A concordat is a formal agreement between the Vatican and a sovereign state, outlining the relationship between the Catholic Church and government institutions. It regulates matters such as church property, religious education, and the legal status of clergy. Discover how concordats impact your country's religious and political landscape by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
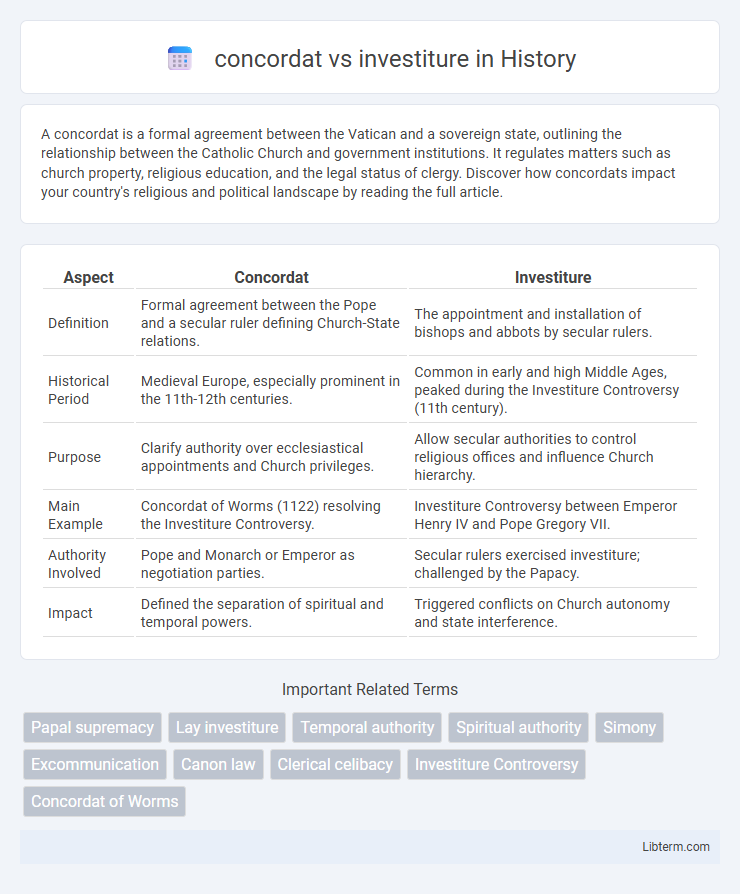
| Aspect | Concordat | Investiture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal agreement between the Pope and a secular ruler defining Church-State relations. | The appointment and installation of bishops and abbots by secular rulers. |
| Historical Period | Medieval Europe, especially prominent in the 11th-12th centuries. | Common in early and high Middle Ages, peaked during the Investiture Controversy (11th century). |
| Purpose | Clarify authority over ecclesiastical appointments and Church privileges. | Allow secular authorities to control religious offices and influence Church hierarchy. |
| Main Example | Concordat of Worms (1122) resolving the Investiture Controversy. | Investiture Controversy between Emperor Henry IV and Pope Gregory VII. |
| Authority Involved | Pope and Monarch or Emperor as negotiation parties. | Secular rulers exercised investiture; challenged by the Papacy. |
| Impact | Defined the separation of spiritual and temporal powers. | Triggered conflicts on Church autonomy and state interference. |
Introduction to Concordat and Investiture
The Concordat refers to an agreement between the Pope and a secular government defining the relationship between the church and state, particularly concerning ecclesiastical appointments and privileges. Investiture involves the formal installation of a bishop or abbot into their office, traditionally symbolized by the granting of ring and staff, often a point of conflict between secular and religious authorities. The Investiture Controversy in the 11th and 12th centuries highlights the tension resolved partly through Concordats, balancing authority over church appointments.
