Experience luxury and comfort in a villa designed to cater to your every need, featuring spacious rooms, private pools, and breathtaking views. Villas offer privacy and exclusivity, perfect for families or groups seeking a serene getaway. Discover the ultimate villa experience and explore all the benefits in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
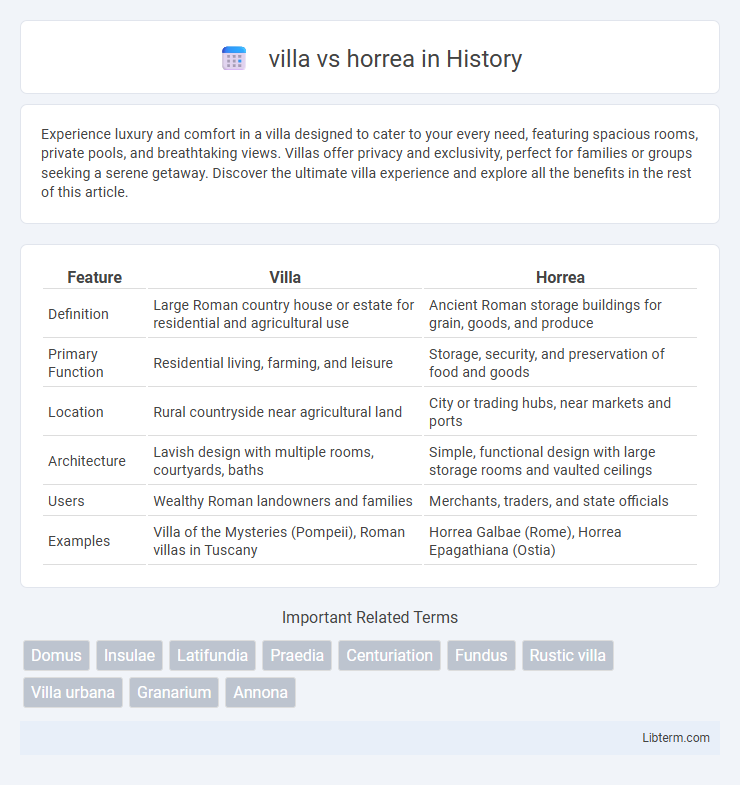
| Feature | Villa | Horrea |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large Roman country house or estate for residential and agricultural use | Ancient Roman storage buildings for grain, goods, and produce |
| Primary Function | Residential living, farming, and leisure | Storage, security, and preservation of food and goods |
| Location | Rural countryside near agricultural land | City or trading hubs, near markets and ports |
| Architecture | Lavish design with multiple rooms, courtyards, baths | Simple, functional design with large storage rooms and vaulted ceilings |
| Users | Wealthy Roman landowners and families | Merchants, traders, and state officials |
| Examples | Villa of the Mysteries (Pompeii), Roman villas in Tuscany | Horrea Galbae (Rome), Horrea Epagathiana (Ostia) |
Introduction to Villas and Horrea
Villas were expansive rural estates in ancient Rome, serving as luxurious residences and agricultural hubs that showcased wealth and social status. Horrea functioned as large storage warehouses essential for preserving grain, produce, and goods, playing a crucial role in Rome's urban economy and supply chain. Distinct in purpose and design, villas emphasized comfort and aesthetics, while horrea prioritized functionality and capacity.
Historical Background of Villas
Villas originated in ancient Rome as luxurious countryside estates primarily used by wealthy patricians for leisure, agriculture, and as status symbols during the Republic and Empire periods. These residential complexes evolved to include elaborate architectural features such as peristyles, bathing facilities, and agricultural buildings, reflecting the fusion of domestic comfort and rural productivity. In contrast, horrea primarily served as public or private storage warehouses, emphasizing utility over residential or aesthetic qualities in Roman urban and rural settings.
Historical Significance of Horrea
Horrea were essential ancient Roman storage buildings designed to preserve grain, foodstuffs, and valuable goods, playing a crucial role in the empire's economy and urban infrastructure. Unlike villas, which served as luxurious rural residences for the elite, horrea ensured the stability of Rome's grain supply, preventing shortages and supporting the city's large population. Archaeological findings of horrea reveal insights into Roman trade, logistics, and administrative control essential for maintaining societal order.
Architectural Features: Villas vs Horrea
Villas in ancient Rome showcased expansive layouts with multiple rooms, courtyards, and elaborate frescoes, reflecting luxury and residential comfort. Horrea, on the other hand, were utilitarian storage buildings characterized by thick walls, narrow windows, and modular cella to optimize grain, oil, or wine preservation. Architectural differences highlight villas as private, residential estates, while horrea served as practical, secure warehouses.
Primary Functions and Uses
Villas primarily functioned as luxurious country residences for wealthy Roman elites, combining residential spaces with agricultural estates to manage farming activities and produce surplus crops. Horrea served as large, utilitarian warehouses designed for storing grain, foodstuffs, and commercial goods essential for urban supply and trade logistics. While villas integrated living quarters with economic production, horrea focused exclusively on secure, organized storage and distribution within Roman cities.
Social and Economic Roles
Villas in ancient Rome functioned as luxurious residences and agricultural estates supporting elite social status and generating wealth through farming and production of goods. Horrea served primarily as public or private warehouses, crucial for economic stability by storing grain, olive oil, wine, and other commodities, facilitating trade and supply management. The villa symbolized social prestige and economic power, while horrea played a central role in urban commerce and resource distribution.
Geographic Distribution and Location
Villas predominantly appear in Mediterranean regions, especially throughout Italy and Southern France, where fertile land supports agricultural estates. Horrea, conversely, are primarily located in urban centers across the Roman Empire, such as Rome, Ostia, and Pompeii, serving as warehouses and storage facilities near ports and marketplaces. The geographic distribution highlights villas as rural residences and agricultural hubs, while horrea functioned within city infrastructure for commercial storage and distribution.
Construction Materials and Techniques
Villas in the Roman era were typically constructed using stone, brick, and concrete, featuring advanced techniques such as opus caementicium for durability and elaborate mosaics for decoration. Horrea, designed for storage, employed robust materials like thick stone walls and fired bricks to ensure protection from moisture and pests, often incorporating vaulted ceilings to maximize space and structural integrity. Both structures utilized arches and buttresses, but villas emphasized aesthetic finishes, while horrea prioritized functionality and preservation of goods.
Preservation and Archaeological Discoveries
Villas and horrea reveal distinct approaches to preservation, with villas often showcasing well-preserved residential architecture, frescoes, and mosaics that provide insight into Roman domestic life. Horrea, as specialized storage structures, offer archaeological evidence of ancient trade and commerce through remnants of amphorae, grain, and other goods conserved within their robust, utilitarian designs. Excavations of both site types enhance understanding of economic and social systems in Roman antiquity through preserved material culture and architectural features.
Legacy and Influence in Modern Architecture
The Roman villa, with its emphasis on luxury, spatial organization, and integration with the landscape, directly influenced the development of modern residential architecture, inspiring the open floor plans and indoor-outdoor living spaces seen today. Horrea, as large-scale storage buildings, contributed to the evolution of functional warehouse design, emphasizing durability, modular construction, and ventilation techniques still employed in contemporary industrial architecture. Together, these structures shaped foundational principles in architecture by balancing aesthetic appeal and practical utility, leaving a lasting legacy evident in both private homes and commercial buildings.
villa Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com