Obeisance refers to a gesture or movement expressing deep respect or submission, often seen in cultural or religious contexts. Understanding its significance can enhance your appreciation of various traditions and interpersonal dynamics. Discover more about the origins and meanings of obeisance in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
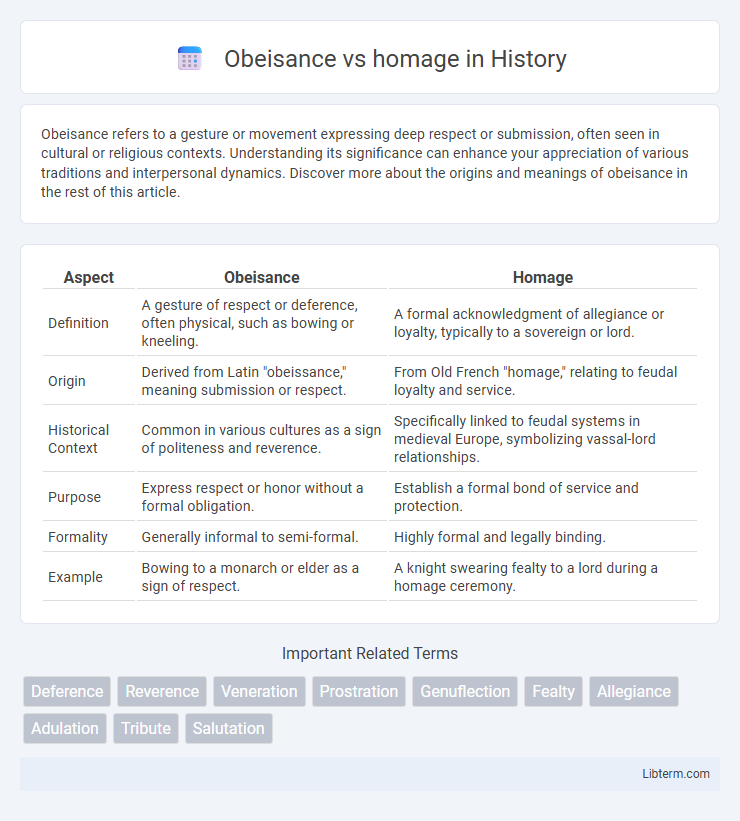
| Aspect | Obeisance | Homage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A gesture of respect or deference, often physical, such as bowing or kneeling. | A formal acknowledgment of allegiance or loyalty, typically to a sovereign or lord. |
| Origin | Derived from Latin "obeissance," meaning submission or respect. | From Old French "homage," relating to feudal loyalty and service. |
| Historical Context | Common in various cultures as a sign of politeness and reverence. | Specifically linked to feudal systems in medieval Europe, symbolizing vassal-lord relationships. |
| Purpose | Express respect or honor without a formal obligation. | Establish a formal bond of service and protection. |
| Formality | Generally informal to semi-formal. | Highly formal and legally binding. |
| Example | Bowing to a monarch or elder as a sign of respect. | A knight swearing fealty to a lord during a homage ceremony. |
Understanding Obeisance: Definition and Origins
Obeisance refers to a gesture or act of respect, such as bowing or kneeling, often rooted in cultural or religious traditions to signify submission or reverence. Originating from the Latin word "obeissantia," obeisance has historically been practiced in monarchies and temples to demonstrate loyalty and honor to authority figures or deities. Understanding the nuances of obeisance reveals its role as a physical manifestation of respect deeply embedded in social hierarchies and ritual practices.
Exploring the Meaning of Homage
Homage refers to a public show of respect or honor, often expressed through ceremonial acts or declarations, recognizing someone's high status, achievements, or contributions. Unlike obeisance, which primarily involves physical gestures of deference such as bowing or kneeling, homage encompasses broader expressions including verbal praise, tributes, or symbolic gestures. Exploring the meaning of homage reveals its roots in feudal traditions where vassals pledged loyalty to their lords, evolving into a modern concept of honoring individuals, cultures, or ideals with respect and admiration.
Obeisance vs Homage: Key Differences
Obeisance involves a physical gesture of respect such as bowing or kneeling, often indicating submission or reverence in hierarchical contexts. Homage denotes a formal declaration of loyalty or honor, typically used in feudal or ceremonial situations to show allegiance or admiration. The key difference lies in obeisance being an act of bodily respect, whereas homage centers on verbal or symbolic affirmation of respect or fealty.
Historical Contexts of Obeisance and Homage
Obeisance originated in ancient religious and cultural rituals signifying deep respect or submission, often involving physical gestures such as bowing or kneeling. Homage evolved in medieval Europe as a feudal ceremony where a vassal pledged loyalty and service to a lord, establishing a mutual bond of protection and duty. While obeisance emphasizes reverence and acknowledgement, homage centers on political allegiance and social hierarchy within historical power structures.
Cultural Variations in Showing Respect
Obeisance and homage reflect culturally distinct forms of showing respect, with obeisance often involving physical gestures like bowing or kneeling prominently seen in Asian and Middle Eastern traditions. Homage, rooted in medieval European customs, typically entails verbal declarations or symbolic acts of loyalty toward a leader or deity. Understanding these variations highlights how respect is expressed through diverse rituals shaped by historical and cultural contexts worldwide.
Modern Usage: How Obeisance and Homage Appear Today
Obeisance in modern usage typically denotes a physical gesture of respect or submission, such as bowing or kneeling, often seen in formal or traditional ceremonies. Homage today frequently refers to symbolic or verbal expressions of respect or admiration, especially in artistic, cultural, or historical contexts. Both terms underline reverence, but obeisance emphasizes bodily acts while homage highlights tribute through acknowledgment or dedication.
Symbolic Gestures: Physical Acts of Obeisance and Homage
Physical acts of obeisance often include bowing, kneeling, or prostrating, symbolizing deep respect and subservience to a higher authority or deity. Homage typically involves gestures like raising a hand in oath or kneeling before a sovereign, signifying allegiance and honor within a feudal or ceremonial context. Both gestures serve as powerful nonverbal communications that reinforce social hierarchies and express acknowledgment of power or reverence.
Language and Nuance: Obeisance vs Homage in Literature
Obeisance in literature conveys a formal, often physical gesture of respect or submission, highlighting hierarchical relationships and cultural rituals. Homage denotes an act of honoring or showing deep respect, frequently reflecting admiration or allegiance, and is used to acknowledge influence or inspiration. The nuanced distinction lies in obeisance emphasizing deference with a ceremonial tone, while homage focuses on tribute and recognition within literary contexts.
When to Use Obeisance or Homage Correctly
Obeisance is used to describe a physical gesture of respect or submission, such as bowing or kneeling, typically in formal or religious contexts. Homage refers to showing respect or honor, often in a broader sense, such as paying tribute to someone's work or legacy. Use obeisance when emphasizing a ritualistic or ceremonial act, and homage when acknowledging esteem or admiration without necessarily involving a physical act.
Common Misconceptions About Obeisance and Homage
Common misconceptions about obeisance and homage often arise from their overlapping associations with respect and submission, yet obeisance specifically involves physical gestures such as bowing or kneeling, symbolizing deep reverence or subservience. Homage, rooted in feudal traditions, refers to a formal acknowledgment of allegiance or honor, typically without obligatory physical movements, distinguishing it from mere courtesy or respect. Misunderstandings frequently blur obeisance's physicality with homage's ceremonial allegiance, obscuring their nuanced differences in cultural and historical contexts.
Obeisance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com