Antiquarianism involves the study and collection of ancient artifacts, manuscripts, and historical objects to understand past cultures and civilizations. This discipline combines meticulous research with hands-on preservation techniques to uncover valuable insights from antiquity. Discover how antiquarianism can deepen your connection to history by exploring the rich details presented in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
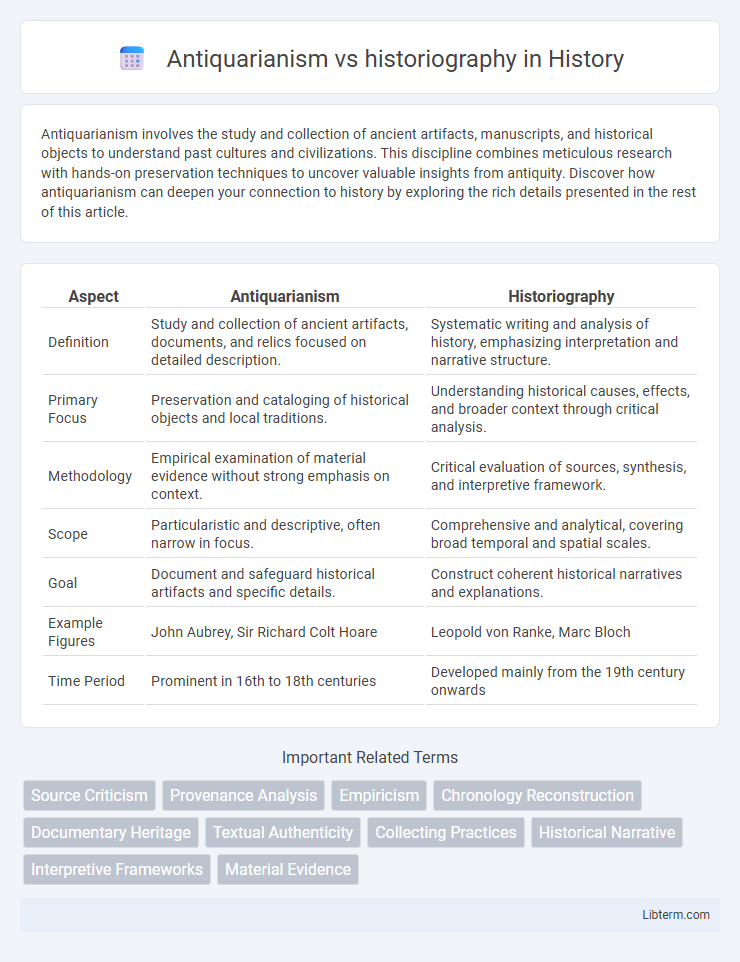
| Aspect | Antiquarianism | Historiography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study and collection of ancient artifacts, documents, and relics focused on detailed description. | Systematic writing and analysis of history, emphasizing interpretation and narrative structure. |
| Primary Focus | Preservation and cataloging of historical objects and local traditions. | Understanding historical causes, effects, and broader context through critical analysis. |
| Methodology | Empirical examination of material evidence without strong emphasis on context. | Critical evaluation of sources, synthesis, and interpretive framework. |
| Scope | Particularistic and descriptive, often narrow in focus. | Comprehensive and analytical, covering broad temporal and spatial scales. |
| Goal | Document and safeguard historical artifacts and specific details. | Construct coherent historical narratives and explanations. |
| Example Figures | John Aubrey, Sir Richard Colt Hoare | Leopold von Ranke, Marc Bloch |
| Time Period | Prominent in 16th to 18th centuries | Developed mainly from the 19th century onwards |
Introduction to Antiquarianism and Historiography
Antiquarianism involves the detailed collection and study of historical artifacts, manuscripts, and relics to understand the past through tangible evidence. Historiography, in contrast, focuses on the systematic writing and analysis of history, emphasizing the interpretation of historical events and the methodology behind historical research. The introduction to antiquarianism highlights its foundation in preserving material culture, while historiography introduces the critical frameworks for constructing and evaluating historical narratives.
