Zara stands out as a leading global fashion brand known for its trendy and affordable apparel that caters to diverse styles and preferences. Its fast-fashion model ensures that the latest runway trends reach Your wardrobe quickly, combining quality with accessibility. Discover more about how Zara shapes modern fashion and fits into Your lifestyle throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
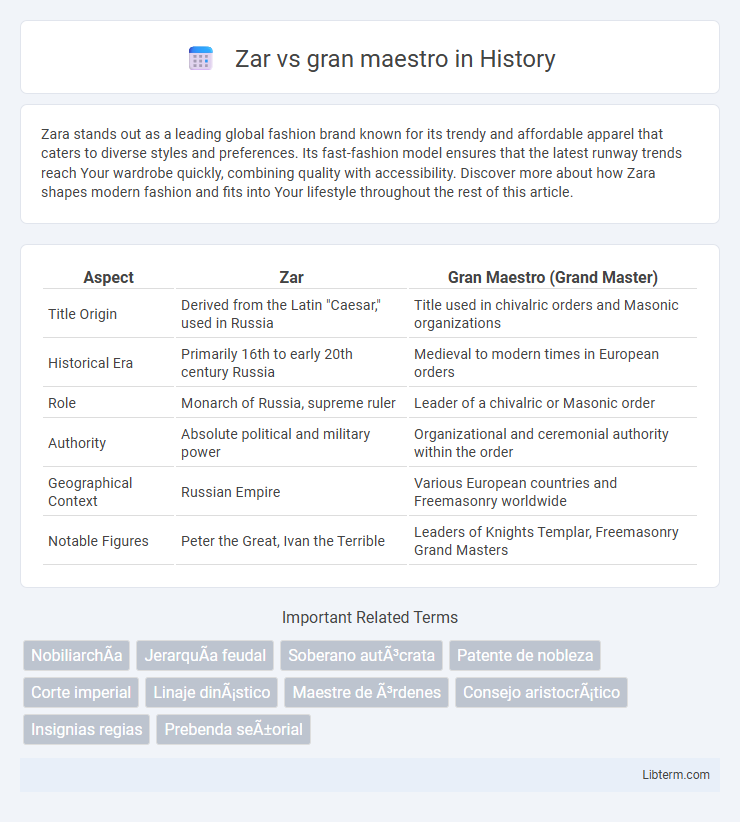
| Aspect | Zar | Gran Maestro (Grand Master) |
|---|---|---|
| Title Origin | Derived from the Latin "Caesar," used in Russia | Title used in chivalric orders and Masonic organizations |
| Historical Era | Primarily 16th to early 20th century Russia | Medieval to modern times in European orders |
| Role | Monarch of Russia, supreme ruler | Leader of a chivalric or Masonic order |
| Authority | Absolute political and military power | Organizational and ceremonial authority within the order |
| Geographical Context | Russian Empire | Various European countries and Freemasonry worldwide |
| Notable Figures | Peter the Great, Ivan the Terrible | Leaders of Knights Templar, Freemasonry Grand Masters |
Zar vs Gran Maestro: Key Differences Explained
Zar and Gran Maestro differ primarily in their strategic approaches to game management, with Zar emphasizing aggressive expansion and resource acquisition, while Gran Maestro prioritizes defensive tactics and long-term positioning. The Zar gameplay style leverages rapid development and offensive maneuvers to outpace opponents, contrasting with Gran Maestro's methodical control of key territories to secure victory. Understanding these key differences aids players in choosing the optimal strategy tailored to their preferred playstyle and game objectives.
Historical Background of Zar and Gran Maestro
Zar is an ancient ritualistic tradition originating in Northeast Africa and the Middle East, historically linked to spiritual healing and exorcism practices designed to appease spirits believed to cause illness or misfortune. Gran Maestro refers to the title given to the highest-ranking leader in various fraternal organizations, particularly within Freemasonry, where the role carries significant historical influence in shaping secret societies since the early 18th century. Both Zar and Gran Maestro embody distinct cultural heritages, with Zar rooted in traditional spiritual ceremonies and Gran Maestro representing hierarchical leadership in structured, esoteric orders.
