval economy by redistributing wealth, regulating agricultural production, and defining obligations that underpinned local and territorial power structures.
Vassalage and Overlordship in Different Cultures
Vassalage and overlordship manifested distinctly across cultures, with medieval Europe emphasizing personal loyalty sworn by vassals to their lords, often sealed through ceremonies like homage and fealty. In feudal Japan, the relationship resembled vassalage but was embedded within the bushido code, where samurai served their daimyos with strict honor and duty, reflecting both loyalty and military obligation. African societies such as the Ashanti established overlordship through hierarchical clan systems, where subordinate chiefs owed allegiance and tribute to paramount rulers, integrating political authority with kinship and spiritual beliefs.
Legacy and Modern Interpretations of Vassalage and Overlordship
Vassalage and overlordship, integral to medieval feudal systems, established hierarchical loyalties and land tenure that shaped governance structures. Their legacy persists in modern legal principles of allegiance and sovereignty, influencing contemporary concepts of state relationships and diplomatic obligations. Current interpretations emphasize the transformation of these roles into symbolic or contractual relationships rather than absolute authority, reflecting evolving political and legal frameworks.
Vassalage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com