Defining Antiquarianism: Focus and Methods
Antiquarianism centers on the detailed collection and study of ancient artifacts, documents, and customs to preserve historical evidence, emphasizing empirical observation over interpretative narratives. Its methods involve meticulous cataloging, classification, and description, often prioritizing material culture and inscriptions as primary sources. This approach contrasts with historiography, which seeks to construct broader historical interpretations and narratives based on critical analysis of cause, context, and significance.
Understanding Historiography: Purpose and Practice
Historiography involves the critical study of historical writing and methods, aiming to interpret past events through evidence and context, whereas antiquarianism focuses on collecting and preserving artifacts and documents without necessarily analyzing their historical significance. The purpose of historiography is to construct coherent narratives and explanations that reflect changing interpretations and theoretical frameworks over time. Practicing historiography requires engaging with sources critically, evaluating biases, and situating historical knowledge within broader intellectual and cultural debates.
Key Differences Between Antiquarianism and Historiography
Antiquarianism focuses on the collection and preservation of artifacts, documents, and curiosities without necessarily interpreting their historical context, whereas historiography emphasizes the analysis, interpretation, and critical evaluation of historical events and sources to construct coherent narratives. Antiquarians prioritize empirical evidence and tangible objects, often engaging in detailed description, while historians use methodological frameworks to understand cause-and-effect relationships and broader social, political, and cultural impacts. The key difference lies in antiquarianism's descriptive and preservationist approach compared to historiography's analytical and interpretive nature.
The Historical Origins of Antiquarianism
Antiquarianism originated during the Renaissance as a systematic study of ancient artifacts, inscriptions, and monuments, emphasizing detailed empirical evidence over broad historical narratives. Unlike historiography, which constructs interpretive historical accounts by integrating diverse sources to explain human events, antiquarianism primarily focused on collecting, cataloging, and preserving material culture to support the authenticity and chronology of history. The historical origins of antiquarianism reveal its foundational role in shaping the methodologies of modern historical research by prioritizing primary physical evidence and localized historical inquiry.
Development and Evolution of Historiography
Antiquarianism, emerging in the Renaissance, focused on collecting and preserving artifacts and historical curiosities without a critical narrative, laying foundational knowledge for historiography. Historiography evolved by incorporating analytical methods, critical evaluation of sources, and a broader contextual understanding of events, shifting from mere collection to interpretation. This development allowed historians to construct more coherent and evidence-based narratives, advancing the discipline beyond antiquarian cataloging.
Contributions of Antiquarians to Historical Knowledge
Antiquarians significantly enriched historical knowledge by systematically collecting and preserving artifacts, manuscripts, and inscriptions that might otherwise have been lost. Their detailed attention to material culture and local records provided foundational primary sources for later historiographical analysis, enabling historians to construct more accurate and nuanced narratives. By emphasizing empirical evidence over literary tradition, antiquarians broadened the scope and methodology of historical research.
Criticisms and Limitations of Antiquarianism
Antiquarianism faces criticism for its excessive focus on collecting and describing artifacts without providing broader historical context or narrative, leading to fragmented and superficial understandings of the past. Its limitations include a tendency to prioritize detail over interpretation, often neglecting the social, cultural, and political dynamics that historiography seeks to analyze. This narrow approach can inhibit the development of a cohesive and analytical historical methodology, reducing the value of antiquarian findings to mere curiosity rather than a foundation for comprehensive historical knowledge.
The Impact of Historiographical Analysis on Modern History
Historiographical analysis transforms modern history by emphasizing critical evaluation of sources, methodologies, and historical narratives, moving beyond mere antiquarian collection of artifacts and documents. This approach fosters a deeper understanding of historical contexts, biases, and interpretations, enabling scholars to construct more nuanced and dynamic representations of the past. The shift from antiquarianism to historiography significantly enhances historical scholarship by prioritizing analytical rigor and theoretical frameworks over simple accumulation of historical data.
Bridging the Gap: Integrating Antiquarianism with Historiography
Integrating antiquarianism with historiography enriches historical analysis by combining detailed artifact examination with broader narrative frameworks. Antiquarian focus on primary sources, such as manuscripts and relics, provides invaluable empirical evidence that grounds historiographical interpretations in tangible reality. Bridging these disciplines enhances historical accuracy, allowing scholars to construct nuanced, contextually rich accounts that acknowledge both material culture and thematic historical developments.
Antiquarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com