Roles and Responsibilities: Zar versus Gran Maestro
Zar acts as a spiritual healer and intermediary between the physical and supernatural realms, responsible for conducting rituals to appease spirits and cleanse individuals from possession. Gran Maestro holds a leadership role within esoteric traditions, guiding ceremonies, imparting wisdom, and maintaining doctrinal purity in the practice. Both roles emphasize mediation and spiritual authority, but Zar concentrates on spirit possession healing, while Gran Maestro focuses on ceremonial leadership and esoteric knowledge transmission.
Influence and Power: A Comparative Analysis
Zar and Gran Maestro wield significant influence and power within their respective domains, with Zar commanding a vast network of strategic alliances and covert operations, while Gran Maestro exerts authority through cultural leadership and intellectual dominance. Zar's influence extends into political and military spheres, leveraging intelligence and tactical precision to sway outcomes, whereas Gran Maestro shapes society via philosophical teachings and artistic patronage. Both figures exemplify distinct models of power: Zar's pragmatic control contrasts with Gran Maestro's ideological sway, highlighting diverse mechanisms of leadership and authority.
Cultural Significance: Zar vs Gran Maestro
Zar and Gran Maestro represent distinct cultural identities with Zar rooted in traditional African spiritual practices, emphasizing ritual healing and community connection. Gran Maestro, often associated with European classical music mastery, signifies artistic excellence and cultural refinement in Western traditions. Their contrast highlights the diverse ways cultures preserve heritage, embodying spiritual depth versus artistic sophistication.
Leadership Styles of Zar and Gran Maestro
Zar's leadership style is characterized by authoritative decision-making and a top-down approach, emphasizing control and clear directives to achieve organizational goals efficiently. Gran Maestro adopts a transformational leadership style, inspiring team members through vision, motivation, and fostering collaboration to drive innovation and collective success. Both leadership styles impact organizational dynamics differently, with Zar focusing on structure and discipline, while Gran Maestro prioritizes empowerment and adaptability.
Symbolism Attached to Zar and Gran Maestro Titles
The title "Zar" symbolizes spiritual authority and traditional healing, often associated with rituals that bridge the physical and supernatural realms in cultures such as those in Ethiopia and Sudan. In contrast, "Gran Maestro" signifies supreme leadership within structured organizations like Freemasonry, embodying wisdom, governance, and mastery over esoteric knowledge. Both titles reflect distinct forms of power--Zar rooted in mysticism and cultural heritage, Gran Maestro in hierarchical order and intellectual sovereignty.
Notable Figures: Famous Zars and Gran Maestros
Famous Zars such as Ivan the Terrible and Peter the Great significantly shaped Russian history with their autocratic rule and modernization efforts. Gran Maestros including notable figures like Christopher Columbus and Jacques de Molay, respected as leaders of prestigious orders, influenced exploration and medieval chivalry. These prominent personas embody the power and legacy associated with their titles in governance and hierarchical societies.
Modern Perception: Zar vs Gran Maestro Today
The Zar and Gran Maestro traditions continue to influence modern spiritual practices with Zar often perceived as a healing ritual rooted in East African and Middle Eastern cultures, focusing on spirit possession and exorcism. Gran Maestro is recognized as a symbol of authority in Freemasonry, embodying leadership and esoteric knowledge within modern fraternal organizations. Contemporary interpretations highlight Zar's role in community healing and cultural identity, while Gran Maestro symbolizes hierarchical structure and moral guidance in Masonic lodges worldwide.
Which Title Holds More Prestige?
The title of Gran Maestro, or Grandmaster, holds significantly more prestige than Zar in the world of chess, as it represents the highest official ranking awarded by FIDE based on exceptional skill and tournament performance. Zar is often a regional or unofficial title with limited recognition compared to the universal acclaim and rigorous qualification standards associated with the Grandmaster title. Consequently, the Gran Maestro title serves as a global benchmark for elite mastery and competitive excellence in professional chess.
Zar Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com