Augur is a decentralized prediction market platform built on blockchain technology that enables users to create and trade event outcome contracts with transparency and security. It leverages crowd-sourced information to forecast real-world events, providing valuable insights based on collective intelligence. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Augur can empower your decision-making process and investment strategies.
Table of Comparison
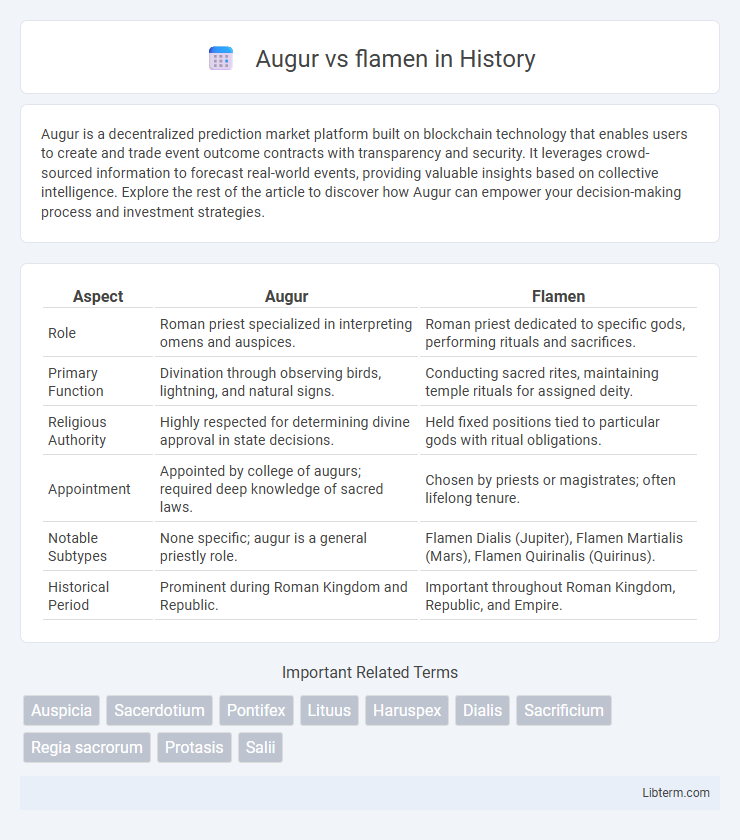
| Aspect | Augur | Flamen |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Roman priest specialized in interpreting omens and auspices. | Roman priest dedicated to specific gods, performing rituals and sacrifices. |
| Primary Function | Divination through observing birds, lightning, and natural signs. | Conducting sacred rites, maintaining temple rituals for assigned deity. |
| Religious Authority | Highly respected for determining divine approval in state decisions. | Held fixed positions tied to particular gods with ritual obligations. |
| Appointment | Appointed by college of augurs; required deep knowledge of sacred laws. | Chosen by priests or magistrates; often lifelong tenure. |
| Notable Subtypes | None specific; augur is a general priestly role. | Flamen Dialis (Jupiter), Flamen Martialis (Mars), Flamen Quirinalis (Quirinus). |
| Historical Period | Prominent during Roman Kingdom and Republic. | Important throughout Roman Kingdom, Republic, and Empire. |
Introduction: Augur vs Flamen
Augur and Flamen were important religious officials in ancient Roman society, each with distinct roles and responsibilities. Augurs specialized in interpreting the will of the gods through the observation of natural signs, particularly the flight patterns of birds, to guide public decision-making. Flamens served as priests assigned to particular deities, performing specific sacrifices and rituals to maintain divine favor and protect the state.
