Rational thinking enhances decision-making by focusing on facts and logical analysis rather than emotions. It helps you solve problems efficiently and make informed choices that lead to better outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical ways to develop and apply rational thinking in your daily life.
Table of Comparison
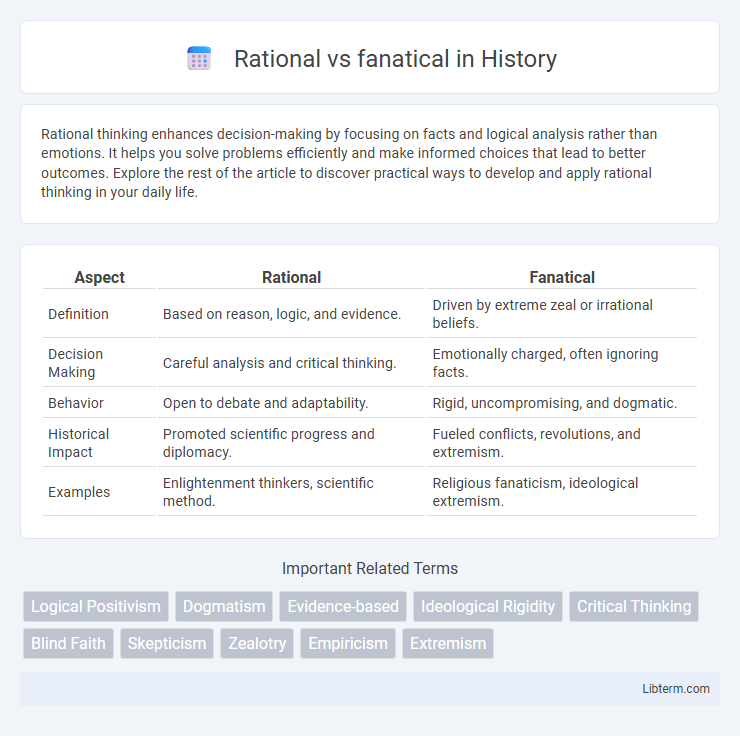
| Aspect | Rational | Fanatical |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Based on reason, logic, and evidence. | Driven by extreme zeal or irrational beliefs. |
| Decision Making | Careful analysis and critical thinking. | Emotionally charged, often ignoring facts. |
| Behavior | Open to debate and adaptability. | Rigid, uncompromising, and dogmatic. |
| Historical Impact | Promoted scientific progress and diplomacy. | Fueled conflicts, revolutions, and extremism. |
| Examples | Enlightenment thinkers, scientific method. | Religious fanaticism, ideological extremism. |
Understanding Rational and Fanatical Mindsets
Rational mindsets prioritize logic, evidence, and critical thinking to make informed decisions, relying on balanced analysis and openness to new information. Fanatical mindsets are characterized by unwavering beliefs, emotional intensity, and resistance to opposing views, often leading to rigid and biased perspectives. Understanding these contrasting approaches helps in recognizing the value of reasoned judgment versus the pitfalls of dogmatic thinking.
Key Traits of Rational Thinking
Rational thinking emphasizes evidence-based decision-making, logical analysis, and openness to revising beliefs in light of new information. It prioritizes critical evaluation, emotional regulation, and effective problem-solving skills to arrive at balanced conclusions. Unlike fanatical reasoning, rational thinkers avoid cognitive biases and dogmatic adherence to ideology, fostering intellectual flexibility and informed judgment.
Defining Fanaticism: What Sets It Apart
Fanaticism is defined by an intense, uncritical zeal that overrides rational thought and open-mindedness, often leading to extreme behaviors detached from objective reasoning. Unlike rationality, which relies on evidence and balanced judgment, fanaticism is marked by emotional obsession and a refusal to consider alternate perspectives. This distinction is crucial in understanding how fanaticism can drive divisive actions and inhibit constructive dialogue.
Cognitive Processes Behind Rationality
Rationality is grounded in cognitive processes such as critical thinking, evidence evaluation, and logical reasoning, enabling individuals to make decisions based on objective analysis and probability assessments. Fanaticism bypasses these processes, often relying on emotional biases, cognitive distortions, and confirmation bias, which reinforce rigid beliefs without critical scrutiny. Understanding these cognitive mechanisms highlights the contrast between open-minded rationality and the closed reasoning characteristic of fanaticism.
Psychological Roots of Fanaticism
Fanaticism often stems from deep psychological needs for certainty, identity, and belonging, contrasting with rationality that values evidence and flexibility. Cognitive biases, such as confirmation bias and black-and-white thinking, fuel rigid beliefs and emotional devotion in fanatics. Social and emotional factors, including fear, anxiety, and group dynamics, reinforce fanaticism by creating an echo chamber that resists critical examination and change.
Impact of Rational versus Fanatical Beliefs
Rational beliefs foster critical thinking, informed decision-making, and promote open-minded dialogue that leads to progressive societal outcomes. Fanatical beliefs often incite intolerance, hinder constructive communication, and can escalate conflicts resulting in social division and violence. The impact of rational versus fanatical beliefs is evident in governance, education, and community resilience where rationality supports sustainable development and fanaticism precipitates instability.
Examples from History: Rationality and Fanaticism
Rationality in history is exemplified by leaders like Abraham Lincoln, whose decisions during the American Civil War were grounded in logical analysis and a commitment to preserving the Union through reasoned debate. In contrast, fanatical figures such as Adolf Hitler exhibited unwavering ideological extremism, leading to destructive policies and catastrophic consequences driven by blind devotion rather than critical thinking. These examples highlight how rationality promotes deliberate problem-solving, while fanaticism fuels irrational actions with devastating impacts.
How Media Fuels Rational or Fanatical Perspectives
Media platforms often emphasize sensationalism, amplifying fanatical perspectives through emotionally charged headlines and selective coverage that prioritizes engagement over accuracy. Rational viewpoints may struggle for visibility amid algorithms that favor content generating strong reactions, skewing public perception towards polarized extremes. The cyclical reinforcement of such media consumption patterns solidifies biased narratives, impeding balanced discourse and critical thinking.
Cultivating Rational Thinking in Daily Life
Developing rational thinking in daily life involves analyzing facts, questioning assumptions, and making decisions based on evidence rather than emotions or biases. Practicing mindfulness and critical evaluation of information helps prevent fanatical tendencies rooted in unexamined beliefs. Consistent reflection and open-mindedness cultivate a balanced mindset essential for thoughtful problem-solving and effective communication.
Strategies to Address Fanatical Behavior
Effective strategies to address fanatical behavior include promoting critical thinking skills and encouraging open dialogue to challenge extreme beliefs. Implementing educational programs that emphasize empathy and perspective-taking can reduce rigidity and promote understanding. Engaging community leaders and mental health professionals aids in creating support systems that help individuals move away from fanaticism towards more balanced viewpoints.
Rational Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com