Treasury functions play a crucial role in managing an organization's liquidity, risk, and financial operations to ensure sustainable growth and stability. Efficient treasury management helps optimize cash flow, control financial risks, and support strategic decision-making. Explore this article to understand how strengthening your treasury processes can enhance your financial performance.
Table of Comparison
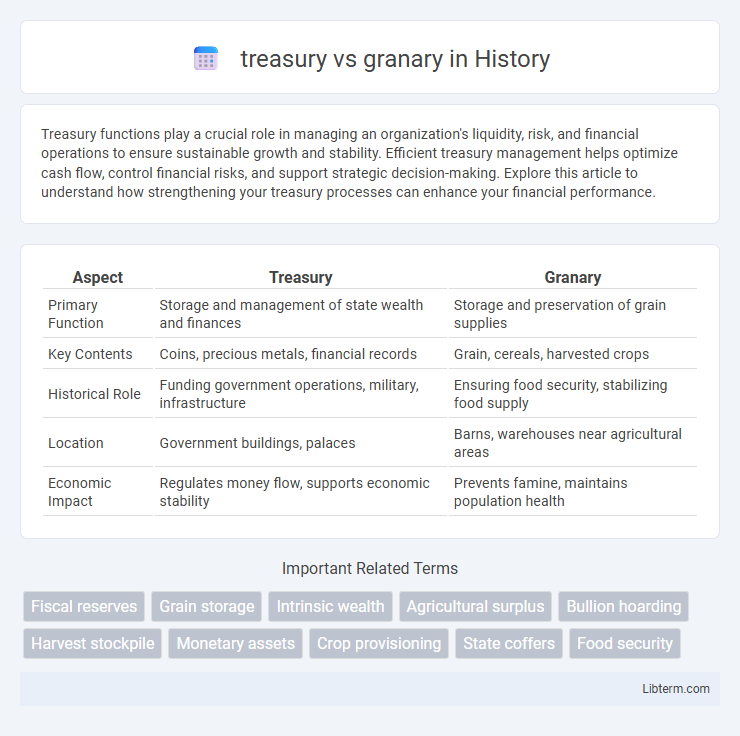
| Aspect | Treasury | Granary |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Storage and management of state wealth and finances | Storage and preservation of grain supplies |
| Key Contents | Coins, precious metals, financial records | Grain, cereals, harvested crops |
| Historical Role | Funding government operations, military, infrastructure | Ensuring food security, stabilizing food supply |
| Location | Government buildings, palaces | Barns, warehouses near agricultural areas |
| Economic Impact | Regulates money flow, supports economic stability | Prevents famine, maintains population health |
Understanding Treasury and Granary: Core Definitions
A treasury is a secure place where funds, valuables, or important financial records are stored and managed, often by governments or organizations to ensure economic stability and resource allocation. A granary, by contrast, is a storage facility specifically designed for preserving harvested grains, safeguarding food supplies against spoilage and pests. Understanding these core definitions highlights the treasury's role in financial security versus the granary's function in food security, reflecting distinct yet vital resource management systems.
Historical Roles of Treasuries and Granaries
Treasuries historically functioned as secure repositories for wealth, valuables, and financial records, playing a critical role in managing and safeguarding state resources and funding governmental activities. Granaries served as essential storage facilities for surplus grain, ensuring food security and stabilizing economies during periods of scarcity or seasonal fluctuations. Both institutions were vital in sustaining ancient civilizations by supporting economic stability and resource management.
Key Functions: Managing Wealth vs. Managing Resources
Treasuries prioritize managing wealth by overseeing financial assets, investments, and revenue flows to ensure economic stability and growth within an organization or state. Granaries focus on managing resources by storing, preserving, and distributing grain or food supplies essential for sustaining populations and supporting agricultural economies. Efficient treasury operations drive fiscal health, while effective granary management secures food security and resource availability.
Infrastructure and Design: Secure Storage Solutions
Treasuries are fortified structures designed for maximum security, incorporating thick walls, reinforced vaults, and advanced locking mechanisms to protect valuable assets such as gold, currency, and important documents. Granaries, while also constructed for protection, emphasize ventilation, moisture control, and pest prevention to preserve large quantities of grain and other foodstuffs. The design differences reflect their distinct functions: treasuries prioritize impenetrability and restricted access, whereas granaries focus on environmental stability and efficient storage capacity.
Treasury vs. Granary: Economic and Social Impact
Treasuries served as central storage for a state's wealth, enabling large-scale economic planning, funding military campaigns, and supporting governmental administration, while granaries primarily focused on food security by storing surplus grain to stabilize food supply and prevent famine. The economic impact of treasuries fostered state power and expansion, whereas granaries contributed to social stability by ensuring a reliable food resource for the population during droughts or crop failures. Together, treasuries and granaries formed complementary pillars of ancient economies, balancing financial capital with essential sustenance.
Governance and Administration Differences
Treasuries primarily manage a state's financial resources, focusing on revenue collection, budgeting, and expenditure control, whereas granaries deal with the storage and distribution of grain to ensure food security and price stability. Governance of treasuries involves financial oversight, auditing, and monetary policy implementation, often overseen by specialized officials or ministries. Granary administration requires managing agricultural supply chains, inventory control, and rationing systems, typically under agricultural or food security departments.
Notable Examples Through History
The Treasury of Atreus in Mycenae exemplifies ancient granary architecture repurposed for wealth storage, highlighting multifunctional use in the Bronze Age. The Egyptian granaries at Giza, designed to store surplus grain during times of famine, were critical for economic stability and resource management. The Roman aerarium, functioning as the state treasury, stored both gold reserves and grain supplies, reflecting the interconnectedness of food security and fiscal control in ancient governance.
Security Measures: Protecting Assets and Provisions
Treasuries implement advanced security technologies such as biometric access controls, reinforced vault doors, and 24/7 surveillance systems to protect financial assets and sensitive documents from theft and cyber threats. Granaries rely on physical barriers including sturdy walls, pest control methods, and climate regulation to safeguard stored grains from spoilage, rodents, and unauthorized access. Both facilities prioritize asset protection through tailored security measures addressing the unique risks associated with financial valuables and agricultural provisions.
Evolution in Modern Times: Digital Treasury and Food Storage
The evolution of treasury systems into digital treasuries has revolutionized financial management by utilizing blockchain technology and real-time data analytics for secure, transparent transactions. Modern granaries have transitioned to smart storage facilities equipped with IoT sensors and automated climate controls to optimize grain preservation and reduce spoilage. These advancements in digital treasury and smart granary systems reflect a shift towards integrating technology to enhance efficiency and security in resource management.
Importance in Crisis Management and Sustainability
The treasury plays a crucial role in crisis management by ensuring financial liquidity and stabilizing the economy during economic downturns or emergencies. Granaries contribute to sustainability by preserving food reserves, safeguarding against famine, and maintaining long-term food security. Both entities are essential for balancing immediate crisis demands with enduring resource management to foster resilient communities.
treasury Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com