Historical Context of Augurs and Flamines
Augurs and flamines were prominent religious officials in ancient Rome, with augurs specializing in interpreting the will of the gods through bird flight patterns known as auspices, crucial for public decision-making and military ventures. Flamines served as priests assigned to specific deities, performing rituals and maintaining sacred rites essential for religious and political stability, particularly the flamines maiores who served major gods like Jupiter, Mars, and Quirinus. Their roles highlight the intertwining of religious authority and governance in Roman society from the Republic through the Empire, reflecting the importance of divine favor in state affairs.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Augurs were ancient Roman priests specializing in interpreting the will of the gods by studying the flight patterns of birds and omens, ensuring religious rites aligned with divine approval. Flamens, on the other hand, served as high-ranking priests dedicated to specific deities, performing daily rituals and sacrifices to maintain the favor of those gods. While augurs focused on prophecy and divination, flamens were responsible for the practical execution of religious ceremonies and maintaining sacred traditions.
Ritual Practices: Contrasts and Comparisons
Augurs specialized in interpreting the will of the gods by observing the flight patterns of birds, performing elaborate rituals to ensure accurate divination and state-sanctioned decisions. Flamens served as priests dedicated to specific deities, conducting daily sacrifices and maintaining sacred rites within the Roman religious calendar to uphold divine favor. Unlike augurs whose rituals were primarily predictive and external, flamens' practices were continuous, internal religious duties centered around the worship and appeasement of their assigned gods.
Religious Significance in Ancient Rome
Augurs held a crucial role in Ancient Rome by interpreting the will of the gods through the observation of birds, influencing political and military decisions with their auspices. Flamens served as specialized priests dedicated to specific gods, performing sacred rituals and maintaining the religious traditions tied to deities like Jupiter, Mars, and Quirinus. The religious significance of augurs lay in their divinatory authority over public affairs, while flamens embodied the persevering sacerdotal guardianship of Rome's foundational cults.
Authority and Social Status
Augurs held significant religious authority in ancient Rome, recognized for interpreting the will of the gods through bird omens, which granted them high social status and influence over political decisions. Flamens, as priests dedicated to specific deities, possessed exclusive ritual duties but generally ranked lower in public authority compared to augurs. The augurs' ability to legitimize political actions elevated their status above flamens, embedding them deeply within Rome's power structures.
Selection and Training Processes
Augurs underwent rigorous apprenticeship focusing on interpreting bird flight patterns and celestial events, emphasizing observational skills and ritual precision integral to Roman religious practice. Flamens, priests dedicated to specific deities like Jupiter or Mars, received specialized training in intricate ceremonial rites, privy to secret prayers and taboos essential for maintaining divine favor. Selection for augurs often relied on social status and political connections, while flamens typically came from patrician families with hereditary roles reinforcing their exclusive priestly functions.
Interactions with Roman Political Life
Augurs wielded significant influence in Roman political life by interpreting the will of the gods through bird omens, directly affecting the legitimacy of public decisions and elections. Flamens, as priests assigned to specific deities, maintained ritual purity and performed essential ceremonies that reinforced the religious foundation of Roman political authority. Their roles intertwined with state functions, where augural signs could validate laws or military endeavors while flamen rituals upheld the sacred traditions that supported the ruling elite's power.
Influence on Roman Festivals and Ceremonies
Augurs held significant influence over Roman festivals and ceremonies by interpreting the will of the gods through the observation of bird flight patterns and other omens, ensuring that public events aligned with divine approval. Flamens, as specialized priests dedicated to specific deities like Jupiter and Mars, played a key role in performing ritual sacrifices and maintaining sacred rites crucial for the smooth execution of religious festivals. Together, augurs and flamens structured the spiritual framework of Roman public life, intertwining divination and ritual practice to legitimize and guide communal celebrations.
Legacy of Augurs and Flamines in Modern Studies
The legacy of Augurs and Flamines in modern studies highlights their crucial roles in ancient Roman religion, where Augurs interpreted divine will through bird omens while Flamines served as priests dedicated to specific gods, maintaining ritual purity and tradition. Contemporary scholarship emphasizes their influence on understanding Roman religious hierarchy and the sociopolitical power embedded in divine sanction. Archaeological findings and literary sources continue to reveal how these priestly offices shaped religious practices and governance in ancient Rome, informing modern interpretations of ritual and authority.
Augur Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com