Historical Background of Concordat
The Concordat refers to agreements between the Holy See and sovereign states that regulate the church's rights and privileges within a nation, emerging prominently during the Middle Ages to resolve conflicts such as the Investiture Controversy. This historical conflict centered on whether secular rulers or the pope held the authority to appoint church officials, a struggle that culminated in the Concordat of Worms in 1122, which symbolically separated spiritual and temporal powers. Concordats have since played a crucial role in delineating church-state relations, balancing religious influence and political sovereignty throughout history.
Origins of the Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy originated in the 11th century as a conflict between the Holy Roman Emperor and the Pope over the appointment of church officials, specifically bishops. This power struggle aimed to determine whether secular rulers or the papacy held the authority to invest bishops with their spiritual symbols of office. The Concordat of Worms in 1122 ultimately resolved this dispute by distinguishing the emperor's secular role in granting temporal authority and the pope's spiritual authority in ecclesiastical investiture.
Key Differences Between Concordat and Investiture
Concordat and investiture differ primarily in their nature and scope; a concordat is a formal agreement between the Vatican and a sovereign state outlining church-state relations, while investiture refers to the ceremony and process by which religious or secular officials are formally granted authority or office. Concordats typically address broader issues such as clergy privileges, education, and religious freedom, whereas investiture focuses on the legitimization of individual appointments within hierarchical structures. The key distinction lies in concordat being a diplomatic treaty governing institutional interaction, whereas investiture is a ritualistic or legal act conferring specific power or titles.
Major Concordats in History
Major concordats in history, such as the Concordat of Worms (1122) and the Lateran Concordat (1929), played pivotal roles in resolving conflicts between secular rulers and the Catholic Church over investiture rights. The Concordat of Worms ended the investiture controversy by distinguishing between the spiritual and temporal powers involved in appointing bishops. The Lateran Concordat established Vatican City's sovereignty and regulated church-state relations in Italy, highlighting the evolving negotiation of authority between religious and political entities.
The Role of the Papacy in Investiture
The papacy played a crucial role in the investiture controversy by asserting its authority over the appointment of bishops and abbots, challenging secular rulers who traditionally controlled these appointments. The Concordat of Worms in 1122 marked a compromise, allowing the Church to invest spiritual symbols of office while emperors retained the right to grant secular authority. This agreement underscored the papacy's growing influence in ecclesiastical matters and helped define the separation of spiritual and temporal powers.
Political and Religious Implications
The Concordat represents a formal agreement between the papacy and a secular ruler, delineating the boundaries of authority in appointing church officials, thus reducing conflicts over investiture rights. Investiture, the practice of secular leaders appointing bishops and abbots, often led to power struggles, challenging the church's spiritual authority and political autonomy. The resolution through concordats solidified the separation of political and religious spheres, influencing medieval governance and church-state relations significantly.
Long-Term Effects on Church-State Relations
The Concordat established a framework for cooperation between the Church and state, allowing both to maintain distinct roles while minimizing conflicts over appointments and authority. This agreement often led to stabilized church-state relations by recognizing papal spiritual authority alongside sovereign political power, influencing governance models in Europe for centuries. Investiture contests, characterized by disputes over appointment rights, generally resulted in prolonged power struggles that weakened both institutions and spurred reforms that redefined the balance between secular and ecclesiastical jurisdictions.
Notable Figures Involved in the Disputes
The Investiture Controversy prominently featured Emperor Henry IV and Pope Gregory VII, whose conflict over the appointment of bishops marked a pivotal moment in medieval church-state relations. The Concordat of Worms (1122) involved Emperor Henry V and Pope Callixtus II, resolving the dispute by differentiating spiritual and temporal powers in bishop investitures. Key figures like Archbishop Lanfranc of Canterbury also influenced the broader conflict between secular rulers and the papacy during this era.
Conclusion: Lasting Significance in Modern Context
The Concordat and Investiture Controversy established foundational principles for church-state relations, emphasizing the balance of spiritual authority and secular power. These historical agreements influence modern legal frameworks that govern religious freedoms and political sovereignty worldwide. Their lasting significance lies in shaping contemporary dialogues on the separation of religion and government authority.
concordat Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com